目录
- 1、什么是key
- 2、key的更新原理
- 3、key的分类
- GlobalKey
- LocalKey
- 总结
1、什么是key
Widget中有个可选属性key,顾名思义,它是组件的标识符,当设置了key,组件更新时会根据新老组件的key是否相等来进行更新,可以提高更新效率。但一般我们不会去设置它,除非对某些具备状态且相同的组件进行添加、移除、或者排序时,就需要使用到key,不然就会出现一些莫名奇妙的问题。
例如下面的demo:
| import 'dart:math'; | |
| import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; | |
| void main() { | |
| runApp(const MyApp()); | |
| } | |
| class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { | |
| const MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key); | |
| Widget build(BuildContext context) { | |
| return MaterialApp( | |
| title: 'test', | |
| home: Scaffold( | |
| appBar: AppBar( | |
| title: const Text('key demo'), | |
| ), | |
| body: const KeyDemo(), | |
| ), | |
| ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| class KeyDemo extends StatefulWidget { | |
| const KeyDemo({Key? key}) : super(key: key); | |
| State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _KeyDemo(); | |
| } | |
| class _KeyDemo extends State<KeyDemo> { | |
| final List<ColorBlock> _list = [ | |
| const ColorBlock(text: ''), | |
| const ColorBlock(text: ''), | |
| const ColorBlock(text: ''), | |
| const ColorBlock(text: ''), | |
| const ColorBlock(text: ''), | |
| ]; | |
| Widget build(BuildContext context) { | |
| return Column( | |
| children: [ | |
| ..._list, | |
| ElevatedButton( | |
| onPressed: () { | |
| _list.removeAt(); | |
| setState(() {}); | |
| }, | |
| child: const Text('删除'), | |
| ) | |
| ], | |
| ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| class ColorBlock extends StatefulWidget { | |
| final String text; | |
| const ColorBlock({Key? key, required this.text}) : super(key: key); | |
| State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _ColorBlock(); | |
| } | |
| class _ColorBlock extends State<ColorBlock> { | |
| final color = Color.fromRGBO( | |
| Random().nextInt(), Random().nextInt(256), Random().nextInt(256), 1.0); | |
| Widget build(BuildContext context) { | |
| return Container( | |
| width: double.infinity, | |
| height:, | |
| color: color, | |
| child: Text(widget.text), | |
| ); | |
| } | |
| } |
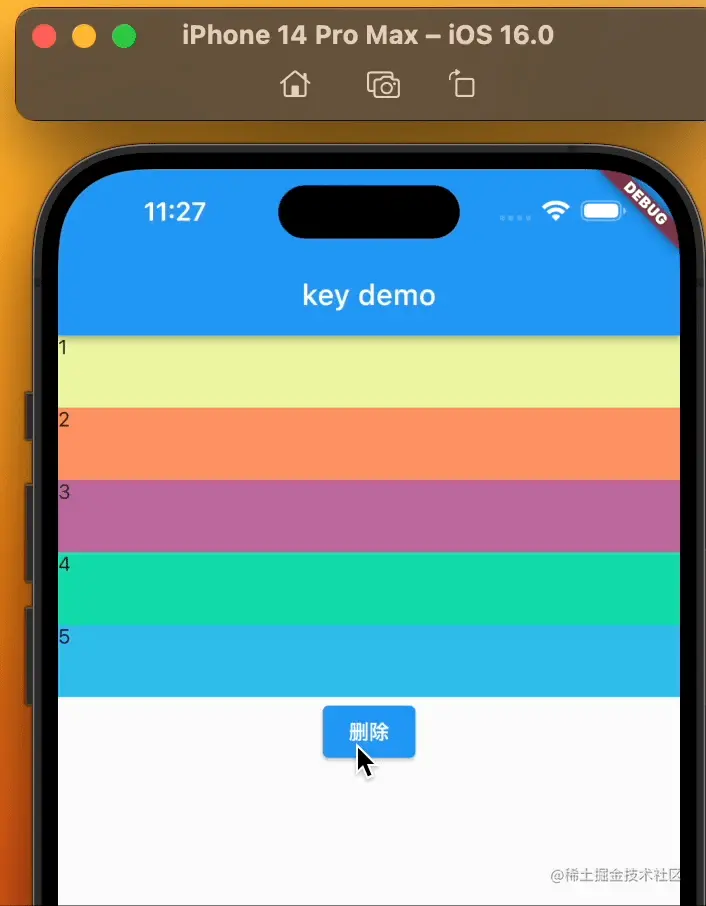
点击删除按钮,从ColorBlock的列表中删除第一个元素,可以观察到颜色发生了错乱,删除了1号色块,它的颜色状态转移到了2号身上。这种情况在实际开发中往往会造成不小的麻烦。
这时,就需要为每个ColorBlock设置key值,来避免这个问题。
| final List<ColorBlock> _list = [ | |
| const ColorBlock(key: ValueKey(''), text: '1'), | |
| const ColorBlock(key: ValueKey(''), text: '2'), | |
| const ColorBlock(key: ValueKey(''), text: '3'), | |
