目录
- Vue项目结构
- 主要配置文件
- Vue项目启动代码执行流程分析
- Vue加载时文件的执行顺序
- Vue内部页面的执行顺序
- 总结
Vue项目结构
使用webpack构建的Vue项目的结构如下所示:
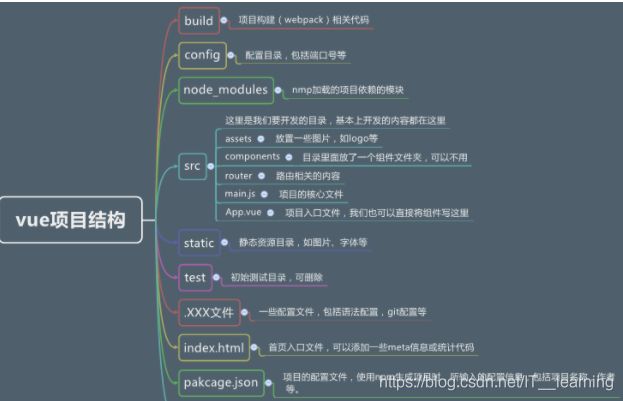
主要配置文件
1、package.json
package.json是一个json文件,这是vue项目的表述文件。
package.json定义了项目所需要的各种模块,以及项目的配置信息(名称、版本、许可证等),npm install命令也是根据这个配置文件自动下载项目所需的模块。
| { | |
| "name": "myvue", | |
| "version": ".0.0", | |
| "description": "A Vue.js project", | |
| "author": "LearningJun <@qq.com>", | |
| "private": true, | |
| "scripts": { | |
| "dev": "webpack-dev-server --inline --progress --config build/webpack.dev.conf.js", | |
| "start": "npm run dev", | |
| "unit": "jest --config test/unit/jest.conf.js --coverage", | |
| "ee": "node test/e2e/runner.js", | |
| "test": "npm run unit && npm run ee", | |
| "build": "node build/build.js" | |
| }, | |
| "dependencies": { | |
| "axios": "^.18.0", | |
| "echarts": ".6.0", | |
| "echarts-stat": "^.2.0", | |
| "element-ui": "^.13.2", | |
| "js-cookie": "^.2.1", | |
| "moment": "^.24.0", | |
| "qs": "^.7.0", | |
| "vue": "^.5.2", | |
| "vue-amap": "^.5.9", | |
| "vue-axios": "^.1.4", | |
| "vue-baidu-map": "^.21.22", | |
| "vue-cookies": "^.5.6", | |
| "vue-echarts": "^.0.0-beta.0", | |
| "vue-puzzle-vcode": "^.0.7", | |
| "vue-router": "^.0.1", | |
| "vue-video-player": "^.0.2", | |
| "vue-verify": "^1.1.5", | |
| "vuex": "^.1.0", | |
| "vxe-table": "^.9.22", | |
| "xe-utils": "^.7.12" | |
| }, | |
| "devDependencies": { | |
| "autoprefixer": "^.1.2", | |
| "babel-core": "^.22.1", | |
| "babel-helper-vue-jsx-merge-props": "^.0.3", | |
| "babel-loader": "^.1.1", | |
| "babel-plugin-syntax-jsx": "^.18.0", | |
| "babel-plugin-transform-runtime": "^.22.0", | |
| "babel-plugin-transform-vue-jsx": "^.5.0", | |
| "babel-preset-env": "^.3.2", | |
| "babel-preset-stage-": "^6.22.0", | |
| "chalk": "^.0.1", | |
| "copy-webpack-plugin": "^.0.1", | |
| "css-loader": "^.28.0", | |
| "extract-text-webpack-plugin": "^.0.0", | |
| "file-loader": "^.1.4", | |
| "friendly-errors-webpack-plugin": "^.6.1", | |
| "html-webpack-plugin": "^.30.1", | |
| "node-notifier": "^.1.2", | |
| "node-sass": "^.12.0", | |
| "optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin": "^.2.0", | |
| "ora": "^.2.0", | |
| "portfinder": "^.0.13", | |
| "postcss-import": "^.0.0", | |
| "postcss-loader": "^.0.8", | |
| "postcss-url": "^.2.1", | |
| "rimraf": "^.6.0", | |
| "sass-loader": "^.3.1", | |
| "semver": "^.3.0", | |
| "shelljs": "^.7.6", | |
| "style-loader": "^.0.0", | |
| "uglifyjs-webpack-plugin": "^.1.1", | |
| "url-loader": "^.5.8", | |
| "vue-loader": "^.3.0", | |
| "vue-style-loader": "^.0.1", | |
| "vue-template-compiler": "^.5.2", | |
| "webpack": "^.6.0", | |
| "webpack-bundle-analyzer": "^.9.0", | |
| "webpack-dev-server": "^.9.1", | |
| "webpack-merge": "^.1.0" | |
| }, | |
| "engines": { | |
| "node": ">=.0.0", | |
| "npm": ">=.0.0" | |
| }, | |
| "browserslist": [ | |
| ">%", | |
| "last versions", | |
| "not ie <=" | |
| ] | |
| } | |
- name:包名
- version:包的版本号
- main:入口文件,一般都是 index.js
- scripts:支持的脚本,默认是一个空的 test
