前端面试实录CSS篇
1. CSS 选择器以及优先级?
- • CSS 选择器 选择器格式优先级权重id 选择器#id100类选择器.classname10属性选择器[title]/[title="one"]10伪类选择器div:hover10标签选择器div1伪元素选择器input::after1子选择器ul>li0后代选择器li a0通配符选择器*0
- • CSS 选择器优先级
- • 参考 MDN:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/CSS/Specificity
- 1. !important 例外,优先级最高
- 2. 内联样式
- 3. id 选择器
- 4. 类选择器,属性选择器,伪类选择器
- 5. 标签选择器,伪元素选择器
- 6. 子选择器,后代选择器,通配符选择器
- • 选择器权重
- • 参考 W3C:
https://www.w3.org/TR/selectors/#specificity - • 例子:
./Demo/css_selector_and_priority.html
2. link 和 @import 的区别?
- •
link: 链接外部资源的标签,此标签决定了文档与外部资源的关系,常用于链接样式表(css),网页站点图标(favicon)。 - • 用法;
<link rel="stylesheet,icon,image/png,shortlink,help,author,image/svg+xml" href="网络路径/相对路径/绝对路径"/> - • 属性:
- 1. rel: 表示关系:realtionship,
- 2. href: 网络路径/相对路径/绝对路径
- 3. size: icon 的大小
- 4. disabled: 仅对 rel = "stylesheet" 类型生效
- 1. 从属差异:link 为 html 标签,可以加载 css, 也可以引入网站图标(facaion), 定义 rel 链接属性,而 @import 是 css 提供,只能用于加载 css
- 2. 加载差异:link 引用的 css,在页面加载时同时加载。而 @import 在页面加载完后才加载
- 3. 兼容性:link 是 html 标签,没有兼容问题。而 @ import 是 css2.1 提出的,IE5 以下的浏览器不支持。
- 4. 可操作性:link 可使用 js 来控制 DOM 去改变样式,而 @import 不支持,因为 DOM 方法是基于文档的。
- 5. 权重差异:
- • 在样式中:link 样式的权重高于 @import 的权重吗,例如:
| |
| body, |
| html { |
| background-color: aquamarine; |
| } |
| |
- • 在页面中:不存在权重问题,谁在最低下就使用谁的样式
| <!DOCTYPE html> |
| <html lang="en"> |
| <head> |
| <meta charset="UTF-8" /> |
| <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> |
| <meta |
| name="viewport" |
| content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" |
| /> |
| <title>Document</title> |
| </head> |
| <body> |
| <div class="container"></div> |
| </body> |
| </html> |
| <link rel="stylesheet" href="./01.css" /> |
| <style> |
| @import "./03.css"; |