| const ColorBlock(key: ValueKey(''), text: '4'), | |
| const ColorBlock(key: ValueKey(''), text: '5'), | |
| ]; |
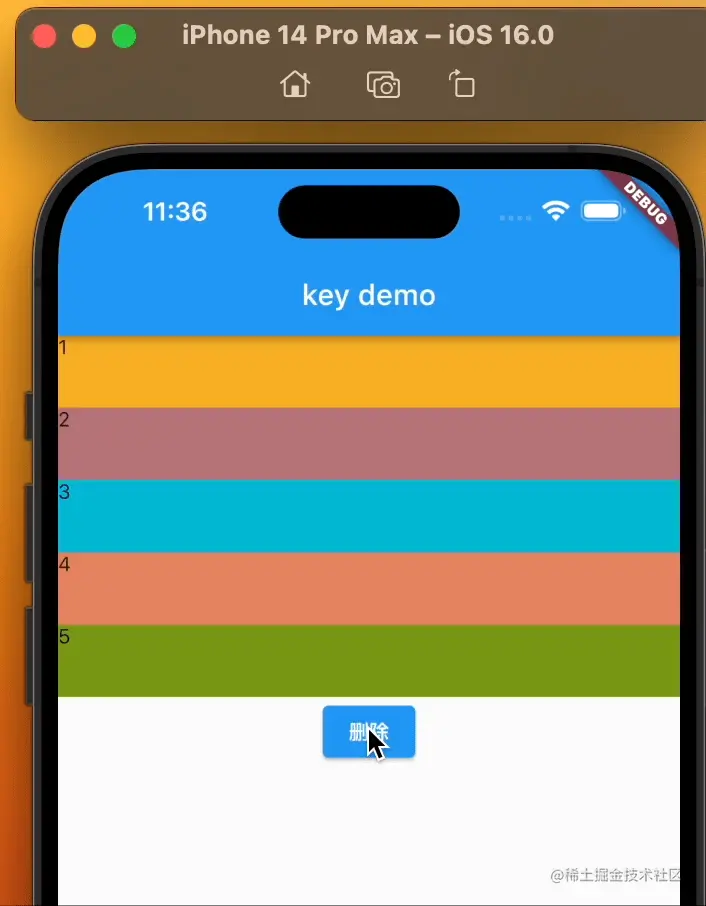
点击删除按钮,可以看到颜色错乱的现象消失了,一切正常。那么有没有想过,为什么ColorBlock有key和没key会出现这种差异?
2、key的更新原理
我们来简单分析下key的更新原理。
首先,我们知道Widget是组件配置信息的描述,而Element才是Widget的真正实现,负责组件的布局和渲染工作。在创建Widget时会对应的创建Element,Element保存着Widget的信息。
当我们更新组件时(通常指调用setState方法)会遍历组件树,对组件进行新旧配置的对比,如果同个组件信息不一致,则进行更新操作,反之则不作任何操作。
| /// Element | |
| Element? updateChild(Element? child, Widget? newWidget, Object? newSlot) { | |
| if (newWidget == null) { | |
| if (child != null) | |
| deactivateChild(child); | |
| return null; | |
| } | |
| final Element newChild; | |
| /// 更新逻辑走这里 | |
| if (child != null) { | |
| bool hasSameSuperclass = true; | |
| if (hasSameSuperclass && child.widget == newWidget) { | |
| if (child.slot != newSlot) | |
| updateSlotForChild(child, newSlot); | |
| newChild = child; | |
| } else if (hasSameSuperclass && Widget.canUpdate(child.widget, newWidget)) { | |
| /// 判断新旧组件为同一个组件则进行更新操作 | |
| if (child.slot != newSlot) | |
| updateSlotForChild(child, newSlot); | |
| child.update(newWidget); | |
| newChild = child; | |
| } else { | |
| deactivateChild(child); | |
| newChild = inflateWidget(newWidget, newSlot); | |
| if (!kReleaseMode && debugProfileBuildsEnabled) | |
| Timeline.finishSync(); | |
| } | |
| } else { | |
| /// 创建逻辑走这里 | |
| newChild = inflateWidget(newWidget, newSlot); | |
| } | |
| return newChild; | |
| } |
通过Element中的updateChild进行组件的更新操作,其中Widget.canUpdate是判断组件是否需要更新的核心。
| /// Widget | |
| static bool canUpdate(Widget oldWidget, Widget newWidget) { | |
| return oldWidget.runtimeType == newWidget.runtimeType | |
| && oldWidget.key == newWidget.key; | |
| } |
canUpdate的代码很简单,就是对比新老组件的runtimeType和key是否一致,一致刚表示为同一个组件需要更新。
结合demo,当删除操作时,列表中第一个的组件oldWidget为ColorBlock(text: '1'),newWidget为ColorBlock(text: '2') ,因为我们将text和color属性都存储在State中,所以 oldWidget.runtimeType == newWidget.runtimeType为true,oldWidget.key == newWidget.key 为null,也等于true。
于是调用udpate进行更新
| /// Element | |
| void update(covariant Widget newWidget) { | |
| _widget = newWidget; | |
| } |
可以看出,update也只是简单的更新Element对Widget的引用。 最终新的widget更新为ColorBlock(text: '2'),State依旧是ColorBlock(text: '1')的State,内部的状态保持不变。
如果添加了Key,刚oldWidget.key == newWidget.key为false,不会走update流程,也就不存在这个问题。
3、key的分类
key有两个子类GlobalKey和LocalKey。
GlobalKey
GlobalKey全局唯一key,每次build的时候都不会重建,可以长期保持组件的状态,一般用来进行跨组件访问Widget的状态。
| class GlobalKeyDemo extends StatefulWidget { | |
