写在前面
这是笔者在中秋无聊写着玩的,假期闲暇之余憋出来的帖子。麻雀虽小,但五脏俱全,涉及到的方方面面还是蛮全的。所以就设计了一个黛梦(demo)------ 打通了GraphQL的接口与前端交互的流程,并且将数据存入MYSQL,分享下React和GraphQL的使用,大致内容如下:
- GraphQL的增删改查接口设计与实现
- CRUD包mysql的使用
- React 和 React Hooks的使用
因为涉及到React、GraphQL,还有MySQL的一张用户表User,所以我本来是想起一个“搞人实验”的名字,后来斟酌了一下,啊着,太粗暴了。还是文艺点,诗意点,就叫它”黛梦“吧,哈哈哈哈哈哈。
这边文章着重介绍GraphQL的使用,关于它的一些概念烦请看我去年写的这篇文章,GraphQL的基础实践------ https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000021895204
技术实现
技术选型
最近在用taro写h5和小程序,混个脸熟,所以前端这边我选用React,因为黛梦也不是很大,所以没必要做前后端分离,用html刀耕火种意思下得了。后端这块是Node结合express和GraphQL做的接口,数据库用的是MySQL。
GraphQL的接口设计
我们先抛开GraphQL,就单纯的接口而言。比如说抽象出一个User类,那么我们对其进行的操作不外乎增删改查对吧。然后我们再带上GraphQL,结合已知的业务逻辑去熟悉新技术那么我们可以这么一步一步来,一口气是吃不成胖子的。
- 先定义用户实体和相应的接口,不做细节实现,访问相应的接口能返回相应的预期
- 定义一个全局变量(或者写进一个文件)去模仿数据库操作,返回相应的结果
- 结合数据库去实现细节,访问相应的接口能返回相应的预期
全局变量Mock数据库的实现
第一步:导包
const express = require('express');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
上面分别导入了相应的包,express用来创建相应的HTTP服务器,buildSchema用来创建相应的类型、Query和Mutation的定义。graphqlHTTP用来将相应的实现以中间件的形式注入到express中。
第二步:定义全局变量
const DB = {
userlist: [],
};
这里定义一个全局变量去模仿数据库操作
第三步:定义相应的Schema
const schema = buildSchema(`
input UserInput {
name: String
age: Int
}
type User {
id: ID,
name: String,
age: Int
}
type Query {
getUsers: [User]
}
type Mutation {
createUser(user: UserInput): User
updateUser(id: ID!, user: UserInput): User
}
`);
这里定义了用户输入的类型以及用户的类型,然后Query中的getUsers模拟的是返回用户列表的接口,返回User实体的列表集。Mutation是对其进行修改、删除、新增等操作。这里createUser接收一个UserInput的输入,然后返回一个User类型的数据,updateUser接受一个ID类型的id,然后一个UserInput类型的user
第四步:对楼上Schema的Query和Mutation的实现
const root = {
getUsers() {
return DB.userlist || [];
},
createUser({ user }) {
DB.userlist.push({ id: Math.random().toString(16).substr(2), ...user });
return DB.userlist.slice(-1)[0];
},
updateUser({ id, user }) {
let res = null;
DB.userlist.forEach((item, index) => {
if (item.id === id) {
DB.userlist[index] = Object.assign({}, item, { id, ...user });
res = DB.userlist[index];
}
});
return res;
},
};
第五步:创建服务器并暴露想要的端口
const app = express();
app.use(
'/api/graphql',
graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
})
);
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running in http://localhost:3000/api/graphql');
});
文件地址:https://gitee.com/taoge2021/study-nodejs/blob/master/07-graphql/express/01-graphql/server-3.js
打开 http://localhost:3000/api/graphql,可以在playground粘贴下楼下的测试用例试一下
query {
getUsers {
id
name
age
}
}
mutation {
createUser(user: {name: "ataola", age: 18}) {
id
name
age
}
}
mutation {
updateUser(id: "5b6dd66772afc", user: { name: "daming", age: 24 }) {
id,
name,
age
}
}
文件地址:https://gitee.com/taoge2021/study-nodejs/blob/master/07-graphql/express/01-graphql/server-3.query
结合MySQL的实现
这里就不像楼上一样展开了,直接贴代码吧
const express = require('express');
const { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
const { cmd } = require('./db');
const schema = buildSchema(`
input UserInput {
"姓名"
name: String
"年龄"
age: Int
}
type User {
"ID"
id: ID,
"姓名"
name: String,
