VueCli 自定义创建项目
1.安装脚手架 (已安装)
npm i @vue/cli -g
2.创建项目
vue create hm-exp-mobile
- 选项
| Vue CLI v5.0.8 | |
| ? Please pick a preset: | |
| Default ([Vue 3] babel, eslint) | |
| Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint) | |
| > Manually select features 选自定义 |
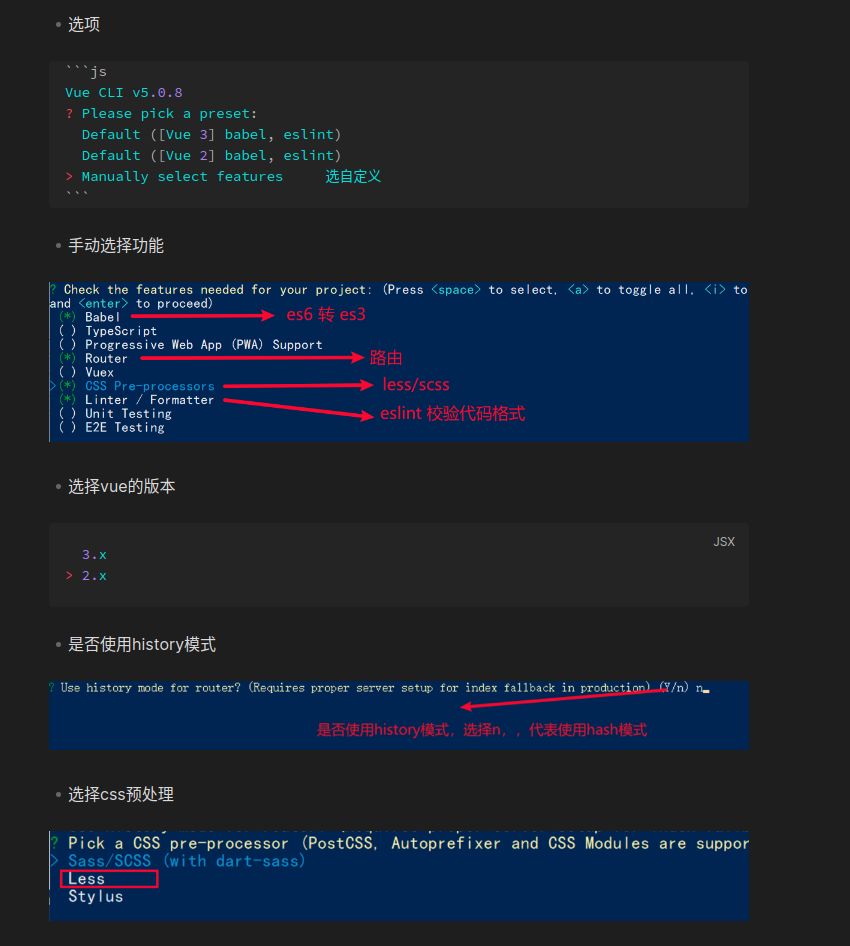
- 选择eslint的风格 (eslint 代码规范的检验工具,检验代码是否符合规范)
- 比如:const age = 18; => 报错!多加了分号!后面有工具,一保存,全部格式化成最规范的样子

- 启动项目
npm run serve
Vuex
Vuex 是一个 Vue 的 状态管理工具,状态就是数据。 大白话:Vuex 是一个插件,可以帮我们管理 Vue 通用的数据 (多组件共享的数据)。例如:购物车数据 个人信息数
基本使用
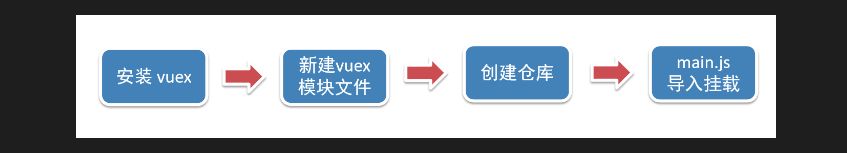
1.安装 vuex
安装vuex与vue-router类似,vuex是一个独立存在的插件,如果脚手架初始化没有选 vuex,就需要额外安装。
yarn add vuex@3 或者 npm i vuex@3
2.新建 store/index.js 专门存放 vuex
为了维护项目目录的整洁,在src目录下新建一个store目录其下放置一个index.js文件。 (和 `router/index.js` 类似)

.创建仓库 store/index.js
| // 导入 vue | |
| import Vue from 'vue' | |
| // 导入 vuex | |
| import Vuex from 'vuex' | |
| // vuex也是vue的插件, 需要use一下, 进行插件的安装初始化 | |
| Vue.use(Vuex) | |
| // 创建仓库 store | |
| const store = new Vuex.Store() | |
| // 导出仓库 | |
| export default store |
4 在 main.js 中导入挂载到 Vue 实例上
| import Vue from 'vue' | |
| import App from './App.vue' | |
| import store from './store' | |
| Vue.config.productionTip = false | |
| new Vue({ | |
| render: h => h(App), | |
| store | |
| }).$mount('#app') |
此刻起, 就成功创建了一个 空仓库!!
