游戏服务器并不是什么高大上的东西,说的简单点,就是个消息转发+数据存储的一个程序.
下图展示的就是一个最简单的单进程服务器示意图:
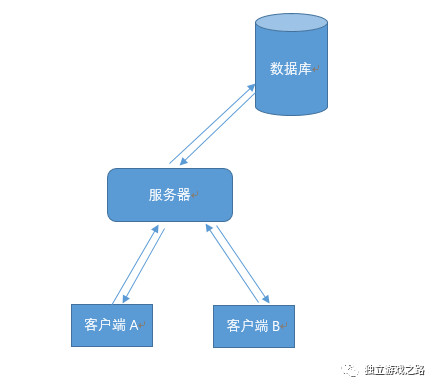
服务器模块的划分:
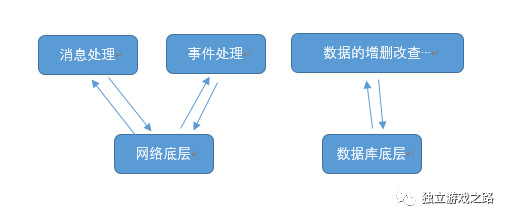
网络底层,它指的是对于数据的自动处理,比如string->byte这样的,还有粘包和分包的处理,解析协议名,解析协议等.
消息处理, 比如网络底层解析出了网络底层的消息.然后消息处理模块会很好的解析到数据,并用在游戏中,比如,它接收到了一个Move的协议,并带有xyz三个数值,那么它就可以使用这3个数值.
事件处理,这里我们专门用它来处理玩家上线和下线的功能,可千万不要以为,一个简简单单的上线和下线,还要用一个专门的模块来处理,其实这是 非常有必要的.玩家上线的时候,我们的一些初始化,不是单单一条协议就可以的,同样的,下线也一样.许多数据的保存操作要做.
数据库底层,这个就是数据库的一些操作,以及防止sql注入等功能.是服务器和数据库交互的一层封装.
从服务器角度来看,一个客户端会经历连接,登录,获取玩家数据,操作交互,保存数据和下线这6个操作.
千万不要以为,连接和登录是一起的,其实在用户登录之前,还有许多事要做.比如:请求大区列表,你选择大区之后,才到登录这一步骤.登录完成之后.立马获取此玩家的信息,然后到游戏中,开始用户交互,接着是保存数据,这个保存数据可以是每隔5秒保存一次,也可以是每隔5分钟保存一次,也可以是下线之前保存 一次,不同的方式有不同方式的优缺点,这个要看具体项目需求.
编写代码。
先新建一个C#控制台程序.其次在程序中新建两个文件夹. 一个script.代表所有的脚本都放在这个文件夹中.
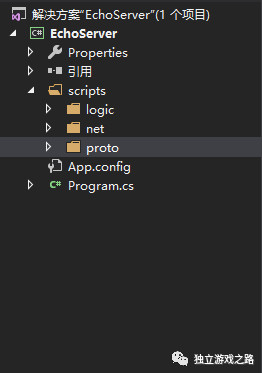
其中scrippt文件夹中包含net和proto两个目录. Net文件夹代表网络.存放服务器端程序的网络模块.Proto代表协议.存放一些协议文件.
这个结构看起来与客户端的结构似乎差不多.里面的代码文件也差不多.节省时间.我们直接复制.首先我们将客户端那协议文件.BattleMsg.cs和SysMsg.cs复制到proto文件夹下.将缓冲区类,ByteArray.cs,和协议基类MsgBase.cs,复制到net文件夹下.
当然这么复制进去是会报错的。我们需要把using UnityEngine;这个头文件给删了.
还需要一个引入dll文件:
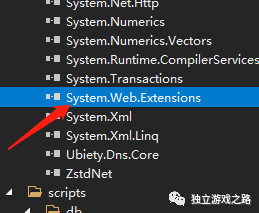
位置就在如图的这样的一个位置VS2019中已经自带
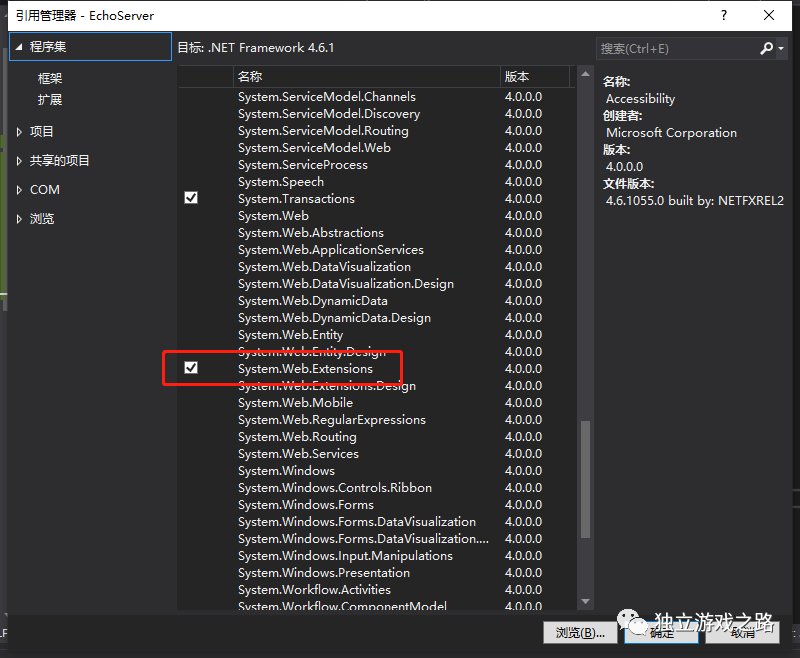
这个dll文件是用来json解析的.添加完之后我们就可以去修改Msgbase类:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Web.Script.Serialization; | |
| public class MsgBase | |
| { | |
| //协议名 | |
| public string protoName = ""; | |
| //实例json解析类 | |
| static JavaScriptSerializer js = new JavaScriptSerializer(); | |
| /// <summary> | |
| ///编码协议名 | |
| /// </summary> | |
| /// <param name="msgBase">继承MsgBase的子类</param> | |
| /// <returns>byte[]类型协议名 </returns> | |
| public static byte[] EncodeName(MsgBase msgBase) | |
| { | |
| byte[] nameBytes = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(msgBase.protoName); | |
| //协议名长度 | |
| Int16 len = (Int16)nameBytes.Length; | |
| byte[] bytes = new byte[2 + len]; | |
| //组装协议长度byte数组 | |
| bytes[0] = (byte)(len % 256); | |
| bytes[1] = (byte)(len / 256); | |
| Array.Copy(nameBytes, 0, bytes, 2, len); | |
| return bytes; | |
| } | |
| /// <summary> | |
| /// 解码协议名 | |
| /// </summary> | |
| /// <param name="bytes">协议字节数组</param> | |
| /// <param name="offset">开始解码的字节下标</param> | |
| /// <param name="count"></param> | |
| /// <returns></returns> | |
| public static string DecodeName(byte[] bytes, int offset, out int count) | |
| { | |
| count = 0; | |
| // | |
| if (offset + 2 > bytes.Length) | |
| return ""; | |
| //读取长度 | |
| Int16 len = (Int16)(bytes[offset + 1] << 8 | bytes[offset]); | |
| if (offset + 2 + len > bytes.Length) | |
| return ""; | |
| //解析协议名 | |