"年龄"
age: Int
}
type Query {
"获取所有用户"
getUsers: [User]
"获取单个用户信息"
getUser(id: ID!): User
}
type Mutation {
"创建用户"
createUser(user: UserInput): Int
"更新用户"
updateUser(id: ID!, user: UserInput): Int
"删除用户"
deleteUser(id: ID!): Boolean
}
`);
const root = {
async getUsers() {
const { results } = await cmd('SELECT id, name, age FROM user');
return results;
},
async getUser({ id }) {
const { results } = await cmd(
'SELECT id, name, age FROM user WHERE id = ?',
[id]
);
return results[0];
},
async createUser({ user }) {
const id = Math.random().toString(16).substr(2);
const data = { id, ...user };
const {
results: { affectedRows },
} = await cmd('INSERT INTO user SET ?', data);
return affectedRows;
},
async updateUser({ id, user }) {
const {
results: { affectedRows },
} = await cmd('UPDATE user SET ? WHERE id = ?', [user, id]);
return affectedRows;
},
async deleteUser({ id }) {
const {
results: { affectedRows },
} = await cmd('DELETE FROM user WHERE id = ?', [id]);
return affectedRows;
},
};
const app = express();
app.use(
'/api/graphql',
graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
})
);
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.use(express.static('public'));
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running in http://localhost:3000/api/graphql');
});
这里跟全局变量不同的是,我这边对所有字段和方法增加了相应的注释(GraphQL就是好, 接口即文档),然后封装了mysql数据库的操作方法,引入后去实现相关的接口。
MYSQL增删改查的封装
这里简单点,我们期望是传入一条SQL和相应的参数,返回相应的执行结果。
const mysql = require('mysql');
const pool = mysql.createPool({
host: '122.51.52.169',
port: 3306,
user: 'ataola',
password: '123456',
database: 'test',
connectionLimit: 10,
});
function cmd(options, values) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
pool.getConnection(function (err, connection) {
if (err) {
reject(err);
} else {
connection.query(options, values, (err, results, fields) => {
if (err) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve({ err, results, fields });
}
connection.release();
});
}
});
});
}
module.exports = {
cmd,
};
这里导入了Mysql这个npm包,在它的基础上创建了一个连接池,然后暴露一个cmd方法,它返回一个Promise对象,是我们上面传入sql和参数的结果。
文件地址如下:https://gitee.com/taoge2021/study-nodejs/blob/master/07-graphql/express/01-graphql/db.js
有的时候我们写代码,不可能一次就写成我们想要的结果,比如可能写错了一个单词啊,或者参数什么,所以这里需要对增删改查的sql做测试,具体的如下:
const { cmd } = require('./db');
// insert
// (async () => {
// const res = await cmd('INSERT INTO user SET ?', {
// id: 'beb77a48b7f9f',
// name: '张三',
// age: 100,
// });
// console.log(res);
// })();
// {
// error: null,
// results: OkPacket {
// fieldCount: 0,
// affectedRows: 1,
// insertId: 0,
// serverStatus: 2,
// warningCount: 0,
// message: '',
// protocol41: true,
// changedRows: 0
// },
// fields: undefined
// }
// delete
// (async () => {
// const res = await cmd('DELETE FROM user WHERE id = ?', ['beb77a48b7f9f']);
// console.log(res);
// })();
// {
// error: null,
// results: OkPacket {
// fieldCount: 0,
// affectedRows: 1,
// insertId: 0,
// serverStatus: 2,
// warningCount: 0,