| const GlobalKeyDemo({Key? key}) : super(key: key); | |
| State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _GlobalKeyDemo(); | |
| } | |
| class _GlobalKeyDemo extends State<GlobalKeyDemo> { | |
| GlobalKey _globalKey = GlobalKey(); | |
| Widget build(BuildContext context) { | |
| return Column( | |
| children: [ | |
| ColorBlock( | |
| key: _globalKey, | |
| ), | |
| ElevatedButton( | |
| onPressed: () { | |
| /// 通过GlobalKey可以访问组件ColorBlock的内部 | |
| (_globalKey.currentState as _ColorBlock).setColor(); | |
| setState(() {}); | |
| }, | |
| child: const Text('更新为红色'), | |
| ) | |
| ], | |
| ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| class ColorBlock extends StatefulWidget { | |
| const ColorBlock({Key? key}) : super(key: key); | |
| State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _ColorBlock(); | |
| } | |
| class _ColorBlock extends State<ColorBlock> { | |
| Color color = Colors.blue; | |
| setColor() { | |
| color = Colors.red; | |
| } | |
| Widget build(BuildContext context) { | |
| return Container( | |
| width: double.infinity, | |
| height:, | |
| color: color, | |
| ); | |
| } | |
| } |
将组件的key设置为GlobalKey,可以通过实例访问组件的内部属性和方法。达到跨组件操作的目的。
LocalKey
LocalKey局部key,可以保持当前组件内的子组件状态,用法跟GlobalKey类似,可以访问组件内部的数据。
LocalKey有3个子类ValueKey、ObjectKey、UniqueKey。
- ValueKey
可以使用任何值做为key,比较的是两个值之间是否相等于。
| class ValueKey<T> extends LocalKey { | |
| const ValueKey(this.value); | |
| final T value; | |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { | |
| if (other.runtimeType != runtimeType) | |
| return false; | |
| return other is ValueKey<T> | |
| && other.value == value; | |
| } | |
| /// ... | |
| } |
- ObjectKey:
可以使用Object对象作为Key,比较的是两个对象内存地址是否相同,也就是说两个对象是否来自同一个类的引用。
| class ObjectKey extends LocalKey { | |
| const ObjectKey(this.value); | |
| final Object? value; | |
| bool operator ==(Object other) { | |
| if (other.runtimeType != runtimeType) | |
| return false; | |
| /// identical函数: 检查两个引用是否指向同一对象 | |
| return other is ObjectKey | |
| && identical(other.value, value); | |
| } | |
| /// ... | |
| } |
- UniqueKey
独一无二的key,Key的唯一性,一旦使用UniqueKey,那么将不存在element复用
| class UniqueKey extends LocalKey { | |
| UniqueKey(); | |
| String toString() => '[#${shortHash(this)}]'; | |
| } |
总结
1、key是Widget中的唯一标识,如果列表中包含有状态组件,对其进行添加、移除、或者排序操作,必须增加key。以避免出现乱序现象。
2、出现乱序现象的根本原因是:新旧组件通过runtimeType和key进行对比,key为空的情况下,有状态组件runtimeType对比为true,造成组件更新后依然保持State内部的属性状态。
3、key分为GlobalKey和LocalKey,GlobalKey可以进行跨组件访问Widget,LocalKey只能在同级之下进行。