- keywords:关键字,有助于在人们使用 npm search 搜索时发现你的项目
- description:包的描述
- author: 包的作者
- repository:包代码的repo信息,包括type和URL,type可以是git或者svn,url则是包的repo地址。
- license:默认是 [MIT],项目许可证,让使用者知道是如何被允许使用此项目。
- dependencies:生产环境依赖包列表
- devDependencies:开发环境、测试环境依赖包列表
- engines: 声明项目需要的node或npm版本范围
(1)添加、更新依赖
①添加依赖
可以手动添加或者使用命令npm install <package_name> --save(将这个包名及对应的版本添加到 package.json的 dependencies)或npm install
<package_name> --save-dev(将这个包名及对应的版本添加到 package.json的 devDependencies)
②更新依赖
查询依赖的包是否有新版本可以使用 npm outdated 命令。如果发现有的包有新版本,就可以使用npm update更新它,或者直接 npm update 更新所有。
③卸载本地依赖
npm uninstall < package-name>
(2)脚本执行
npm 可以直接运行运行package.json 中 scripts 指定的脚本。 npm run 是 npm run-script的缩写。命令行输入 npm run dev 或者 npm run-script dev 就会执行 'dev’后面的内容 。
例如:当我们执行npm run dev时,首选执行的是webpack.dev.conf.js;当我们执行npm run build时,首选执行的是build.js
2、config/index.js
| const path = require('path') | |
| module.exports = { | |
| //开发时使用的配置 | |
| dev: { | |
| //输出的子文件夹路径 | |
| assetsSubDirectory: 'static', | |
| //发布路径 | |
| assetsPublicPath: '/', | |
| //配置代理表 | |
| proxyTable: {}, | |
| // Various Dev Server settings | |
| host: 'localhost', // can be overwritten by process.env.HOST | |
| //端口 | |
| port:, // can be overwritten by process.env.PORT, if port is in use, a free one will be determined | |
| //是否自动打开浏览器 | |
| autoOpenBrowser: false, | |
| errorOverlay: true, | |
| notifyOnErrors: true, | |
| poll: false, // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/dev-server/#devserver-watchoptions- | |
| /** | |
| * Source Maps | |
| */ | |
| // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#development | |
| devtool: 'cheap-module-eval-source-map', | |
| // If you have problems debugging vue-files in devtools, | |
| // set this to false - it *may* help | |
| // https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/options.html#cachebusting | |
| cacheBusting: true, | |
| cssSourceMap: true | |
| }, | |
| //打包时使用的配置 | |
| build: { | |
| // Template for index.html | |
| // 输入的index.html的路径 | |
| index: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist/index.html'), | |
| // 输出的目标文件夹路径 | |
| assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist'), | |
| assetsSubDirectory: 'static', | |
| assetsPublicPath: '/', | |
| /** | |
| * Source Maps | |
| */ | |
| //是否使用SourceMap | |
| productionSourceMap: true, | |
| // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#production | |
| devtool: '#source-map', | |
| // Gzip off by default as many popular static hosts such as | |
| // Surge or Netlify already gzip all static assets for you. | |
| // Before setting to `true`, make sure to: | |
| // npm install --save-dev compression-webpack-plugin | |
| // 是否开启Gzip | |
| productionGzip: false, | |
| //Gzip的压缩文件类型 | |
| productionGzipExtensions: ['js', 'css'], | |
| // Run the build command with an extra argument to | |
| // View the bundle analyzer report after build finishes: | |
| // `npm run build --report` | |
| // Set to `true` or `false` to always turn it on or off | |
| bundleAnalyzerReport: process.env.npm_config_report | |
| } | |