| </style> |
3. 对盒模型的理解?
- • 组成:由四部分组成:margin, padding, border, content
- • 分类:标准盒模型 和 怪异盒模型(IE 盒模型)
- • 标准盒模型:width 和 height 的范围只包含了 content
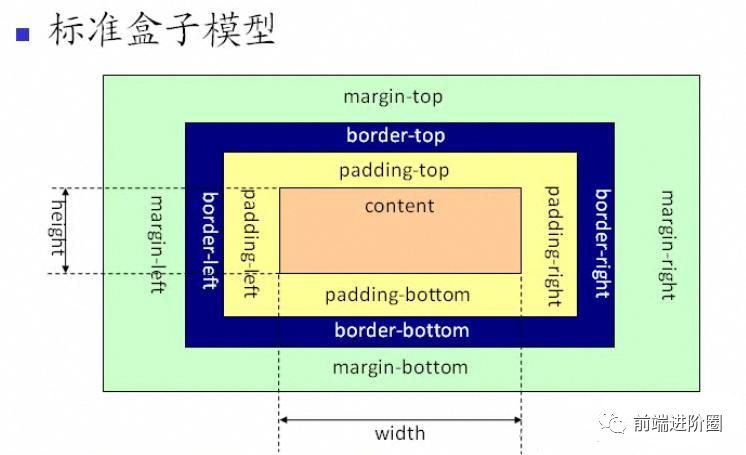
- • 怪异盒模型:width 和 height 的范围只包含了 border, padding, content
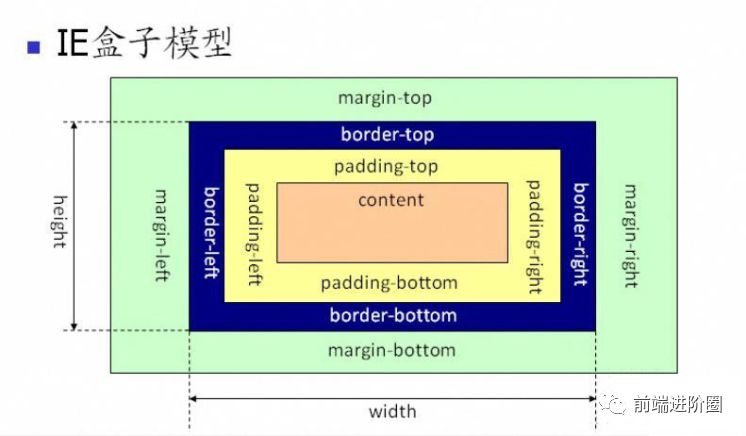
- • 两者区别:在于 width 和 height 所包含的范围不同
- • 属性:
- • 标准盒模型:
box-sizing: content-box; - • 怪异盒模型:
box-sizing: border-box;
4. 隐藏元素的方法有哪些?
- 1.
display: none;: 不会渲染该元素,不会占位,也不会响应绑定的监听事件 - 2.
visibility: hidden;: 会渲染,但是不会显示且会占位,也不会响应绑定的监听事件 - 3.
opacity: 0;: 将元素的透明度设置为 0, 以此来达到隐藏元素的效果,会占位,能够响应绑定的监听事件 - 4.
position: absolute;: 使用绝对定位将元素移除了可视区域外,不会占位,以此来实现元素的隐藏 - 5.
z-index:负值;: 使用其他元素将该元素隐藏,会占位 - 6.
clip:position:absolute; clip: rect(200px, 200px, 200px, 200px);/clip-path:clip-path: circle(0); : 使用元素裁切的 方式实现元素隐藏,会占位,不会响应绑定的监听事件 - 7.
transform: scale(0,0): 使用缩放,来实现元素的隐藏,会占位,但是不会响应绑定的监听事件 - 8.
filter: opacity(0): 使用元素滤镜来改变元素的透明度, 会占位
5. 伪元素和伪类的区别和作用?
- • 伪类:将某种状态时添加到已有元素上,这个状态是根据用户的行为变化而变化为的。比如: hover,active, visited
- • 伪元素:用于创建一些原本不在文档树中的元素或样式, 比如:::after,::before。
- • 区别:
- • 伪类操作的对象是文档树种已有的元素或样式
- • 伪元素则是创建一个文档树以外的元素或样式
- • : 表示伪类
- • :: 表示伪元素
- • 作用:
- • 伪类:通过在元素选择器上加入伪类改变元素的状态
- • 伪元素:通过对元素的操作进而改变元素
6. CSS3 有哪些新特性?
- • 圆角:
border-radius: 8px; - • 阴影:
text-shadown: 2px 2px #ff0000; box-shadown: 10px 10px 5px #888888; - • 文字方向:
text-decoration - • 渐变:
linear-gradient: 线性渐变 radial-gradient 径向渐变 - • 旋转:
transform - • css选择器:
伪类选择器:first-child, 伪元素选择器,否定选择器(:not),属性选择器[title="one"] - • 多列布局:
multi-column: - • column: 规定列宽和列数
- • column-count: 列的数量
- • column-width: 列宽
- • column-gap: 列间隙
- • column-rule: 列之间的宽度,样式和颜色
- • column-span:
- • column-fill: 列填充:auto: 根据内容填充。balance: 每列平均
7. 对媒体查询的理解?