// message: '',
// protocol41: true,
// changedRows: 0
// },
// fields: undefined
// }
// update
// (async () => {
// const res = await cmd('UPDATE user SET ? where id = ?', [
// { name: '大明', age: 25 },
// 'beb77a48b7f9f',
// ]);
// console.log(res);
// })();
// {
// error: null,
// results: OkPacket {
// fieldCount: 0,
// affectedRows: 1,
// insertId: 0,
// serverStatus: 2,
// warningCount: 0,
// message: '(Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0',
// protocol41: true,
// changedRows: 1
// },
// fields: undefined
// }
// select
// (async () => {
// const res = await cmd('SELECT id, name, age FROM user');
// console.log(res);
// })();
// {
// error: null,
// results: [ RowDataPacket { id: 'beb77a48b7f9f', name: '大明', age: 25 } ],
// fields: [
// FieldPacket {
// catalog: 'def',
// db: 'test',
// table: 'user',
// orgTable: 'user',
// name: 'id',
// orgName: 'id',
// charsetNr: 33,
// length: 765,
// type: 253,
// flags: 20483,
// decimals: 0,
// default: undefined,
// zeroFill: false,
// protocol41: true
// },
// FieldPacket {
// catalog: 'def',
// db: 'test',
// table: 'user',
// orgTable: 'user',
// name: 'name',
// orgName: 'name',
// charsetNr: 33,
// length: 765,
// type: 253,
// flags: 0,
// decimals: 0,
// default: undefined,
// zeroFill: false,
// protocol41: true
// },
// FieldPacket {
// catalog: 'def',
// db: 'test',
// table: 'user',
// orgTable: 'user',
// name: 'age',
// orgName: 'age',
// charsetNr: 63,
// length: 11,
// type: 3,
// flags: 0,
// decimals: 0,
// default: undefined,
// zeroFill: false,
// protocol41: true
// }
// ]
// }
// select
(async () => {
const res = await cmd('SELECT id, name, age FROM user WHERE id = ?', [
'beb77a48b7f9f',
]);
console.log(res);
})();
// {
// error: null,
// results: [ RowDataPacket { id: 'beb77a48b7f9f', name: '大明', age: 25 } ],
// fields: [
// FieldPacket {
// catalog: 'def',
// db: 'test',
// table: 'user',
// orgTable: 'user',
// name: 'id',
// orgName: 'id',
// charsetNr: 33,
// length: 765,
// type: 253,
// flags: 20483,
// decimals: 0,
// default: undefined,
// zeroFill: false,
// protocol41: true
// },
// FieldPacket {
// catalog: 'def',
// db: 'test',
// table: 'user',
// orgTable: 'user',
// name: 'name',
// orgName: 'name',
// charsetNr: 33,
// length: 765,
// type: 253,
// flags: 0,
// decimals: 0,
// default: undefined,
// zeroFill: false,
// protocol41: true
// },
// FieldPacket {
// catalog: 'def',
// db: 'test',
// table: 'user',
// orgTable: 'user',
// name: 'age',
// orgName: 'age',
// charsetNr: 63,
// length: 11,
// type: 3,
// flags: 0,
// decimals: 0,
// default: undefined,
// zeroFill: false,
// protocol41: true
// }
// ]
// }
在测试完成后,我们就可以放心地引入到express和graphql的项目中去了。额,这里的服务器我就不避讳打星号了,快到期了,有需要的同学可以连上去测试下,这里用的也是测试服务器和账号哈哈哈,没关系的。
相关的query文件在这:https://gitee.com/taoge2021/study-nodejs/blob/master/07-graphql/express/01-graphql/server-4.query
贴张图
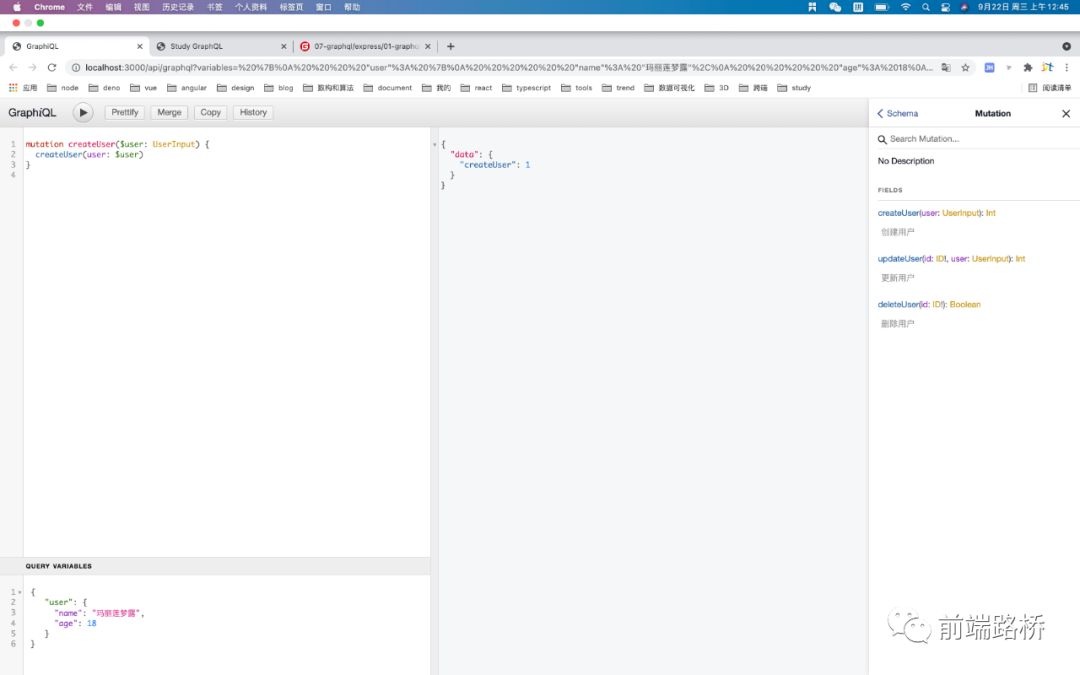
React的前端设计