5.测试打印Vuex
App.vue
| created(){ | |
| console.log(this.$store) | |
| } |
state 状态
如何给仓库存储数据, 如果取出使用仓库的数据
提供数据(存入数据)
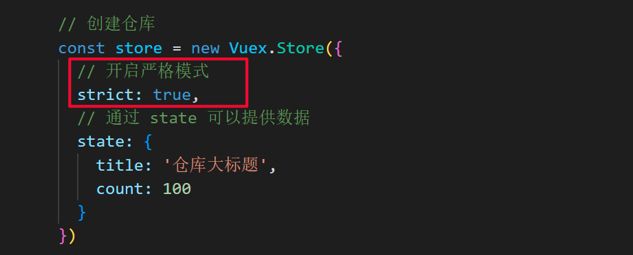
State提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到Store中的State中存储。 打开项目中的store.js文件,在state对象中可以添加我们要共享的数据。
| // 创建仓库 store | |
| const store = new Vuex.Store({ | |
| // state 状态, 即数据, 类似于vue组件中的data, | |
| // 区别: | |
| // 1.data 是组件自己的数据, | |
| // 2.state 中的数据整个vue项目的组件都能访问到 | |
| state: { | |
| count: 101 | |
| } | |
| }) |
访问数据
| 获取 store: | |
| 1.Vue模板中获取 this.$store | |
| 2.js文件中获取 import 导入 store | |
| 模板中: {{ $store.state.xxx }} | |
| 组件逻辑中: this.$store.state.xxx | |
| JS模块中: store.state.xxx |
如果数据量变大, 那么使用这种方法明显就比较累坠了。所以我们可以通过使用辅助函数来帮助我们把store中的数据映射到 组件的计算属性中, 它属于一种方便的用法

通过数组的方式得到对象
第一步:导入mapState (mapState是vuex中的一个函数)
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
第二步:采用数组形式引入state属性
mapState(['count']) // count 就是我们仓库中的属性名
上面代码的最终得到的是 类似于
| count () { | |
| return this.$store.state.count | |
| } |
第三步:利用展开运算符将导出的状态映射给计算属性
| computed: { | |
| ...mapState(['count']) | |
| } | |
| <div> state的数据:{{ count }}</div> |
注意:
通过这样方式如果修改属性会报错, 因为vuex默认开启了严选模式 也就是说通过**vuex** 得到的数据是单项流模式, 组件是不能直接修改仓库中的数据。
state数据的修改只能通过mutations,并且mutations必须是同步的
核心概念mutations
定义mutations
| const store = new Vuex.Store({ | |
| state: { | |
| count: 0 | |
| }, | |
| // 定义mutations | |
| mutations: { | |
| } | |
| }) |
mutations是一个对象, 对象中存放的是修改state的方法
| mutations: { | |
| // 方法里参数 第一个参数是当前store的state属性 | |
| // payload 载荷 运输参数 调用mutaiions的时候 可以传递参数 传递载荷 | |
| addCount (state) { | |
| state.count += 1 | |
| } | |
| }, |
组件中提交mutations
通过点击事件实现修改方法的触发, 然后在通过下面语句实现调用mustations中的addCount方法
| <button @click="add()">值 + 5</button> | |
| methods: { | |
| add(){ | |
| this.$store.commit('addCount') | |
| } | |
| } |
带参数的mutations函数
**提交 mutation 是可以传递参数的 **this.$store.commit('xxx', 参数) 在定义mutations中的方法的时候可以直接通过下面的类似语句进行修改。
| mutations: { | |
| addCount (state, count) { | |
| state.count = count | |
| } | |
| }, |
注意: 提交的参数只能是一个, 如果有多个参数要传, 可以传递一个对象
通过input标签修改state数据