- • 使用
@media 查询,可针对不同的媒体类型定义不同的样式,@media 可针对不同的屏幕尺寸设置不同的样式,特别是设置响应式的页面, @media 非常有用。当重置浏览器大小的过程中,页面会根据浏览器的宽度和高度重新渲染页面。
8. 对 BFC 的理解,如何创建 BFC?
- • 定义:
- • Box: CSS 布局的对象和基本单位,一个页面由很多个 box 组成,这个 Box 就是我们常说的盒模型
- • Formatting context: 块级格式化上下文,页面中的一个渲染区域,有一套渲染规则,它决定了其子元素如何定位,以及其他元素的关系和相互作用。
- • 理解:BFC(Block Formatting Context, BFC) 块级格式化上下文,页面布局盒模型的一种 CSS 渲染模式,是一个独立的容器,在这个容器中里面的元素和外部的元素互不影响。
- • 创建 BFC 的条件:
- 1. 根元素:html,body
- 2. 浮动:float 除 none 以外的值
- 3. 定位:position 为绝对定位(absoluate) 和 固定定位(fixed)
- 4. dispaly 属性:表格布局(grid: table-cell,table-caption) 和 flex(flex-items,flow-root) 布局
- 5. multi column(多列布局): column
- 6. overflow: 值为 hidden, auto, scroll
- 1. 垂直方向上,自上而下排列,和文档流的排列方式一致
- 2. 在 BFC 中上下两个相邻的两个容器的 margin 会重叠
- 3. 计算 BFC 的高度时,需要计算浮动元素的高度
- 4. BFC 区域不会与浮动的容器发生重叠
- 5. BFC 是独立的容器,容器内部的元素不会影响外部元素
- 6. 每个元素的 margin-left 值和容器的 border-left 相接触
- 1. 解决 margin 重叠问题:由于 BFC 是一个独立的区域,内部的元素和外部的元素互不影响,将两个元素变为两个 BFC,就解决了 margin 重叠的问题。
- 2. 解决高度塌陷问题:在对子元素设置浮动后,父元素会发生高度塌陷,也就是父元素的高度变为 0。解决这个问题,只需要把父元素变成一个 BFC。常用的办法是给父元素设置
overflow:hidden。 - 3. 创建自适应两栏布局:可以用来创建自适应两栏布局:左边的宽度固定,右边的宽度自适应。
9. 如何设置小于 12px 的字体?
- • 使用 webkit 内核的:
-webkit-text-size-adjust: none;。chrome 27 版本后不可用了。 - • 使用 css3 的 transform 属性:
transform: scale(0.5); - • 内容固定不变的情况下,将文字内容做成图片,使用图片来解决
10. 单行/多行文本溢出?
| |
| display: -webkit-box; |
| -webkit-box-orient:vertical; |
| -webkit-line-clamp:3; |
| overflow: hidden; |
| text-overflow: ellipsis; |
| |
| |
| |
| white-space: nowrap; |
| overflow: hidden; |
| text-overflow: ellipsis; |
11. 实现一个三角形?
| <!DOCTYPE html> |
| <html lang="en"> |
| <head> |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> |
| <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> |
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> |
| <title>Document</title> |
| </head> |
| <body> |
| <div class="div1"></div> |
| <div class="div2"></div> |
| <div class="div3"></div> |
| <div class="div4"></div> |
| </body> |
| </html> |
| <style> |
| div{ |
| width: 0px; |
| height: 0px; |
| border: 50px solid transparent; |
| } |
| .div1{ |
| border-top-color: red; |
| } |
| .div2{ |
| border-bottom-color: red; |
| } |
| .div3{ |
| border-left-color: red; |
| } |
| .div4{ |
| border-right-color: red; |
| } |
| </style> |
12. 实现一个扇形?
| <!DOCTYPE html> |
| <html lang="en"> |
| <head> |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> |
| <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> |
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> |
| <title>Document</title> |
| </head> |
| <body> |
| <div class="div1"></div> |
| </body> |
| </html> |
| <style> |
| .div1{ |
| width: 0; |
| height: 0; |
| border-radius: 100px; |
| border: 100px solid transparent; |
| border-top-color: red; |
| } |
| </style> |
13. 画一条0.5px的线?