| count = len + 2;//在字节数组占用的总长度 | |
| string name = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, offset + 2, len); | |
| return name; | |
| } | |
| //json->byte[] | |
| public static byte[] Encode(MsgBase msgBase) | |
| { | |
| string s = js.Serialize(msgBase); | |
| return System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(s); | |
| } | |
| /// <summary> | |
| /// byte[] ->json | |
| /// </summary> | |
| /// <param name="protoName">协议名</param> | |
| /// <param name="bytes">json字节</param> | |
| /// <param name="offset">便宜量</param> | |
| /// <param name="count">要转换的长度</param> | |
| /// <returns></returns> | |
| public static MsgBase Decode(string protoName, byte[] bytes, int offset, int count) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("解析出来的协议名:" + protoName); | |
| string s = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, offset, count); | |
| MsgBase msgBase =(MsgBase) js.Deserialize(s, Type.GetType(protoName)); | |
| return msgBase; | |
| } | |
| } |
我们可以先用代码来测试一下这个功能是否完善,在Main函数中写入以下的测试代码:
| MsgMove msgMove = new MsgMove { | |
| x =100, | |
| y =200 | |
| }; | |
| byte[] bytes = MsgBase.Encode(msgMove); | |
| string s = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes); | |
| Console.WriteLine(s); |
运行一下:
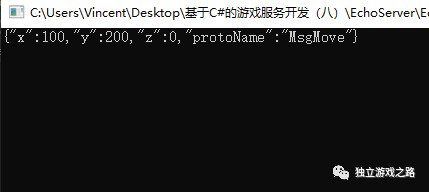
好的,说明这里已经没有问题.可以就行下一步.
这里的服务器程序与之前说的在程序的结构上基本类似,但是在之前的那种模式下增加了一个粘包半包的处理,协议的解析,数据库储存等功能,除了之前我们复制客户端的协议解析与加密之外,模块还多了一个4个部分,第一个是处理select多路复用的网络管理器NetManager第2个是定义客户端信息的Clientstate第三是处理网络消息的MsgHandler以及第4个事件处理的类EventHandler.
在服务端程序中添加logic文件夹,代表游戏的逻辑部分,再创建一个net文件夹.
ClientState,接客户端信息每一个客户端连接会对应的实例一个ClientState 对象,里面包含了与客户端连接的套接字socket和读取缓冲区readbuff.
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| using System.Net.Sockets; | |
| //每一个玩家对应一个类 | |
| public class ClientState | |
| { | |
| public Socket socket; | |
| public ByteArray readBuff = new ByteArray(); | |
| } |
服务端的网络管理器功能与客户端的网络管理器功能相似,都有处理连接,分发消息,和网络事件的功能,不同的是服务器是监听方,客户端是连接方,所以服务器需要更多的连接数,为了管理比较多的客户端连接,所以,服务器端用到了多路复用技术,也就是select,那么既然是用了多路复用,所以服务器得有一个地方来储存,列表于字典是一个很好的选择:
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| using System.Net.Sockets; | |
| using System.Net; | |
| using System.Reflection; | |
| class NetManager | |
| { | |
| //监听的socket | |
| public static Socket listenfd; | |
| //所有玩家皆在此字典中 | |
| public static Dictionary<Socket, ClientState> clients = | |
| new Dictionary<Socket, ClientState>(); | |
| //select 的检查列表 select 挨个便利socket,筛选出符合规范的 | |
| static List<Socket> checkRead = new List<Socket>(); | |
| ... | |
| } |
接下来写服务器的监听方法经过实例socket->bind->Listen这3个步骤之后,经过while()循环进行监听客户端的连接消息.