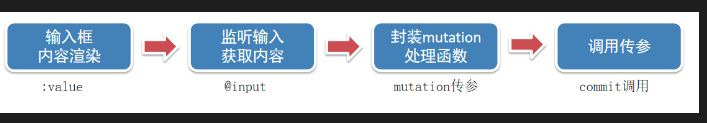
| <input :value="count" ="handleInput" type="text"> | |
| export default { | |
| methods: { | |
| handleInput (e) { | |
| // 1. 实时获取输入框的值 | |
| const num = +e.target.value | |
| // 2. 提交mutation,调用mutation函数 | |
| this.$store.commit('changeCount', num) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
然后在store/index.js文件中
| mutations: { | |
| changeCount (state, newCount) { | |
| state.count = newCount | |
| } | |
| }, |
辅助函数 - mapMutations
mapMutations和mapState很像,它把位于mutations中的方法提取了出来,我们可以将它导入
在所要使用的组件中
| import { mapMutations } from 'vuex' | |
| methods: { | |
| ...mapMutations(['addCount']) | |
| } |
上面代码的含义是将mutations的方法导入了methods中,等价于
| methods: { | |
| // commit(方法名, 载荷参数) | |
| addCount () { | |
| this.$store.commit('addCount') | |
| } | |
| } |
此时,就可以直接通过this.addCount调用了
<button @click="addCount">值+1</button>
注意: Vuex中mutations中要求不能写异步代码,如果有异步的ajax请求,应该放置在actions中
核心概念 - actions
state是存放数据的,mutations是同步更新数据 (便于监测数据的变化, 更新视图等, 方便于调试工具查看变化),actions则负责进行异步操作
说明:mutations必须是同步的
需求: 一秒钟之后, 要给一个数 去修改state
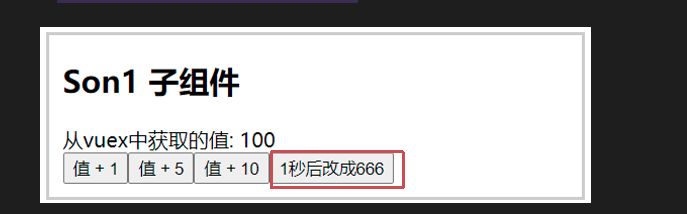
- 在组件中通过点击事件修改
| <button ="setAfter()" >1s 后修改为 666</button> | |
| // script格式中 | |
| methods: { | |
| setAfter(){ | |
| const val = 666 | |
| this.$store.dispatch('change', val) | |
| } | |
| } |
- 通过
this.$store.dispatch('方法名', 参数)调用store/index.js中的方法
| // 创建仓库 store | |
| const store = new Vuex.Store({ | |
| state: { | |
| ount: 100 | |
| }, | |
| mutations: { | |
| changeCount(state, count){ | |
| state.ount = count | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| actions: { | |
| // 不能在actions中直接修改, 需要调用mutations中的方法 | |
| change(context, count) { | |
| setTimeout(() => { | |
| //调用mutations 的changeCount, 从而修改 | |
| context.commit('changeCount', count) | |
| },2000) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }) |

辅助函数 - mapActions
mapActions 是把位于 actions中的方法提取了出来,映射到组件methods中, 不需要在写方法来调用了
| import { mapActions } from 'vuex' | |
| methods: { | |
| ...mapActions(['changeCountAction']) | |
| } | |
| //mapActions映射的代码 本质上是以下代码的写法 | |