- • 使用 transform 的 scale 来完成
| width: 250px; |
| height: 1px; |
| background-color: gray; |
| transform: scaleY(0.5); |
14. 常见的图片格式以及使用场景?
- 1. bmp: 无损的,此图片格式不会对数据进行压缩,所以 bmp 格式的图片通常都是较大文件
- 2. git: 无损的,特点是文件小,适用场景:对色彩要求不高且文件体积较小
- 3. jpeg,jpg: 有损的,有损压缩会导致图片模糊,文件类型比 gif 较大
- 4. png-8:无损的,png-8 比 gif 文件还小
- 5. png-24: 无损的,优点在于压缩了图片数据
- 6. svg: 无损矢量图,放大不会失真,适用场景:绘制 LOGO, Icon
- 7. webp: 同时支持有损和无损,同质量的图片,webp 拥有更小的文件体积,更好地提升用户体验,
- • 在无损压缩情况下:相同质量的 webp 图片,要比 png 小 26%
- • 在有损压缩情况下,具有相同精度的 webp 图片,文件大小要比 jpeg 小 25%~34%
- • webp 还支持图片透明度,一个无损压缩的 webp 图片,想要支持透明度,只需要 22% 的格外文件大小。
15. CSS 优化和提高性能的方法有哪些?
- 1. css 压缩
- 2. 减少使用属性简写方式
- 3. 减少使用 @import,建议使用 link,
- 1. 减少选择器嵌套层级
- 2. 使用关键的选择器,不要逐层进行选择
- 1. 慎重使用浮动和定位
- 2. 尽量减少重绘和回流的发生
- 3. 删除空规则,也就是预留样式->{}
- 4. 属性值为浮点值时,省略前面的 0
- 5. 不要使用 @import 前缀引用样式,会影响 css 加载速度
- 6. 避免选择器嵌套过深
- 7. 不滥用 web 字体
- 1. 抽离公共样式
- 2. 样式与内容分离
16. ::before 和 :after 的双冒号和单冒号有什么区别?
- 1.
单冒号(:) 表示伪类,双冒号(::)表示伪元素 - 2. 在 CSS2.1 中,伪元素都是使用
单冒号 来表示伪元素的,但在 CSS3 规范中,伪元素的语法被修改为使用 双冒号
17. CSS 预处理器/后处理器是什么?为什么要使用他们?
- • 预处理器:
less, sass, styuls,它们增加了 css 代码的复用性,例如:变量,循环,方法等 - • 后处理器:
postcss,最常做的是给 css 代码添加浏览器前缀,实现跨浏览器兼容性的问题、 - • 为什么要使用他们?
- 1. 结构清晰,便于扩展
- 2. 屏蔽浏览器私有语法的差异
- 3. 使用多重继承
- 4. 提到 css 代码的兼容性
18. z-index 会在什么情况下会失效?
- • 作用及含义:设置元素的堆叠顺序,值越大就越在上层
- • 检查以下情况:
- 1. 该元素是否设置了定位
- 2. 该元素的父级是否已经设置了z-index(检查需比较的元素是否同在一个层叠上下文)
- 1. 在设置 z-index 的元素上必须含有 position 属性为非 static 属性值(relative,absolute,fixed)。
- 2. 同一个父级元素下的元素层叠效果是受父级影响的,就是说如果你的父级z-index很小,那你子级设置再大也没有用
19. 常见的 css 布局单位?
- • 常用布局单位:
像素px,百分比%,em,rem,vw/vh - • vmin: vw 和 vh 的较小值
- • vmax: vw 和 vh 的较大值
- • em:文本相对长度单位,浏览器默认的字体尺寸为 16px;
- • rem: css3 新增的一个相对单位,是相对于根元素 html元素 的 font-size 的倍数,
- • css 像素:web 开发者提供,css 中的一个抽象单位
- • 物理像素:与设备的硬件密度相关,任何设备的物理像素都是固定的
- • 像素px: 页面布局基础,分为css 像素和物理像素
- • 百分比%: 实现响应式效果
- • em和rem: 相对于 px 更具灵活性,它们都是相对长度单位,区别为,em 相对于父元素,rem相对于子元素
- • vw/vh: 视图窗口单位,vw 宽度,vh 高度,还有 vmin 和 vmax 两个相关单位
20. px,em, rem 的区别以及使用场景?