关于React项目的搭建,可以看下我之前写的这篇文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/cnroadbridge/p/13358136.html
在React中,我们可以通过Class和Function的方式创建组件,前者通过Class创建的组件,具有相应的生命周期函数,而且有相应的state, 而后者通过Function创建的更多的是做展示用。自从有了React Hooks之后,在Function创建的组件中也可以用state了,组件间的复用更加优雅,代码更加简洁清爽了,它真的很灵活。Vue3中的组合式API,其实思想上有点React Hooks的味道。
构思页面
根据后端这边提供的接口,这里我们会有张页面,里面有通过列表接口返回的数据,它可以编辑和删除数据,然后我们有一个表单可以更新和新增数据,简单的理一下,大致就这些吧。
增删改查接口的query
function getUser(id) {
const query = `query getUser($id: ID!) {
getUser(id: $id) {
id,
name,
age
}
}`;
const variables = { id };
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch('/api/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query,
variables,
}),
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => {
resolve(data);
});
})
}
function getUsers() {
const query = `query getUsers {
getUsers {
id,
name,
age
}
}`;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch('/api/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query,
}),
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => {
resolve(data)
});
});
}
function addUser(name, age) {
const query = `mutation createUser($user: UserInput) {
createUser(user: $user)
}`;
const variables = {
user: {
name, age
}
};
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch('/api/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query,
variables
}),
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => {
resolve(data)
});
});
}
function updateUser(id, name, age) {
const query = `mutation updateUser($id: ID!, $user: UserInput) {
updateUser(id: $id, user: $user)
}`;
const variables = {
id,
user: {
name, age
}
};
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch('/api/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query,
variables
}),
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => {
resolve(data)
});
});
}
function deleteUser(id) {
const query = `mutation deleteUser($id: ID!) {
deleteUser(id: $id)
}`;
const variables = {
id
};
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch('/api/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Accept: 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query,
variables
}),
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => {
resolve(data)
});
})
}
上面通过自带的fetch请求,分别实现了对给出的graphql接口的相关请求
UserPage页面组件
// 页面
const UserPage = () => {
const [userList, setUserList] = React.useState([]);
const [userForm, setUserForm] = React.useState({ id: '', name: '', age: '', type: 'add' });
const [isReload, setReload] = React.useState(false)
const [id, setId] = React.useState('');
React.useEffect(() => {
refreshUserList();
}, []);
React.useEffect(() => {
if (isReload) {
refreshUserList();
}
setReload(false);
}, [isReload]);
React.useEffect(() => {
if (id) {
getUser(id).then(res => {
const { data: { getUser: user } } = res;
setUserForm({ type: 'edit', ...user });
})
}
}, [id]);
function refreshUserList() {
getUsers().then(res => {
const { data: { getUsers = [] } } = res;