| //methods: { | |
| // changeCountAction (n) { | |
| // this.$store.dispatch('changeCountAction', n) | |
| // }, | |
| //} | |
| <!-- 参数可以直接进行传递, 不需要考虑methods中, 但是还是最多只能传一个, 多了就封装成为对象, 然后通过对象的形式传过去. --> | |
| <button @click="changeCountAction(200)">+异步</button> |
然后在store/index.js中进行修改
| // 创建仓库 store | |
| const store = new Vuex.Store({ | |
| state: { | |
| ount: 100 | |
| }, | |
| mutations: { | |
| addCount(state, count) { | |
| state.ount += count | |
| }, | |
| changeCount(state, count){ | |
| state.ount = count | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| actions: { | |
| // 最好不要自己直接修改, | |
| change(context, count) { | |
| setTimeout(() => { | |
| //调用山寺规模的changeCount, 从而修改 | |
| context.commit('changeCount', count) | |
| },2000) | |
| }, | |
| addFive(context, count) { | |
| setTimeout(() => { | |
| //在这里通过上下文来调用mutations中的方法 | |
| context.commit('addCount', count) | |
| },2000) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }) |
核心概念 - getters
除了state之外,有时我们还需要从state中筛选出符合条件的一些数据,这些数据是依赖state的,此时会用到getters
例如, 组件中定义了list数组, 我们需要筛选出list中 大于 X的数据. 就可以通过getters实现
| state: { | |
| list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] | |
| }, | |
| getters: { | |
| // getters函数的第一个参数是 state | |
| // 必须要有返回值 | |
| filterList: state => state.list.filter(item => item > 5) | |
| } |
使用getters
2.1原始方式-$store
在组件中, 通过$store对象来获取他的getters属性, 然后再获取其中的方法
<div>{{ $store.getters.filterList }}</div>
2.2辅助函数 - mapGetters
| computed: { | |
| ...mapGetters(['filterList']) | |
| } | |
| <div>{{ filterList }}</div> |
四种核心方法使用总结
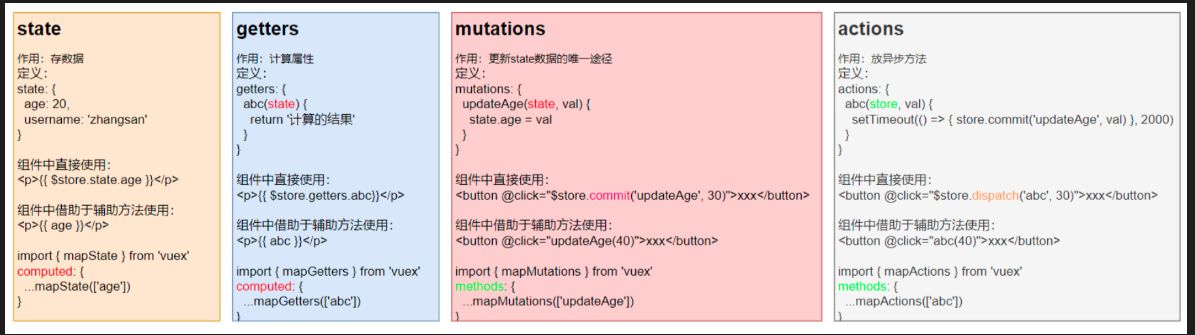
模块module
拆封模块的原因:
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。 这句话的意思是,如果把所有的状态都放在state中,当项目变得越来越大的时候,Vuex会变得越来越难以维护
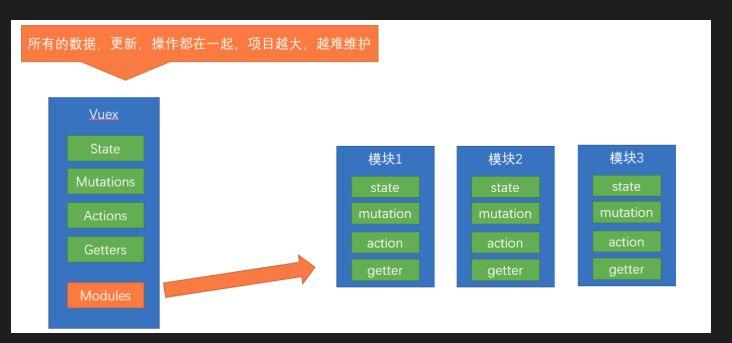
在store中配置module模块。 然后在每个模块中设置state、mutations、actions、getters
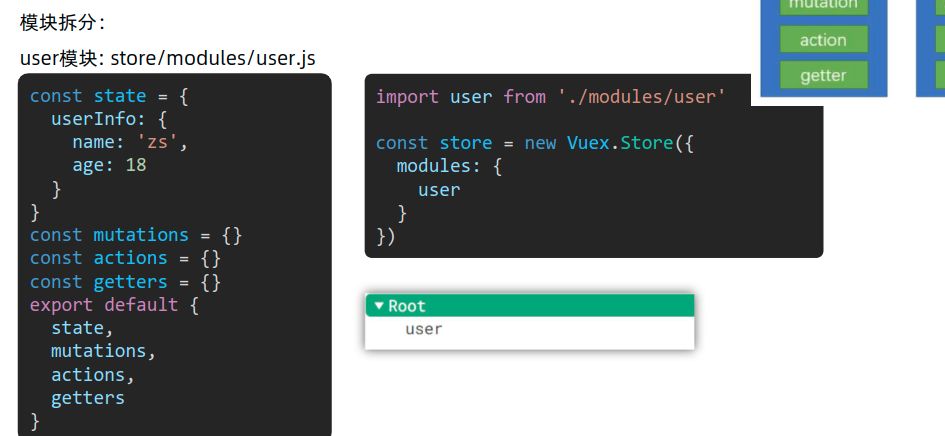
挂载模块
- 在
model/模块名.js定义模块的内容, 设置4个属性, 然后导出
| //settings模块 | |
| const state= { | |
| theme: 'light' , | |
| desc: '测试demo' | |
| } | |
| const mutations = { } | |
| const actions = { } | |