- • 区别:
- • px: 固定像素,无法跟着页面大小而改变
- • em: em 和 rem 相对长度单位,长度不是固定的,会跟着页面大小而改变,更适用于响应式布局
- • em 相对于父元素来设置字体大小,而 rem 是相对于根元素来改变的
- • 使用场景:
- • 适配少部分的移动设备,且对分辨率对页面影响大小的可使用 px
- • 适配各种移动设备,使用 rem
21. 两栏布局的实现
- • 左边固定,右边自适应
- • 利用浮动,将左边元素宽度设置为 200px,并且设置向左浮动。将右边元素的 margin-left 设置为 200px,宽度设置为 auto(默认为 auto,撑满整个父元素)。
| .outer { |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| .left { |
| float: left; |
| width: 200px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| .right { |
| margin-left: 200px; |
| width: auto; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
- • 利用浮动,左侧元素设置固定大小,并左浮动,右侧元素设置 overflow: hidden; 这样右边就触发了 BFC,BFC 的区域不会与浮动元素发生重叠,所以两侧就不会发生重叠。
| .left{ |
| width: 100px; |
| height: 200px; |
| background: red; |
| float: left; |
| } |
| .right{ |
| height: 300px; |
| background: blue; |
| overflow: hidden; |
| } |
- • 利用 flex 布局,将左边元素设置为固定宽度 200px,将右边的元素设置为 flex:1。
| .outer { |
| display: flex; |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| .left { |
| width: 200px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| .right { |
| flex: 1; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
- • 利用绝对定位,将父级元素设置为相对定位。左边元素设置为 absolute 定位,并且宽度设置为 200px。将右边元素的 margin-left 的值设置为 200px。
| .outer { |
| position: relative; |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| .left { |
| position: absolute; |
| width: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| .right { |
| margin-left: 200px; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
- • 利用绝对定位,将父级元素设置为相对定位。左边元素宽度设置为 200px,右边元素设置为绝对定位,左边定位为 200px,其余方向定位为 0。
| .outer { |
| position: relative; |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| .left { |
| width: 200px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| .right { |
| position: absolute; |
| top: 0; |
| right: 0; |
| bottom: 0; |
| left: 200px; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
22. 三栏布局的实现
- • 左右两遍固定。中间自适应
- • 利用绝对定位,左右两栏设置为绝对定位,中间设置对应方向大小的 margin 的值。
| .outer { |
| position: relative; |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| |
| .left { |
| position: absolute; |
| width: 100px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| |
| .right { |
| position: absolute; |
| top: 0; |
| right: 0; |
| width: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
| |
| .center { |
| margin-left: 100px; |
| margin-right: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: lightgreen; |
| } |
- • 利用 flex 布局,左右两栏设置固定大小,中间一栏设置为 flex:1。
| .outer { |
| display: flex; |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| |
| .left { |
| width: 100px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| |
| .right { |
| width: 100px; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
| |
| .center { |
| flex: 1; |
| background: lightgreen; |
| } |
- • 利用浮动,左右两栏设置固定大小,并设置对应方向的浮动。中间一栏设置左右两个方向的 margin 值,注意这种方式,中间一栏必须放到最后:
| .outer { |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| |
| .left { |
| float: left; |
| width: 100px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| |
| .right { |
| float: right; |
| width: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
| |
| .center { |
| height: 100px; |
| margin-left: 100px; |
| margin-right: 200px; |