| } |
3、build/webpack.base.conf.js
- 配置编译入口和输出路径
- 模块resolve的规则
- 配置不同类型模块的处理规则
| const path = require('path') | |
| const utils = require('./utils') | |
| //引入相关配置 | |
| const config = require('../config') | |
| const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf') | |
| //绝对路径 | |
| function resolve (dir) { | |
| return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir) | |
| } | |
| module.exports = { | |
| context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'), | |
| //webpack的入口文件 | |
| entry: { | |
| app: './src/main.js' | |
| }, | |
| output: { | |
| //webpack输出文件的路径 | |
| path: config.build.assetsRoot, | |
| //输出的文件命名格式 | |
| filename: '[name].js', | |
| // webpack编译输出的发布路径 | |
| publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' | |
| ? config.build.assetsPublicPath | |
| : config.dev.assetsPublicPath | |
| }, | |
| resolve: { | |
| extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'], | |
| alias: { | |
| 'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js', | |
| '@': resolve('src'), | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| //配置不同类型模块的处理规则 | |
| module: { | |
| rules: [ | |
| //所有的.vue文件使用vue-loader | |
| { | |
| test: /\.vue$/, | |
| loader: 'vue-loader', | |
| options: vueLoaderConfig | |
| }, | |
| //src和test下的.js文件使用babel-loader | |
| { | |
| test: /\.js$/, | |
| loader: 'babel-loader', | |
| include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')] | |
| }, | |
| //所有的图片文件使用url-loader | |
| { | |
| test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/, | |
| loader: 'url-loader', | |
| options: { | |
| limit:, | |
| name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:].[ext]') | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| //所有的音频文件使用url-loader | |
| { | |
| test: /\.(mp|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(\?.*)?$/, | |
| loader: 'url-loader', | |
| options: { | |
| limit:, | |
| name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:].[ext]') | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| //所有的字体文件使用url-loader | |
| { | |
| test: /\.(woff?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/, | |
| loader: 'url-loader', | |
| options: { | |
| limit:, | |
| name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:].[ext]') | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| { //从这一段上面是默认的!不用改!下面是没有的需要你手动添加,相当于是编译识别sass! | |
| test: /\.scss$/, | |
| loaders: ["style", "css", "sass"] | |
| } | |
| ] | |
| }, | |
| node: { | |
| // prevent webpack from injecting useless setImmediate polyfill because Vue | |
| // source contains it (although only uses it if it's native). | |
| setImmediate: false, | |
| // prevent webpack from injecting mocks to Node native modules | |
| // that does not make sense for the client | |
| dgram: 'empty', | |
| fs: 'empty', | |
| net: 'empty', | |
| tls: 'empty', | |
| child_process: 'empty' | |
| } | |
| } | |
Vue项目启动代码执行流程分析
一般一个初步的Vue项目创建好之后都会有这三个文件:index.html 、main.js 和App.js。
1、index.html
Vue是单页面形式开发,index.html文件在其中起着特别重要的作用。所有组件(后缀名为.vue都被视为组件)都会通过此文件进行渲染加载。