| const getters = { } | |
| // 导出 | |
| export default { | |
| state, | |
| mutations, | |
| actions, | |
| getters | |
| } |
- 在
index.js中进行导入模块和 注册这两个模块
| //导入模块 | |
| import user from './modules/user' | |
| import settings from './modules/settings' | |
| // 创建仓库 store | |
| const store = new Vuex.Store({ | |
| //注册模块 | |
| modules: { | |
| user, | |
| settings | |
| }, | |
| }) |
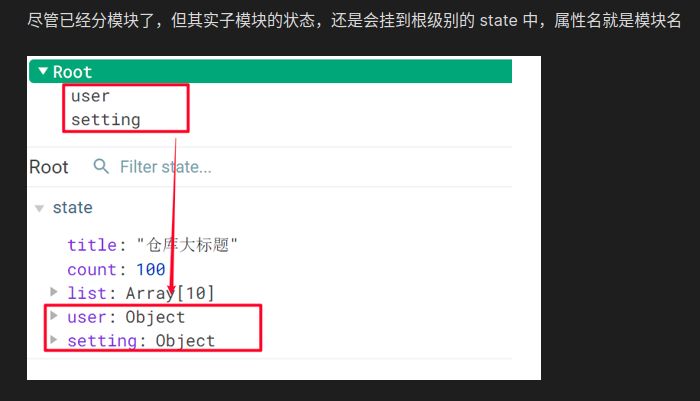
访问模块中的数据
具体细节可以参考之前的核心概念的使用方法 xxx 表示我们需要得到的属性
获取state内容
- 直接通过模块名访问
$store.state.模块名.xxx - 通过 mapState 映射:
- 默认根级别的映射
mapState([ 'xxx' ]) - 子模块的映射 :
mapState('模块名', ['xxx'])- 需要开启命名空间 namespaced:true 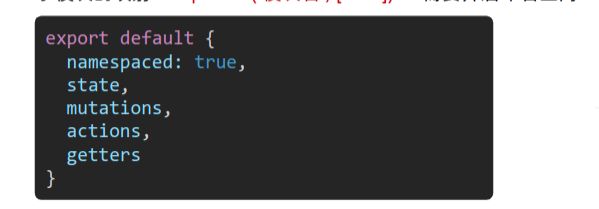
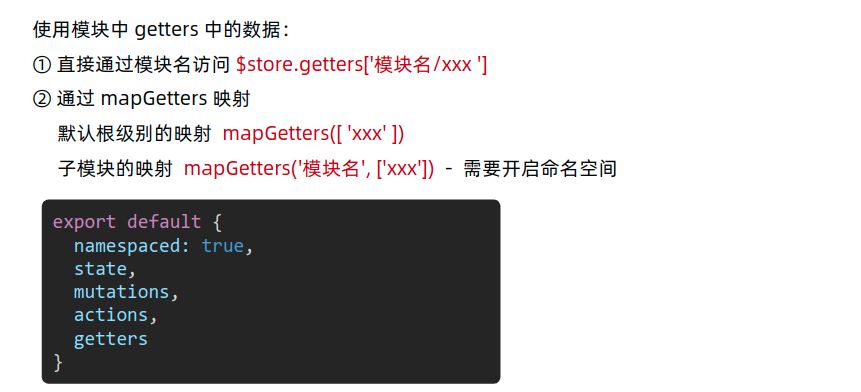
获取getters中的内容
获取mutations中的内容
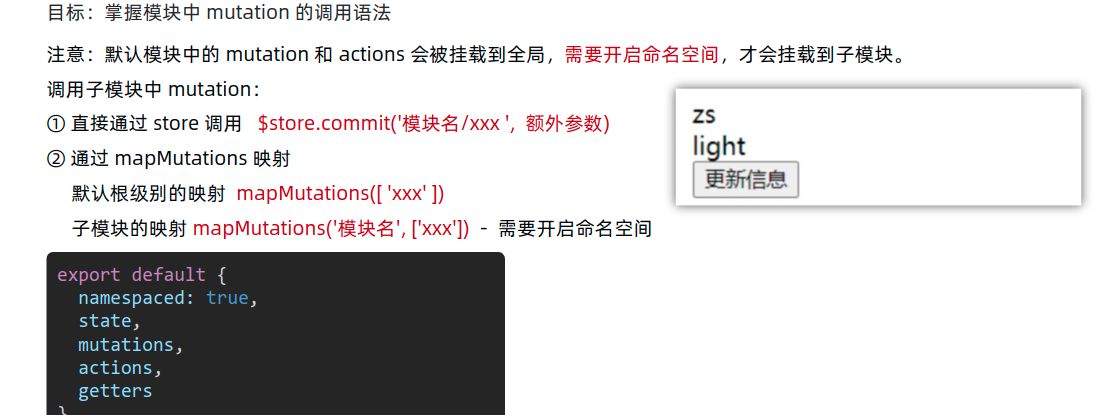
获取actions中的内容

实现案例
获取请求, 然后存入vuex ,最后渲染

- 首先创建模块
modules/cart.js, 然后构建框架
| import { mapActions ,mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations } from "vuex" | |
| // 导出 | |
| export default { | |
| namespaced: true, | |
| state() { | |
| return { | |
| //关于购物车的一个数据[{ } ,{ }] | |
| list: [] | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| mutations: { | |
| }, | |
| actions: { | |
| }, | |
| getters: { | |
| } | |
| } |
通常都是通过一个对象的形式来进行构建数据的
- 注册模块到
index.js
| import Vue from 'vue | |
| import Vuex from 'vuex' | |
| //1. 导入模块 | |
| import cart from './modules/cart' | |
| Vue.use(Vuex) | |
| export default new Vuex.Store({ | |
| modules: { | |
| cart | |
| } | |
| }) |
- 准备需要的
actions和mutations代码( 因为我们获取数据是通过异步的方式, 所以在actions里 )
| export default { | |
| namespaced: true, | |
| state() { | |
| return { | |
| //关于购物车的一个数据[{ } ,{ }] | |
| list: [] | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| mutations: { | |
| //更新List中的数据 | |
| updateList(state, newList){ | |
| state.list = newList | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| actions: { | |
| // 异步更新数据 | |
| async getList(context){ | |
| const res = await axios.get('http://localhost:3000/cart') | |
| // 调用updateList 存入数据 | |