| background: lightgreen; |
| } |
- • 圣杯布局,利用浮动和负边距来实现。父级元素设置左右的 padding,三列均设置向左浮动,中间一列放在最前面,宽度设置为父级元素的宽度,因此后面两列都被挤到了下一行,通过设置 margin 负值将其移动到上一行,再利用相对定位,定位到两边。
| .outer { |
| height: 100px; |
| padding-left: 100px; |
| padding-right: 200px; |
| } |
| |
| .left { |
| position: relative; |
| left: -100px; |
| |
| float: left; |
| margin-left: -100%; |
| |
| width: 100px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| |
| .right { |
| position: relative; |
| left: 200px; |
| |
| float: right; |
| margin-left: -200px; |
| |
| width: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
| |
| .center { |
| float: left; |
| |
| width: 100%; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: lightgreen; |
| } |
- • 双飞翼布局,双飞翼布局相对于圣杯布局来说,左右位置的保留是通过中间列的 margin 值来实现的,而不是通过父元素的 padding 来实现的。本质上来说,也是通过浮动和外边距负值来实现的。
| .outer { |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
| |
| .left { |
| float: left; |
| margin-left: -100%; |
| |
| width: 100px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: tomato; |
| } |
| |
| .right { |
| float: left; |
| margin-left: -200px; |
| |
| width: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: gold; |
| } |
| |
| .wrapper { |
| float: left; |
| |
| width: 100%; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: lightgreen; |
| } |
| |
| .center { |
| margin-left: 100px; |
| margin-right: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| } |
23. 水平垂直居中的方式?
- 1. flex 布局
| .parent { |
| display: flex; |
| justify-content:center; |
| align-items:center; |
| } |
- 1. 绝对定位 + margin
| .parent { |
| position: relative; |
| } |
| |
| .child { |
| position: absolute; |
| top: 50%; |
| left: 50%; |
| margin-top: -50px; |
| margin-left: -50px; |
| } |
- 1. 绝对定位
| .parent { |
| position: relative; |
| } |
| |
| .child { |
| position: absolute; |
| top: 0; |
| bottom: 0; |
| left: 0; |
| right: 0; |
| margin: auto; |
| } |
- 1. 绝对定位 + transform
| .parent { |
| position: relative; |
| } |
| |
| .child { |
| position: absolute; |
| left: 50%; |
| top: 50%; |
| transform: translate(-50%,-50%); |
| } |
24. 响应式设计的概念及基本原理?
- • 响应式设计:也就是一个网站能兼容多个终端,而不是每个终端做一个适配
- • 原理:通过媒体查询
@media 查询检测不同的设备屏幕尺寸做处理 - • 关于兼容:页面头部必须要有 meta 声明的 viewport
25. position 的属性有哪些,区别是什么?
- • absolute: 绝对定位的元素的位置相对于最近的已定位父元素,如果元素没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于
- • relative: 相对定位元素的定位是相对其正常位置
- • fixed: 元素的位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定位置。即使窗口是滚动的它也不会移动:
- • static: HTML 元素的默认值,即没有定位,遵循正常的文档流对象。静态定位的元素不会受到 top, bottom, left, right影响。
- • inherit: 规定从父元素继承 position 属性的
- • sticky: 基于用户的滚动位置来定位
- • 前面三者的定位方式如下:
- • relative:元素的定位永远是相对于元素自身位置的,和其他元素没关系,也不会影响其他元素。

- imgfixed:元素的定位是相对于 window (或者 iframe)边界的,和其他元素没有关系。但是它具有破坏性,会导致其他元素位置的变化。

- imgabsolute:元素的定位相对于前两者要复杂许多。如果为 absolute 设置了 top、left,浏览器会根据什么去确定它的纵向和横向的偏移量呢?答案是浏览器会递归查找该元素的所有父元素,如果找到一个设置了
position:relative/absolute/fixed的元素,就以该元素为基准定位,如果没找到,就以浏览器边界定位。如下两个图所示: 

26. absolute 与 fixed 的共同点与不同点?
- • 共同点:
- • 改变行内元素的呈现方式,将 display 改为 inline-block
- • 使元素脱离普通文档流,不再占据文档物理空间
- • 覆盖非定位文档元素
- • 不同点:
- • absolute 与 fixed 的根元素不同,absolute 的根元素可设置,fixed 的根元素是html
- • 在有滚动的页面中,absolute 会跟随父元素进行滚动,而 fixed 固定在某个位置
27. 如何解决 1px 问题?