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="utf-"> | |
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=.0"> | |
| <title>y</title> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id="app"></div> | |
| <!-- built files will be auto injected --> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |
在body体中只有一个div标签,其id为app,这个id将会连接到src/main.js内容
2、main.js
相当于一个C/Java中的入口函数,控制着初次启动Vue项目要加载的组件。
| import Vue from 'vue' | |
| import App from './App' | |
| import router from './router' | |
| import lhj from './components/lhj' | |
| Vue.config.productionTip = false | |
| import axios from "axios"; | |
| import VueAxios from "vue-axios"; | |
| Vue.use(VueAxios,axios) | |
| /* eslint-disable no-new */ | |
| new Vue({ | |
| el: '#app', | |
| router, | |
| components: { App }, | |
| template: '<App/>', | |
| watch:{} | |
| }) |
在main.js中,新建了一个vue实例,并使用el:#app链接到index.html中的app,并使用template引入组件和路由相关的内容,也就是说通过main.js我们关联到App.vue组件。
(1)import A from ‘B’
这类语句相当于引入B(这一般是路径)然后给它起个名字叫做A;
(2)Vue.use(C)
这个意思是全局方法定义 C。也就是说,定义以后你可以在这个Vue项目的任意地方使用该组件。
(3)el: ‘#app’
这个和index.html中的相挂钩。
模板将会替换挂载的元素,挂载元素的内容都将被忽略。
也就是说:template: ‘< App/>’ 表示用< app>< /app>替换index.html里面的< div id=“app”>,然后index.html文件被初步解析为这种形式
| <body> | |
| <div id="myapp"> | |
| <app></app> | |
| </div> | |
| </body> |
(4)watch : 用来监听路由的变化,可以用来定义页面切换时过渡效果。
3、App.vue
| <template> | |
| <div id="app"> | |
| <img src="./assets/logo.png"> | |
| <router-view/> | |
| </div> | |
| </template> | |
| <script> | |
| export default { | |
| name: 'App' | |
| } | |
| </script> | |
| <style> | |
| #app { | |
| font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; | |
| -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; | |
| -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; | |
| text-align: center; | |
| color: #c3e50; | |
| margin-top:px; | |
| } | |
| </style> |
标准的App.vue模板的形式,包含了<template></template>、<script></script>、<style></style>三部分。
(1)export中的name属性,相当于给这个组件定义一个名字,便于识别和使用。
(2)< template>标签下,除了< img>标签外,还有< router-view>标签,< router-view>标签将会把路由相关内容渲染在这个地方。路由的内容定义在src/router/index.js文件中。
4、src/router/index.js
| import Vue from 'vue' | |
| import Router from 'vue-router' | |
| import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' | |
| Vue.use(Router) | |
| export default new Router({ | |
| routes: [ | |
| { | |
| path: '/', | |
| name: 'HelloWorld', | |
| component: HelloWorld | |
| } | |
| ] | |
| }) |
在index.js的代码中,建立了路由相关的内容,也就会渲染到app.vue下面的< router-view>中。
(1)引入组件的代码
引入的时候注意好格式、路径就行。
(2)routes定义
- path:页面间路由跳转的路径;
- name:该路由的名称;
- component:组件名,要和你引入组件时定义的名字保持一致。
Vue加载时文件的执行顺序
1、执行index.html文件
2、执行main.js文件
3、main.js挂载了app.vue文件,用app.vue的templete替换index.html中的
4、main.js中注入了路由文件,将对应的组件渲染到router-view中 5、router-view中加载Layout文件
6、Layout 加载Navbar, Sidebar, AppMain
Vue内部页面的执行顺序
Vue 推荐在绝大多数情况下使用 template 来创建你的 HTML。但是模板毕竟是模板,不是真实的dom节点。从模板到真实dom节点还需要经过一些步骤:
1、把模板编译为render函数
2、实例进行挂载, 根据根节点render函数的调用,递归的生成虚拟dom
3、对比虚拟dom,渲染到真实dom
4、组件内部data发生变化,组件和子组件引用data作为props重新调用render函数,生成虚拟dom, 返回到步骤3