当然了由于服务器端是select模式,所以他每一次循环都会去判断列表是否有新的客户端连接,或者是有新的客户端发来消,息根据不同的模式,分别调用不同的方法,其中socket.selected的第3个参数1000代表设置了1秒的超时时间,也就是说这个服务器是1秒刷新一次
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| using System.Net.Sockets; | |
| using System.Net; | |
| using System.Reflection; | |
| class NetManager | |
| { | |
| //监听的socket | |
| public static Socket listenfd; | |
| //所有玩家皆在此字典中 | |
| public static Dictionary<Socket, ClientState> clients = | |
| new Dictionary<Socket, ClientState>(); | |
| //select 的检查列表 select 挨个便利socket,筛选出符合规范的 | |
| static List<Socket> checkRead = new List<Socket>(); | |
| public static void StartLoop(int ListenPort) | |
| { | |
| //实例化socket | |
| listenfd = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, | |
| SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); | |
| //Bind | |
| IPAddress ipAdr = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1"); | |
| IPEndPoint ipEp = new IPEndPoint(ipAdr, ListenPort); | |
| listenfd.Bind(ipEp); | |
| //Listen | |
| listenfd.Listen(0); | |
| Console.WriteLine("[*服务器启动成功*]"); | |
| //循环 [Socket select模式] | |
| while (true) | |
| { | |
| ResetCheckRead(); | |
| Socket.Select(checkRead, null, null, 1000); | |
| //检查可读对象 新连接上来的还是已经在线的客户端的消息 | |
| for (int i = checkRead.Count-1; i>=0 ; i--) | |
| { | |
| Socket s = checkRead[i]; | |
| if (s == listenfd) | |
| ReadListenfd(s); | |
| else | |
| ReadClientfd(s); | |
| } | |
| //超时 | |
| Timer(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| //每一次循环都会重新设置checkread列表 | |
| public static void ResetCheckRead() | |
| { | |
| checkRead.Clear(); | |
| checkRead.Add(listenfd); | |
| foreach (ClientState s in clients.Values ) | |
| { | |
| checkRead.Add(s.socket); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| ... | |
| } |
ReadListenfd,是处理监听事件的方法它会调用accept接受客户端连接然后新建一个客户端对象,并将它传入字典中,根据之前的经验这些操作应该在Try catch中实现:
| //处理监听消息 | |
| public static void ReadListenfd(Socket listenfd) | |
| { | |
| try | |
| { | |
| Socket clientfd = listenfd.Accept(); | |
| Console.WriteLine("Accept :" + clientfd.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()); | |
| ClientState state = new ClientState(); | |
| state.socket = clientfd; | |
| clients.Add(clientfd, state); | |
| } | |
| catch (SocketException e ) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine(e.ToString()); | |
| } | |
| } |
接下来应该去实现处理客户端的消息的功能,当然这个也和之前的客户端十分像,我们只需要更改里面一点点的实现方法即可.
| //处理客户端消息 | |
| public static void ReadClientfd(Socket clientfd) | |
| { | |
| ClientState state = clients[clientfd]; | |
| ByteArray readBuff = state.readBuff; | |
| //接收 | |
| int count = 0; | |
| //缓冲区不够,清除,如果依旧不够,只能返回 | |
| //缓冲区只有1024,若单条协议超过缓冲区长度会发生错误.根据需求调整长度 | |
| if (readBuff.remain <= 0) | |
| { | |
| OnReceiveData(state); | |
| readBuff.MoveBytes(); | |
| }; | |
| if (readBuff.remain <= 0) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("Receive Fail ,maybe msg length >buff capacity"); | |
| Close(state); | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| try | |
| { | |
| count = clientfd.Receive(readBuff.bytes, | |
| readBuff.writeIdx, readBuff.remain, 0); | |
| } | |
| catch (SocketException e ) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("Receive SocketFail :" + e.ToString()); | |
| Close(state); | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| //客户端下线 | |
| if (count <= 0) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("SocketClose " + clientfd.RemoteEndPoint.ToString()); | |
| Close(state); | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| //消息处理 | |
| readBuff.writeIdx += count; | |
| //处理二进制流 | |
| OnReceiveData(state); | |
| //移动缓冲区 | |
| readBuff.CheckAndMoveBytes(); | |
| } |
关闭连接Close()方法会处理三件事情,第一是分发Ondisconnect事件让程序在玩家掉线时做出一些处理,其二是调用socket.Close关闭连接,第三是将客户端的状态从state移出字典
| //关闭连接 | |
| public static void Close(ClientState state) | |
| { | |
| //事件分发 | |
| MethodInfo mei = typeof(EventHandler).GetMethod("OnDisconnect"); | |
| object[] ob = { state }; | |
| mei.Invoke(null, ob); | |
| //关闭并移除 | |
| state.socket.Close(); | |
| clients.Remove(state.socket); | |
| } |
接下来是处理协议的方法OnReceiveData(),首先它会判断缓冲区的数据是否足够长如果足够长,它就可以调用方法解析出协议名和协议体,最后做消息分发,当然,它还需要一个参数,这表明该条消息来自哪一个客户端.
| //关闭连接 | |
| //消息处理 | |
| public static void OnReceiveData(ClientState state) | |
| { | |
| ByteArray readBuff = state.readBuff; | |
| //消息长度 | |
| if (readBuff.length <= 2) | |
| { | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| Int16 bodyLength = readBuff.ReadInt16(); | |
| //消息体 | |
| if (readBuff.length < bodyLength) | |
| return; | |
| //解析协议名 | |
| int nameCount = 0; | |
| string protoName = MsgBase.DecodeName(readBuff.bytes, | |
| readBuff.readIdx, out nameCount); | |
| if (protoName == "") | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("OnReceiveData MsgBase .DecodeName fail..."); | |
| Close(state); | |
| } | |
| readBuff.readIdx += nameCount; | |
| //解析协议体 | |
| int bodyCount = bodyLength - nameCount; | |
| MsgBase msgBase = MsgBase.Decode(protoName, readBuff.bytes, | |
| readBuff.readIdx, bodyCount); | |
| readBuff.readIdx += bodyCount; | |
| readBuff.CheckAndMoveBytes(); | |
| //分发消息 | |
| MethodInfo mi = typeof(MsgHandler).GetMethod(protoName ); | |
| object[] o = { state, msgBase }; | |
| Console.WriteLine("Receive " + protoName); | |
| if (mi != null) | |
| { | |
| mi.Invoke(null, o); | |
| } | |
| else | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("OnReceiveData Invoke fail " + protoName); | |
| } | |
| //继续读取消息 | |
| if (readBuff.length > 2) | |
| OnReceiveData(state); | |
| } |
接下来是定时器:
使用的是反射的方法,目前调用的是EventHandler中的OnTimer()
| public static void Timer() | |
| { | |
| MethodInfo mei = typeof(EventHandler).GetMethod("OnTimer"); | |
| object[] ob = { }; | |
| mei.Invoke(null, ob); | |
| } |
目前EventHandler中有处理玩家下线的事件,和定时器事件,不过目前来看他们并没有实质的功能只是搭了一个架子.