- • 1px 问题的本质:在一些
Retina 屏幕上,移动端页面的 1px 会变得很粗,所呈现出来不止是 1px 的效果,原因就是 CSS 中的 1px 不能和移动端的 1px 划等号,他们之间是有一个比例关系。
window.devicePixelRatio = 设备的物理像素 / CSS像素。
- 1. 直接写 0.5px: 通过 js 拿到 window.devicePixelRatio 的值, 然后进行判断处理(如果是 1,则直接返回,否则 1 / window.devicePixelRatio),然后动态的设置 CSS 属性中的值,以此来达到 1px 的效果。
- • 缺点:兼容性不行, andriod 直接不兼容,ios 需要 8.0 以上的版本
<div id="container" data-device={{window.devicePixelRatio}}></div>
- 1. 通过伪元素
| #container[data-device="2"] { |
| position: relative; |
| } |
| #container[data-device="2"]::after{ |
| position:absolute; |
| top: 0; |
| left: 0; |
| width: 200%; |
| height: 200%; |
| content:""; |
| transform: scale(0.5); |
| transform-origin: left top; |
| box-sizing: border-box; |
| border: 1px solid #333; |
| } |
- 1. viewport 缩放来解决
<meta name="viewport" content="initial-scale=0.5, maximum-scale=0.5, minimum-scale=0.5, user-scalable=no">
- • 这里针对像素比为 2 的页面,把整个页面缩放为了原来的 1/2 大小。这样,本来占用 2 个物理像素的 1px 样式,现在占用的就是标准的一个物理像素。根据像素比的不同,这个缩放比例可以被计算为不同的值,用 js 代码实现如下:
| const scale = 1 / window.devicePixelRatio; |
| |
| metaEl.setAttribute('content', `width=device-width,user-scalable=no,initial-scale=${scale},maximum-scale=${scale},minimum-scale=${scale}`); |
28. 如何判断元素进入可视区域?
- 1. offsetTop、scrollTop
- 2. getBoundingClientRect
- 3. Intersection Observer
| `window.innerHeight` 是浏览器可视区的高度; |
| `document.body.scrollTop || document.documentElement.scrollTop` 是浏览器滚动的过的距离; |
| `imgs.offsetTop` 是元素顶部距离文档顶部的高度(包括滚动条的距离); |
| 内容达到显示区域的:`img.offsetTop < window.innerHeight + document.body.scrollTop;` |
- • 方式一:offsetTop、scrollTop
| |
| |
| el.offsetTop - document.documentElement.scrollTop <= viewPortHeight |
| |
| |
| function isInViewPortOfOne (el) { |
| |
| const viewPortHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight |
| const offsetTop = el.offsetTop |
| const scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop |
| const top = offsetTop - scrollTop |
| return top <= viewPortHeight |
| } |
- • 方式二:getBoundingClientRect
- • 返回值是一个 DOMRect对象,拥有left, top, right, bottom, x, y, width, 和 height属性
| const target = document.querySelector('.target'); |
| const clientRect = target.getBoundingClientRect(); |
| console.log(clientRect); |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| function isInViewPort(element) { |
| const viewWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth; |
| const viewHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight; |
| const { |
| top, |
| right, |
| bottom, |
| left, |
| } = element.getBoundingClientRect(); |
| |
| return ( |
| top >= 0 && |
| left >= 0 && |
| right <= viewWidth && |
| bottom <= viewHeight |
| ); |
| } |
- • 方式三:Intersection Observer
- • Intersection Observer 即重叠观察者,从这个命名就可以看出它用于判断两个元素是否重叠,因为不用进行事件的监听,性能方面相比getBoundingClientRect会好很多
- • 使用步骤主要分为两步:创建观察者和传入被观察者
| |
| const options = { |
| |
| |
| threshold: 1.0, |
| root:document.querySelector('#scrollArea') |
| }; |
| |
| const callback = (entries, observer) => { ....} |
| |
| const observer = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options); |
| |
| |
| |
| const callback = function(entries, observer) { |
| entries.forEach(entry => { |
| entry.time; |
| entry.rootBounds; |
| entry.boundingClientRect; |
| entry.intersectionRect; |
| entry.intersectionRatio; |
| entry.target; |
| }); |
| }; |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| const target = document.querySelector('.target'); |
