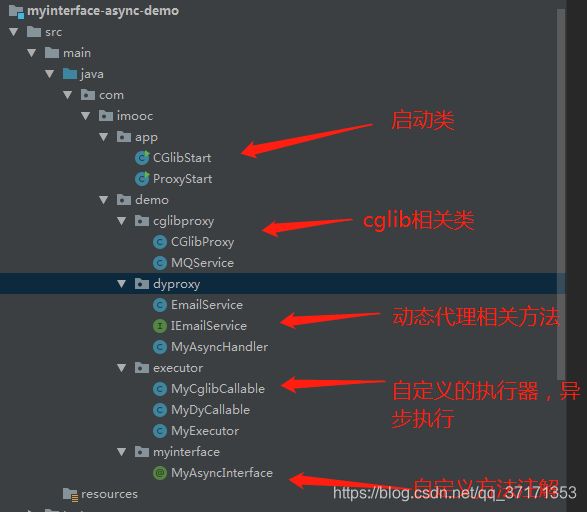
项目目录结构
项目下载
https://github.com/cbeann/Demoo/tree/master/async-demo
实践
pom
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/cglib/cglib -->
<!--cglib依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
自定义标注注解
没有方法参数的注解成为标注注解
//Async注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//方法注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行时注解
public @interface MyAsyncInterface {
}
自定义执行器
package com.imooc.demo.executor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class MyExecutor {
/*
动态代理的异步执行方法,参数就是 invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
*/
public static void submit(Object object, Method method, Object[] args) throws Exception {
//封装成callable接口
MyDyCallable myCallable = new MyDyCallable(object, method, args);
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(myCallable);
//运行线程
new Thread(futureTask).start();
}
/*
cglib的异步执行方法intercept(Object object, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy)
*/
public static void submit(Object object, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Exception {
//封装成callable接口
MyCglibCallable myCglibCallable = new MyCglibCallable(object, method, args, proxy);
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(myCglibCallable);
//运行线程
new Thread(futureTask).start();
}
}
实现动态代理的异步执行
IEmailService接口
public interface IEmailService {
public void sendEmail();
public void speak();
}
IEmailService接口实现类
其中带有MyAsyncInterface我们要使其成为异步方法
package com.imooc.demo.dyproxy;
import com.imooc.demo.myinterface.MyAsyncInterface;
public class EmailService implements IEmailService {
@MyAsyncInterface
@Override
public void sendEmail() {
System.out.println("开始发送email---------->睡10秒");
try {
//处理业务10毫秒
Thread.sleep(1000 * 2);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
System.out.println("结束发发送email<----------");
}
public void speak() {
System.out.println("-----EmailService------");
}
}
MyAsyncHandler (动态代理知识)
package com.imooc.demo.dyproxy;
import com.imooc.demo.myinterface.MyAsyncInterface;
import com.imooc.demo.executor.MyExecutor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class MyAsyncHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//目标对象
private Object target;
//传入代码目标对象
public MyAsyncHandler(Object object) {
this.target = object;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable, Exception {
//method参数是接口的方法,上面是不带@MyAsyncInterface的,我们一般是定义在接口实现类上,所以我们通过接口的method获取target(实现类)的方法,从而获取自定义注解信息
MyAsyncInterface annotation = target.getClass().getMethod(method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes()).getAnnotation(MyAsyncInterface.class);
if (null != annotation) {
//如果该方法有自定义异步注解,启动线程跑
MyExecutor.submit(target, method, args);
} else {
//如果该方法没有自定义异步注解,同步执行
Object invoke = method.invoke(target, args);
}
//如果有结果返回,如果没有就不返回
return null;
}
}
MyDyCallable:实现Callable接口(多线程知识)
目的:如果方法时异步,将参数传入callable,并且启动线程执行
package com.imooc.demo.executor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyDyCallable implements Callable<Object> {
private Object target;
private Method method;
private Object[] args;
public MyDyCallable(Object object, Method method, Object[] args) {
this.target = object;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
}
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
return result;
}
}
ProxyStart:测试类
package com.imooc.app;
import com.imooc.demo.dyproxy.EmailService;
import com.imooc.demo.dyproxy.IEmailService;
import com.imooc.demo.dyproxy.MyAsyncHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IEmailService emailService = new EmailService();
MyAsyncHandler asyncHandler = new MyAsyncHandler(emailService);
Class cls = emailService.getClass();
//创建动态代理对象
IEmailService newProxyInstance = (IEmailService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
cls.getClassLoader(), cls.getInterfaces(), asyncHandler);
//此方法时异步
newProxyInstance.sendEmail();
//此方法时同步
newProxyInstance.speak();
// 执行结果如下:
// -----EmailService------ newProxyInstance.speak()方法
// 开始发送email---------->睡10秒 newProxyInstance.sendEmail();方法
// 结束发发送email<----------
}
}
实现cglib的异步执行
MQService
方法setMessage方法,我们使其成为异步方法
package com.imooc.demo.cglibproxy;
import com.imooc.demo.myinterface.MyAsyncInterface;
public class MQService {
@MyAsyncInterface
public void setMessage(String messgae) {
System.out.println("开始发送MQmessage--------->睡3秒");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 3);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
System.out.println("结束发送MQmessage<-------------");
}
}
CGlibProxy (动态代理cglib知识)
package com.imooc.demo.cglibproxy;
import com.imooc.demo.executor.MyExecutor;
import com.imooc.demo.myinterface.MyAsyncInterface;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class CGlibProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
private Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
public Object getProxy(Class clz) {
enhancer.setSuperclass(clz);
enhancer.setCallback(this);
return enhancer.create();
}
/**
* @param object 目标类的实例
* @param method 目标方法的反射对象
* @param args 目标方法的参数
* @param proxy 代理类的实例
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object object, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
if (method.getAnnotation(MyAsyncInterface.class) != null) {
MyExecutor.submit(object, method, args, proxy);
} else {
proxy.invokeSuper(object, args);
}
return null;
}
}
MyCglibCallable (多线程知识)
package com.imooc.demo.executor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyCglibCallable implements Callable {
private Object object;
private Method method;
private Object[] args;
private MethodProxy proxy;
//参数是intercept(Object object, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy)
public MyCglibCallable(Object object, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) {
this.object = object;
this.args = args;
this.method = method;
this.proxy = proxy;
}
@Override
public Object call() {
try {
proxy.invokeSuper(object, args);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
CGlibStart 测试类
package com.imooc.app;
import com.imooc.demo.cglibproxy.CGlibProxy;
import com.imooc.demo.cglibproxy.MQService;
public class CGlibStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// MQService mqService = new MQService();
// mqService.setMessage("123123");
CGlibProxy cGlibProxy = new CGlibProxy();
MQService proxy = (MQService) cGlibProxy.getProxy(MQService.class);
proxy.setMessage("123");
System.out.println("-----------------------");
// 执行结果
// ----------------------- System.out.println("-----------------------");
// 开始发送MQmessage--------->睡3秒 proxy.setMessage("123");
// 结束发送MQmessage<-------------
}
}
总结
1)需要了解动态代理、多线程知识
2)上面都是按照方法没有返回结果算的,实际情况下是很多是有结果的
3)多线程中Callable是有返回结果的