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| public partial class EventHandler | |
| { | |
| public static void OnDisconnect(ClientState c) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("Close "); | |
| } | |
| public static void OnTimer() | |
| { | |
| } | |
| } |
接下来编写发送协议的方法它需要有2个参数第一个是客户端的实例对象第2个参数是要发送的消息:
| //发送 | |
| public static void Send(ClientState cs, MsgBase msg) | |
| { | |
| //状态判断 | |
| if (cs == null) | |
| return; | |
| if (!cs.socket.Connected) | |
| return; | |
| //数据编码 | |
| byte[] nameBytes = MsgBase.EncodeName(msg); | |
| byte[] bodyBytes = MsgBase.Encode(msg); | |
| int len = nameBytes.Length + bodyBytes.Length; | |
| byte[] sendBytes = new byte[2 + len]; | |
| //组装长度 | |
| sendBytes[0] = (byte)(len % 256); | |
| sendBytes[1] = (byte)(len / 256); | |
| //组装名字 | |
| Array.Copy(nameBytes, 0, sendBytes, 2, nameBytes.Length); | |
| //组装消息体 | |
| Array.Copy(bodyBytes, 0, sendBytes, 2 + nameBytes.Length, bodyBytes.Length); | |
| //简化代码,不设置回调 | |
| try | |
| { | |
| cs.socket.BeginSend(sendBytes, 0, sendBytes.Length, 0, null, null); | |
| } | |
| catch (SocketException e ) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("Socket close onBeginsend" + e.ToString()); | |
| } | |
| } |
接下来我们测试一下,打开Unity,使用之前的Unity客户端.
服务器中也要进行一些改造服务器中也要进行一些改造,Msghandler,这个类是一个局部类:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| class BattleMsgHandler | |
| { | |
| } | |
| public partial class MsgHandler | |
| { | |
| public static void MsgMove(ClientState c, MsgBase msgBase) | |
| { | |
| MsgMove msgMove = (MsgMove)msgBase; | |
| Console.WriteLine(msgMove.x); | |
| msgMove.x++; | |
| NetManager.Send(c, msgMove); | |
| } | |
| } |
局部类就是在可以在任何一个地方去写它的组成部分,比如说可以在SysMessageHandler中也写一个:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| class SysMsgHandler | |
| { | |
| } | |
| public partial class MsgHandler | |
| { | |
| public static void MshPing(ClientState c, MsgBase msgBase) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("MsgPing"); | |
| } | |
| } |
所有的功能都已经书写完毕现在开始测试一下吧在Main函数中直接调用Start loop:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| namespace EchoServer | |
| { | |
| class Program | |
| { | |
| static void Main(string[] args) | |
| { | |
| NetManager.StartLoop(8888); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
点击运行:
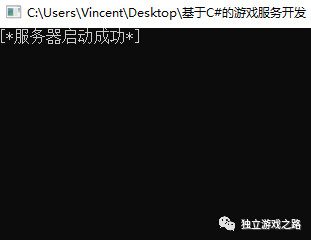
我们再打开unity程序验证一下吗,因为是以前的unity程序,没有做过多的修改,所以直接运行一下:
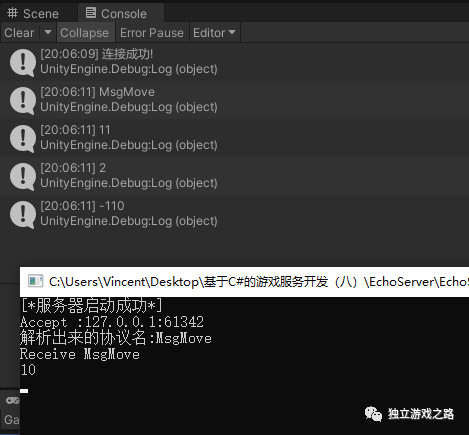
接下来是要写一个心跳检测,客户端会定时地向服务器端发送一个协议,服务器收到之后需要回应一个协议,并记录一下当前回应的时间,由于服务器收到客户端传来的消息和客户端的某些状态息息相关,所以要在clientstate中定义long类型的数据类型.用来记录时间,那么为什么呢?因为服务器端和客户端不同,客户端最多也就运行几个小时,而服务器可能是3,5年都不会关闭所以我们选择了用long类型.
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| using System.Net.Sockets; | |
| //每一个玩家对应一个类 | |
| public class ClientState | |
| { | |
| public Socket socket; | |
| public ByteArray readBuff = new ByteArray(); | |
| //玩家数据后面添加 | |
| //最后一次ping的时间 | |
| public long lastPingTime = 0; | |
| } |
服务端需要判断客户端是否太久没有发送协议,定义一个参数代表他最大的心跳时间,服务器端,客户端的要保持一致,这里写一个30,代表30秒.
| using System.Net.Sockets; | |
| using System.Net; | |
| using System.Reflection; | |
| class NetManager | |
| { | |
| //监听的socket | |
| public static Socket listenfd; | |
| //所有玩家皆在此字典中 | |
| public static Dictionary<Socket, ClientState> clients = | |
| new Dictionary<Socket, ClientState>(); | |
| //select 的检查列表 select 挨个便利socket,筛选出符合规范的 | |
| static List<Socket> checkRead = new List<Socket>(); | |
| //(心跳)Ping的时间间隔 | |
| public static long PingInterval = 30; | |
| ... | |
| } |
那么我们该用什么方法去记录它的间隔时间呢?实践出是其中的一种办法我们就需要用到这种办法,时间戳是指从1970年1月1号零点到现在的秒,我们把这个秒转换成long类型储存起来.