| context.commit('updateList', res.data) | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| getters: {} | |
| } |
仅仅这样在模块中写还无法将数据加载到组件中, 需要在App.vue 组件中调用才行
| <script> | |
| //1. 导入组件和模块 | |
| import { mapActions , mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations} from 'vuex' | |
| import cart from './store/modules/cart' | |
| export default { | |
| name: 'App', | |
| components: { | |
| //组件注册 | |
| CartHeader, | |
| CartFooter, | |
| CartItem | |
| }, | |
| //得到使用vuex中存入的数据 | |
| computed: { | |
| ...mapState('cart', ['list']) | |
| }, | |
| // 通过使用created将数据加载进去 | |
| created() { | |
| // this.$store.dispatch('cart/getList') | |
| //通过this调用 | |
| this.getList() | |
| }, | |
| methods: { | |
| ...mapActions('cart',['getList']) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| </script> |
- 动态渲染
| <template> | |
| <div class="app-container"> | |
| <!-- Header 区域 --> | |
| <cart-header></cart-header> | |
| <!-- 商品 Item 项组件 | |
| 通过mapState得到数据, 然后进行v-for 渲染, 最后通过:item="item" 将对象传入 | |
| 上述就是父传子 | |
| --> | |
| <cart-item v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id" :item="item"></cart-item> | |
| <!-- Foote 区域 --> | |
| <cart-footer></cart-footer> | |
| </div> | |
| </template> |
子组件通过props数据, 然后进行渲染即可
数据更新
- 基于state 来使用getters从而实现 数据的更新
| import axios from "axios" | |
| import { mapActions ,mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations } from "vuex" | |
| // 导出 | |
| export default { | |
| namespaced: true, | |
| state() { | |
| return { | |
| //关于购物车的一个数据[{ } ,{ }] | |
| list: [] | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| mutations: { | |
| //更新List中的数据 | |
| updateList(state, newList){ | |
| state.list = newList | |
| }, | |
| // 对页面作数据更新 | |
| add(state, id) { | |
| const goods = state.list.find((item) => item.id == id) | |
| goods.count += 1 | |
| }, | |
| // 对页面作数据更新 | |
| del(state, id) { | |
| const goods = state.list.find((item) => item.id == id) | |
| goods.count -= 1 | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| actions: { | |
| // 异步更新数据 | |
| async getList(context){ | |