| observer.observe(target); |
| <head> |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> |
| <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> |
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> |
| <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.3/jquery.min.js" integrity="sha512-STof4xm1wgkfm7heWqFJVn58Hm3EtS31XFaagaa8VMReCXAkQnJZ+jEy8PCC/iT18dFy95WcExNHFTqLyp72eQ==" crossorigin="anonymous" referrerpolicy="no-referrer"></script> |
| <title>Document</title> |
| <style> |
| .container { |
| display: flex; |
| flex-wrap: wrap; |
| } |
| |
| .target { |
| margin: 5px; |
| width: 20px; |
| height: 20px; |
| background: red; |
| } |
| </style> |
| </head> |
| |
| <body> |
| <div class="container"></div> |
| </body> |
| |
| </html> |
| <script> |
| (() => { |
| const $container = $(".container"); |
| function createTargets() { |
| const htmlString = new Array(10000).fill('<div class="target"></div>').join("") |
| $container.html(htmlString) |
| } |
| createTargets(); |
| const $targets = $(".target"); |
| function isInViewPort(el){ |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| const viewPortHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight; |
| const viewPortWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth; |
| const {top,right,left,bottom} = el.getBoundingClientRect(); |
| return top >= 0 && left >= 0 && bottom <= viewPortHeight && right <= viewPortWidth |
| } |
| |
| |
| $(window).on("scroll",()=>{ |
| console.log("scroll!!"); |
| $targets.each((index,element)=>{ |
| if(isInViewPort(element)){ |
| $(element).css("background-color","blue") |
| } |
| }) |
| }) |
| })(); |
| </script> |
| <head> |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> |
| <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> |
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> |
| <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.3/jquery.min.js" |
| integrity="sha512-STof4xm1wgkfm7heWqFJVn58Hm3EtS31XFaagaa8VMReCXAkQnJZ+jEy8PCC/iT18dFy95WcExNHFTqLyp72eQ==" |
| crossorigin="anonymous" referrerpolicy="no-referrer"></script> |
| <title>Document</title> |
| <style> |
| * { |
| margin: 0; |
| padding: 0; |
| } |
| |
| .test { |
| width: 200px; |
| height: 1000px; |
| background: orange; |
| } |
| |
| .box { |
| width: 150px; |
| height: 150px; |
| margin: 50px; |
| background: red; |
| } |
| |
| #sta { |
| position: fixed; |
| left: 40%; |
| top: 40%; |
| width: 200px; |
| height: 100px; |
| background: greenyellow; |
| } |
| </style> |
| </head> |
| |
| <body> |
| <div class="test">test</div> |
| <div class="box">box</div> |
| <div id="sta">初始化</div> |
| </body> |
| |
| </html> |
| <script> |
| (() => { |
| var status_node=document.querySelector("#sta"); |
| const box = document.querySelector('.box'); |
| const intersectionObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => { |
| entries.forEach((item) => { |
| if (item.isIntersecting) { |
| box.innerText = '进入可视区域'; |
| status_node.innerText = '进入可视区域'; |
| console.log('进入可视区域'); |
| }else{ |
| box.innerText = '出去了'; |
| status_node.innerText = '出去了'; |
| } |
| }) |
| }); |
| intersectionObserver.observe(box); |
| })(); |
| </script> |
特殊字符描述
•问题标注 Q:(question)
•答案标注 R:(result)
•注意事项标准:A:(attention matters)
•详情描述标注:D:(detail info)
•总结标注:S:(summary)
•分析标注:Ana:(analysis)
•提示标注:T:(tips)