| //获取时间戳 | |
| public static long GetTimeStamp() | |
| { | |
| //从1970年到如今的时间,数据类型为long型数据 | |
| TimeSpan ts = DateTime.UtcNow - new DateTime(1970, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0); | |
| return Convert.ToInt64(ts.TotalSeconds); | |
| } | |
| } |
心跳的2个协议一个是MsgPing一个是MsgPong.服务端收到Ping协议时它需要更新LastInTime并且回Pong协议
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| public partial class MsgHandler | |
| { | |
| public static void MsgPing(ClientState c, MsgBase msgBase) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("MsgPing"); | |
| c.lastPingTime = NetManager.GetTimeStamp(); | |
| MsgPong msgPong = new MsgPong(); | |
| NetManager.Send(c, msgPong); | |
| } | |
| ... | |
| } |
如果超时没有回应那么可以认为该连接已断开判断的方法是四次的协议都没有回应也就是30乘以4等于120秒然后再用Close关闭连接
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| public partial class MsgHandler | |
| { | |
| public static void MsgPing(ClientState c, MsgBase msgBase) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("MsgPing"); | |
| c.lastPingTime = NetManager.GetTimeStamp(); | |
| MsgPong msgPong = new MsgPong(); | |
| NetManager.Send(c, msgPong); | |
| } | |
| public static void OnTimer() | |
| { | |
| CheckPing(); | |
| } | |
| //Ping检查 | |
| public static void CheckPing() | |
| { | |
| //现在的时间戳 | |
| long timeNow = NetManager.GetTimeStamp(); | |
| //遍历所有的客户端,把超时的删除 | |
| foreach (ClientState s in NetManager.clients.Values) | |
| { | |
| //4次心跳都没有回应 | |
| if (timeNow - s.lastPingTime > NetManager.PingInterval * 4) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("Ping Close " | |
| + s.socket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString() | |
| ) ; | |
| NetManager.Close(s); | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
测试的话可以将服务器的时间调小比如是2秒而客户端的时间调为60秒
------------------------------------------------------------------
目前看起来功能已经完善了,其实不然,当客户端连接服务器时,它还只是一个连接,处理的只是网络消息和心跳,当玩家输入了用户名和密码,点击了登录按钮,应该是这个玩家和数据库中的某一个数据进行匹配,并且为客户端的玩家进行对象的赋值,那么现在就需要去实现这个功能,首先需要的是一个PlayerData这样的一个类用来储存玩家的信息,先做一个简单的,仅仅有金币和一个信息:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| //玩家存在云端的数据 | |
| public class PlayerData | |
| { | |
| public int coin = 0; | |
| public string text = "new text"; | |
| } |
这仅仅是代表这个玩家在数据库中储存的信息,玩家在联机的时候还有许多临时的属性,比如它的位置坐标,那么接下来就去协议一个这样的一个类,这个类的名字叫Player
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| //网络传输中需要的数据类 | |
| public class Player | |
| { | |
| public string id = ""; | |
| public ClientState state; | |
| //临时数据 | |
| public int x; | |
| public int y; | |
| public int z; | |
| //数据库数据 | |
| public PlayerData data; | |
| //构造函数 | |
| public Player(ClientState state) | |
| { | |
| this.state = state; | |
| } | |
| //发送消息 (这里方便玩家找玩家,比如互相攻击) | |
| public void Send(MsgBase msgBase) | |
| { | |
| NetManager.Send(state, msgBase); | |
| } | |
| } |
Clear manager的一个类管理所有的玩家
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| //为了快速查找玩家对象 | |
| public class PlayerManager | |
| { | |
| //玩家列表 | |
| static Dictionary<string, Player> players = new Dictionary<string, Player>(); | |
| //玩家是否在线 | |
| public static bool isOnline(string id) | |
| { | |
| return players.ContainsKey(id); | |
| } | |
| //获取玩家 | |
| public static Player GetPlayer(string id) | |
| { | |
| if (players.ContainsKey(id)) | |
| { | |
| return players[id]; | |
| } | |
| return null; | |
| } | |
| //添加玩家 | |
| public static void AddPlayer(string id, Player player) | |
| { | |
| players.Add(id, player); | |
| } | |
| //删除玩家 | |
| public static void RemovePlayer(string id) | |
| { | |
| players.Remove(id); | |
| } | |
| } |
游戏需要保存两种信息,一种是账号信息,是玩家的账号和密码,另一种是玩家信息,包括玩家身上的金币经验等等,这些都会保存在数据库中,那么最常用的数据库是MySQL,从服务器的角度看MySQL数据库是个服务端程序,服务器与数据库通过TCP连接交互数据.
还记得一开始安装的那几个软件吗?这个时候就可以派上用场了.