| const res = await axios.get('http://localhost:3000/cart') | |
| // console.log(res.data) | |
| context.commit('updateList', res.data) | |
| }, | |
| // 新增商品数量 | |
| async addItem(context, item) { | |
| const newCount = item.count + 1 | |
| const res = await axios.patch(`http://localhost:3000/cart/${item.id}`, { | |
| count: newCount | |
| }) | |
| console.log(res.data) | |
| context.commit('add', item.id) | |
| }, | |
| // 减少商品数量 | |
| async delItem(context, item) { | |
| const newCount = item.count - 1 | |
| if(newCount < 1) return | |
| const res = await axios.patch(`http://localhost:3000/cart/${item.id}`, { | |
| count: newCount | |
| }) | |
| context.commit('del', item.id) | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| getters: { | |
| totalCount(state) { | |
| return state.list.reduce((sum,item ) => sum + item.count, 0); | |
| }, | |
| totalMoney(state) { | |
| return state.list.reduce((sum,item ) => sum += item.price*item.count, 0); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
- 然后通过使用
getter实现总数的计算
| <template> | |
| <!-- item页面的update数据 --> | |
| <button class="btn btn-light" @click="delItem(item)">-</button> | |
| <span class="count">{{ item.count }}</span> | |
| <button class="btn btn-light" @click="addItem(item)">+</button> | |
| <!-- 下面是footer页面的和上面不同 --> | |
| <div class="footer-container"> | |
| <!-- 中间的合计 --> | |
| <div> | |
| <span>共 {{totalCount}} 件商品,合计:</span> | |
| <span class="price">¥{{ totalMoney }}</span> | |
| </div> | |
| <!-- 右侧结算按钮 --> | |
| <button class="btn btn-success btn-settle">结算</button> | |
| </div> | |
| </template> | |
| <script> | |
| import { mapActions , mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations} from 'vuex'; | |
| import cart from '../store/modules/cart' | |
| export default { | |
| name: 'CartFooter', | |
| props: { | |
| list: { | |
| type: Array, | |
| required: true //必须传 | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| computed: { | |
| ...mapGetters('cart', ['totalCount','totalMoney']) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| </script> |