setUserList(getUsers);
})
}
return (<div>
<UserList userList={userList} setReload={setReload} setId={setId} />
<UserOperator setUserForm={setUserForm} userForm={userForm} setReload={setReload} />
</div>);
};
这里用了两个React Hooks的钩子, useState使得函数组件可以像Class组件一样可以使用state, useEffect它接受两个参数,第一个是函数,第二个是一个数组,数组中的元素的变化会触发这个钩子的函数的执行。
UserList列表组件
const UserList = (props) => {
const { userList, setReload, setId } = props;
const userItems = userList.map((user, index) => {
return <UserItem key={user.id} user={user} setReload={setReload} setId={setId} />
});
return (<ul>{userItems}</ul>);
};
UserItem单条数据项组件
// 数据项
const UserItem = (props) => {
const { user, setReload, setId } = props;
function handleDelete(id) {
deleteUser(id).then(res => {
const { data: { deleteUser: flag } } = res;
if (flag) {
setReload(true);
}
})
}
function handleEdit(id) {
setId(id);
}
return (<li>
{user.name}: {user.age}岁
<span className="blue pointer" onClick={() => handleEdit(user.id)}>编辑</span>
<span className="red pointer" onClick={() => handleDelete(user.id)}>删除</span>
</li>);
};
UserOperator 操作组件
// 新增
const UserOperator = (props) => {
const [id, setId] = React.useState('');
const [name, setName] = React.useState('');
const [age, setAge] = React.useState('');
const { setUserForm, userForm, setReload } = props;
function handleChange(e, cb) {
cb(e.target.value)
}
function handleSubmit() {
const { type } = userForm;
if (type === 'edit') {
updateUser(id, name, Number(age)).then(res => {
const { data: { updateUser: flag } } = res;
if (flag) {
setReload(true);
setId('');
setName('');
setAge('');
} else {
alert('更新失败');
}
})
} else if (type === 'add') {
if (name && age) {
addUser(name, Number(age)).then(res => {
const { data: { createUser: flag } } = res;
if (flag) {
setReload(true);
setId('');
setName('');
setAge('');
} else {
alert('添加失败');
}
});
}
}
setUserForm({ ...userForm, type: 'add' })
}
React.useEffect(() => {
const { id, name, age } = userForm
setId(id);
setName(name);
setAge(age);
}, [userForm]);
return (<div>
<span>姓名:</span><input type="text" value={name} onChange={e => handleChange(e, setName)} />
<span>年龄:</span><input type="number" value={age} onChange={e => handleChange(e, setAge)} />
<button onClick={() => handleSubmit()}>{BUTTON_MAP[userForm.type]}</button>
</div>)
}
- 根组件
const App = (props) => {
return (<div><h2>{props.title}</h2><UserPage /></div>);
};
const root = document.getElementById('root');
ReactDOM.render(<App title="A Simple GraphQL Demo With React Design By ataola, Have Fun!" />, root);
文件如下:https://gitee.com/taoge2021/study-nodejs/blob/master/07-graphql/express/01-graphql/public/index.html
总结
刀耕火种的时代已然是离我们很远,人类文明发展到现在已然是可以用微波炉煤气灶烧饭做菜,上面的例子只是介绍了GraphQL的使用,并且结合React打通了这样一个流程。实际上在开发中,我们往往会采用社区一些成熟的技术栈,比如你需要进一步了解GraphQL,可以去了解下Apollo这个库。那么前后端的架构就可以是 react-apollo,vue-apollo, 后端的话比如express-apollo,koa-apollo等等。我们在学开车的时候,往往是学手动挡的帕萨特,而在买汽车的时候,往往是喜欢买自动挡的辉腾,因为它比较符合人类文明的发展趋势,虽然外表上看上去和帕萨特差不多,但是自动挡着实是文明的进步啊!