使用Navicat for MySQL连接sql.并新建两个表:
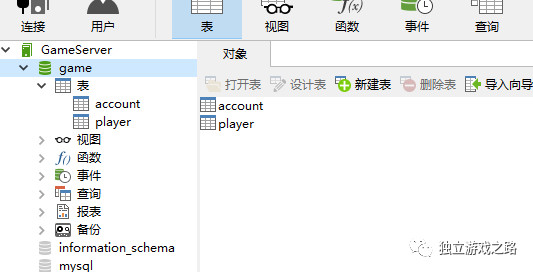
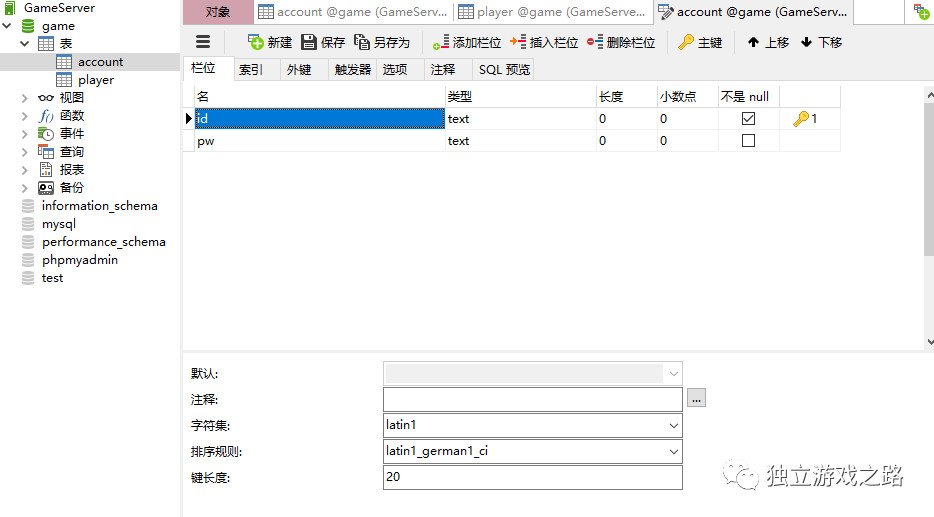
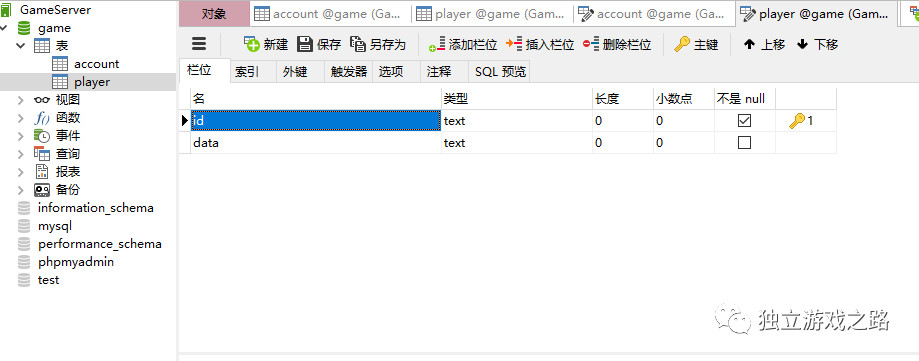
设置如下2图所示:
再到vs中,vs要和数据库进行连接需要一个MySQL的库这个库可以在NuGet中获取到:
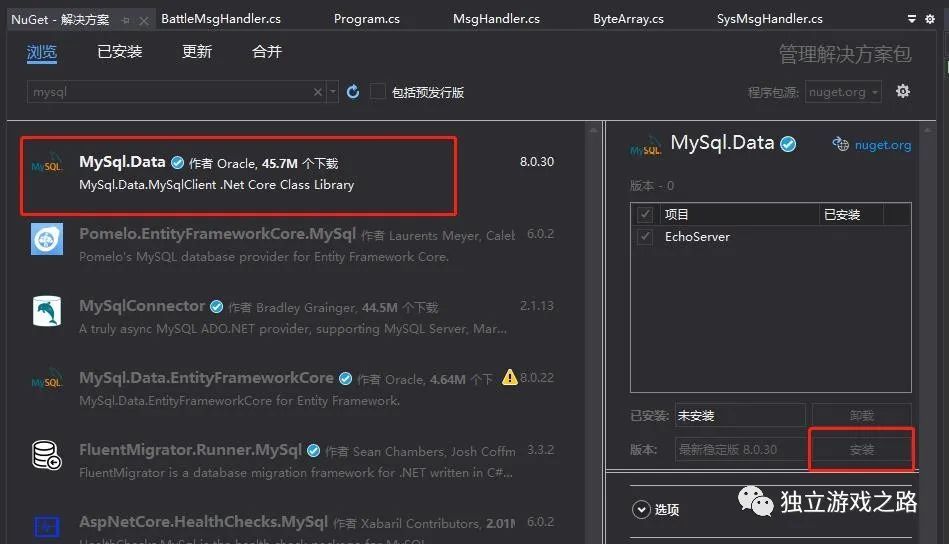
在专门新建一个和数据库连接通讯的一个类:
引入一个命名空间:
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
首先是一数据库的一个连接:
| public static MySqlConnection mysql; | |
| static JavaScriptSerializer Js; | |
| //连接数据库 | |
| public static bool Connect(string db, string ip, int port, string user,string pw) | |
| { | |
| mysql = new MySqlConnection(); | |
| Js = new JavaScriptSerializer(); | |
| //连接参数 | |
| string s = string.Format( | |
| "Database={0};" + | |
| "Data Source ={1};" + | |
| "port={2};" + | |
| "User Id={3};" + | |
| "Password={4}", | |
| db, ip, port, user, pw); | |
| Console.WriteLine(s); | |
| mysql.ConnectionString = s; | |
| //连接 | |
| try | |
| { | |
| mysql.Open(); | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库] 打开成功"); | |
| return true; | |
| } | |
| catch (Exception e) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库] 打开失败" + " " + e.Message); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| } |
在曼函数中的逻辑应该是这样:在服务器端程序开启时先连接数据库,在开启网络监听,如果连接数据库失败,说明服务器端启动失败.测试的代码可以这么写:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| namespace EchoServer | |
| { | |
| class Program | |
| { | |
| static void Main(string[] args) | |
| { | |
| //如果数据库连接失败,就不用再往下执行了 | |
| if (!DbManager.Connect("game", "127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "")) | |
| { | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| NetManager.StartLoop(8888); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
运行之后即可看到数据库连接成功
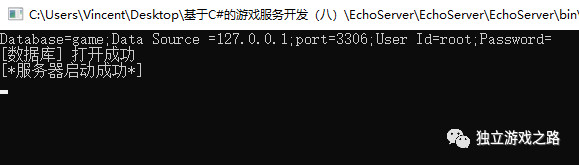
按照顺序接下来应该是数据库的曾删改查操作,其实在做这一步之前还有一个小小的一个操作就是防止SQL注入,简单点来说就是一个安全性的考虑,就是在执行数据库的命令时需要判断它的字符串是否有非法字符这个我们用正则表达式排除一下:
| //判断安全字符 | |
| private static bool IsSafeString(string str) | |
| { | |
| return !Regex.IsMatch(str, @"[-|;|,|\/|\(|\)|\[|\]|\}|\{|%|@|\*|!|\']"); | |
| } |
首先是注册的逻辑:
如果数据库中已经包含了这个玩家,很显然不能再次注册
| //注册账号 | |
| //判断表里是否已经有这个账号了 | |
| public static bool IsAccountExist(string id) | |
| { | |
| if (IsSafeString(id)) | |
| { | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| //SQL语句 | |
| string s = string.Format("select * from account where id ='{0}';", id); | |
| Console.WriteLine(s);//测试语句 | |
| try | |
| { | |
| MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand(s, mysql); | |
| MySqlDataReader dataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(); | |
| bool hasRows = dataReader.HasRows; | |
| dataReader.Close(); | |
| return !hasRows; | |
| } | |
| catch (Exception e ) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库] IsSafeString err " + e.Message); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| } |
当通过了这个判断之后玩家就可以开始注册账号了:
| //注册 | |
| public static bool Register(string id, string pw) | |
| { | |
| //安全检查 | |
| if (!DbManager.IsSafeString(id)) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]用户注册失败,安全检查未通过"); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| if (!DbManager.IsSafeString(pw)) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]用户注册失败,安全检查未通过"); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| //是否可以注册 | |
| if (DbManager.IsAccountExist(id)) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]用户注册失败,已经有此用户名"); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| //写入数据库 | |
| string sql = string.Format("insert into account set id ='{0}', pw ='{1}';", id, pw); | |
| //string sql = string.Format("inset into account ('id','pw')values ('{0}','{1}');", id ,pw ); | |
| Console.WriteLine("注册语句:" + sql); | |
| try | |
| { | |
| MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand(sql, mysql); | |
| cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); | |
| return true; | |
| } | |
| catch (Exception e ) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]account写入数据库失败"+e .Message ); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| } |
我们现在可以在曼函数中写一个测试方法:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| namespace EchoServer | |
| { | |
| class Program | |
| { | |
| static void Main(string[] args) | |
| { | |
| //如果数据库连接失败,就不用再往下执行了 | |
| if (!DbManager.Connect("game", "127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "")) | |
| { | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| //测试数据库写入功能 | |
| if (DbManager.Register("Vincent", "123456")) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("注册成功"); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
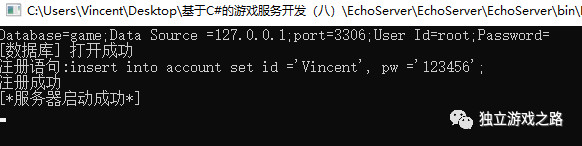
运行之后即可发现数据库中多了一条记录:
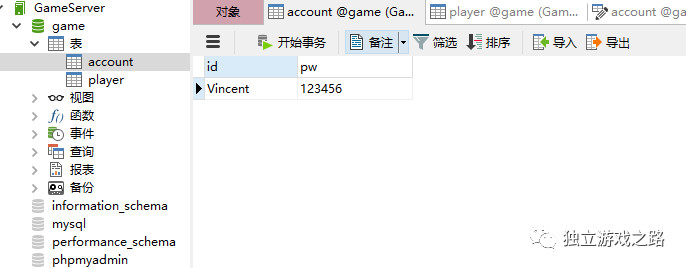
如果你再次运行的话他们会报一个错:
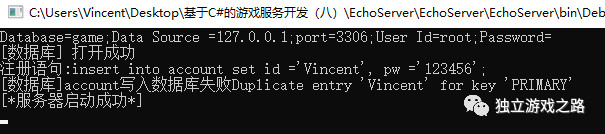
因为已经有同名的用户存在.
接下来我们将玩家的数据写入Player表中,那么为什么要用到2张表呢?因为账户和玩家信息是可以一对多的,一个账户可以对应多个玩家信息,因为有可能是不同款的游戏.
玩家的信息说的数据类型是Json所以我们还需要引入一下:
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
创建玩家的时候默认的Player data里面有默认的属性:
| //创建角色 | |
| public static bool CreatPlayer(string id) | |
| { | |
| //安全检查 | |
| if (!DbManager.IsSafeString(id)) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]用户注册失败,安全检查未通过"); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| //玩家默认信息 | |
| PlayerData playerData = new PlayerData(); | |
| //序列化 | |
| string data = Js.Serialize(playerData); | |
| //写入数据库 | |
| string sql = string.Format("insert into player set id ='{0}',data='{1}';", id, data); | |
| try | |
| { | |
| MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand(sql, mysql); | |
| cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); | |
| return true; | |
| } | |
| catch (Exception e ) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]玩家写入失败!"+e .Message); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| } |
同样的我们在曼函数中写一串代码进行测试:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| namespace EchoServer | |
| { | |
| class Program | |
| { | |
| static void Main(string[] args) | |
| { | |
| //如果数据库连接失败,就不用再往下执行了 | |
| if (!DbManager.Connect("game", "127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "")) | |
| { | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| if (DbManager.CreatPlayer("Yeon")) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("角色创建成功!"); | |
| } | |
| Console.ReadKey(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
运行一下:
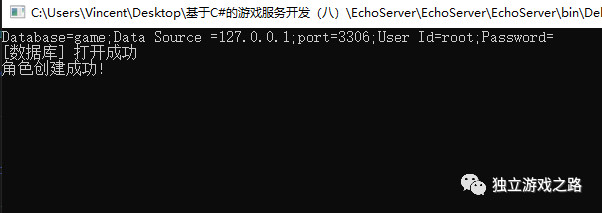
数据库中可以看到:
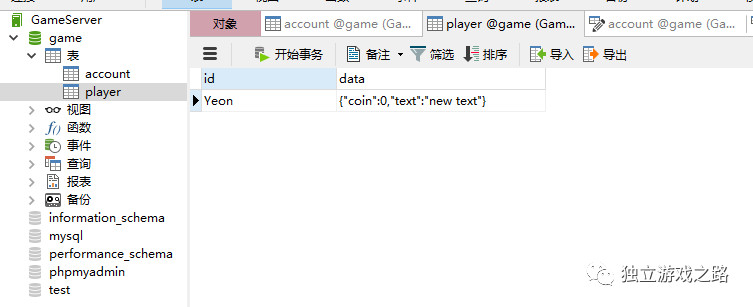
当用户在登录的时候,服务器需要检查玩家输入的用户名和密码是否正确,它实现的方法如下:
| //检查用户的密码 | |
| public static bool CheckPassword(string id, string pw) | |
| { | |
| //安全检查 | |
| if (!DbManager.IsSafeString(id)) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]用户注册失败,安全检查未通过"); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| if (!DbManager.IsSafeString(pw)) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]用户注册失败,安全检查未通过"); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| //查询 | |
| string sql = string.Format("select * from account where id ='{0}' and pw '{1}'", id, pw); | |
| Console.WriteLine(sql ); | |
| try | |
| { | |
| MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand(sql, mysql); | |
| MySqlDataReader dataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(); | |
| bool hasRows = dataReader.HasRows; | |
| dataReader.Close(); | |
| return hasRows; | |
| } | |
| catch (Exception e ) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]密码检查错误,不存在此密码"); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| } |
当然还有读取玩家数据的方法,通过角色账号在表中搜索数据,然后以字符串的形式存放着序列化后的Json数据.
| //从数据库中读取玩家数据 | |
| public static PlayerData GetPlayerData(string id) | |
| { | |
| if (!DbManager.IsSafeString(id)) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]获取玩家信息失败,安全检查未通过"); | |
| return null; | |
| } | |
| string sql = string.Format("select * from player where id = '{0}';", id); | |
| Console.WriteLine(sql); | |
| try | |
| { | |
| //查询 | |
| MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand(sql, mysql); | |
| MySqlDataReader dataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(); | |
| if (!dataReader.HasRows) | |
| { | |
| dataReader.Close(); | |
| return null; | |
| } | |
| //获取数据 | |
| dataReader.Read(); | |
| string data = dataReader.GetString("data"); | |
| //反序列化 | |
| PlayerData playerData = Js.Deserialize<PlayerData>(data); | |
| dataReader.Close(); | |
| return playerData; | |
| } | |
| catch (Exception e) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]获取玩家数据失败!"+e .Message); | |
| return null; | |
| } | |
| } |
测试代码:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| namespace EchoServer | |
| { | |
| class Program | |
| { | |
| static void Main(string[] args) | |
| { | |
| //如果数据库连接失败,就不用再往下执行了 | |
| if (!DbManager.Connect("game", "127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "")) | |
| { | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| PlayerData playerData = DbManager.GetPlayerData("Yeon"); | |
| Console.WriteLine(playerData.coin); | |
| Console.ReadKey(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
运行代码如下:
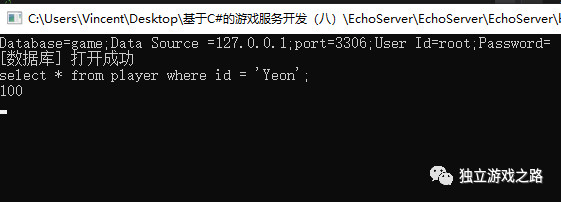
如果玩家的数据在游戏中进行了改变我们还要对数据库中的数据进行一个修改:
| //更新玩家数据 | |
| public static bool UpdatePlayerData(string id,PlayerData playerData) | |
| { | |
| //序列化 | |
| string data = Js.Serialize(playerData); | |
| //sql | |
| string sql = string.Format("update player set data ='{0}' where id ='{1}';", data, id); | |
| Console.WriteLine(sql); | |
| try | |
| { | |
| MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand(sql, mysql); | |
| cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); | |
| return true; | |
| } | |
| catch (Exception e) | |
| { | |
| Console.WriteLine("[数据库]更新玩家数据失败!" + e.Message); | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| } |
测试代码如下:
| using System; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Threading.Tasks; | |
| namespace EchoServer | |
| { | |
| class Program | |
| { | |
| static void Main(string[] args) | |
| { | |
| //如果数据库连接失败,就不用再往下执行了 | |
| if (!DbManager.Connect("game", "127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "")) | |
| { | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| PlayerData playerData = new PlayerData | |
| { | |
| coin = 100, | |
| text = "Hello ,Yeon" | |
| }; | |
| DbManager.UpdatePlayerData("Yeon", playerData); | |
| Console.ReadKey(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
运行一下:
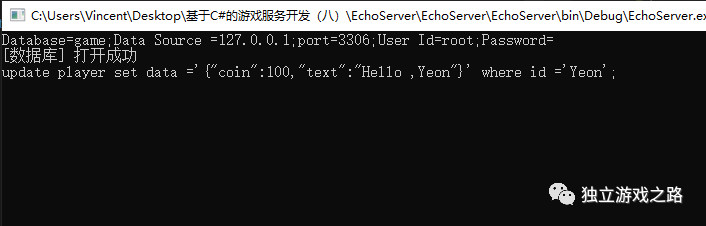
数据库中也已经同步修改:
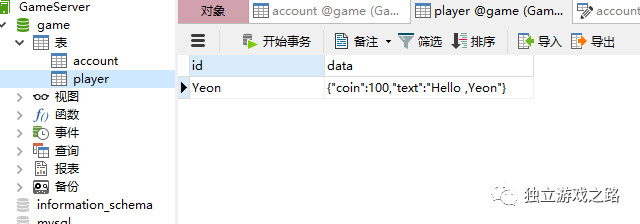
到目前为止我们已经完成了服务器端的所有基础模块.