使用JMX
JAVA Management Extensions的缩写,Java自带的一种管理资源的技术,比如对Java 应用程序,系统和网络等
java自带的获取各种信息的工具类
java自带的java.lang.management.ManagementFactory 可以看到它提供的一些列方法:
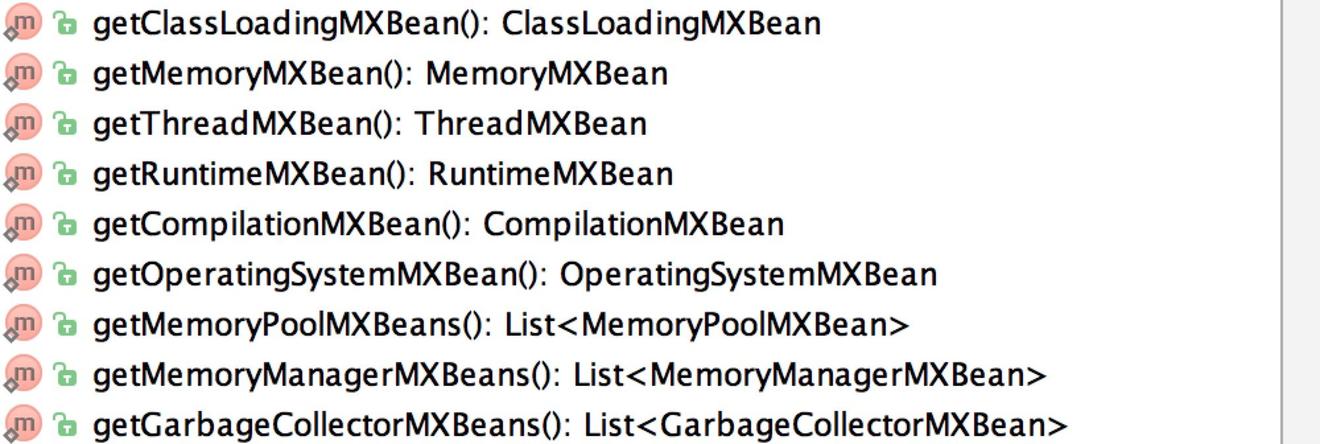
可以看到它提供了包括类加载、内存、线程等MXBean
以Memory为例,它包括两部分,MemoryMXBean和MemoryPoolMXBean
| /** | |
| * Returns the managed bean for the memory system of | |
| * the Java virtual machine. | |
| * | |
| * @return a {@link MemoryMXBean} object for the Java virtual machine. | |
| */ | |
| public static MemoryMXBean getMemoryMXBean() { | |
| return ManagementFactoryHelper.getMemoryMXBean(); | |
| } |
MemoryMXBean提供获取堆内存和非堆内存的方法,返回对象MemoryUsage相应包含最大、已使用等信息
| /** | |
| * Returns the current memory usage of the heap that | |
| * is used for object allocation. The heap consists | |
| * of one or more memory pools. The <tt>used</tt> | |
| * and <tt>committed</tt> size of the returned memory | |
| * usage is the sum of those values of all heap memory pools | |
| * whereas the <tt>init</tt> and <tt>max</tt> size of the | |
| * returned memory usage represents the setting of the heap | |
| * memory which may not be the sum of those of all heap | |
| * memory pools. | |
| * <p> | |
| * The amount of used memory in the returned memory usage | |
| * is the amount of memory occupied by both live objects | |
| * and garbage objects that have not been collected, if any. | |
| * | |
| * <p> | |
| * <b>MBeanServer access</b>:<br> | |
| * The mapped type of <tt>MemoryUsage</tt> is | |
| * <tt>CompositeData</tt> with attributes as specified in | |
| * {@link MemoryUsage#from MemoryUsage}. | |
| * | |
| * @return a {@link MemoryUsage} object representing | |
| * the heap memory usage. | |
| */ | |
| public MemoryUsage getHeapMemoryUsage(); | |
| /** | |
| * Returns the current memory usage of non-heap memory that | |
| * is used by the Java virtual machine. | |
| * The non-heap memory consists of one or more memory pools. | |
| * The <tt>used</tt> and <tt>committed</tt> size of the | |
| * returned memory usage is the sum of those values of | |
| * all non-heap memory pools whereas the <tt>init</tt> | |
| * and <tt>max</tt> size of the returned memory usage | |
| * represents the setting of the non-heap | |
| * memory which may not be the sum of those of all non-heap | |
| * memory pools. | |
| * | |
| * <p> | |
| * <b>MBeanServer access</b>:<br> | |
| * The mapped type of <tt>MemoryUsage</tt> is | |
| * <tt>CompositeData</tt> with attributes as specified in | |
| * {@link MemoryUsage#from MemoryUsage}. | |
| * | |
| * @return a {@link MemoryUsage} object representing | |
| * the non-heap memory usage. | |
| */ | |
| public MemoryUsage getNonHeapMemoryUsage(); |
MemoryPoolMXBean能够获取 memory pool的名字,比如是否是Eden区,old区等等
| /** | |
| * Returns a list of {@link MemoryPoolMXBean} objects in the | |
| * Java virtual machine. | |
| * The Java virtual machine can have one or more memory pools. | |
| * It may add or remove memory pools during execution. | |
| * | |
| * @return a list of <tt>MemoryPoolMXBean</tt> objects. | |
| * | |
| */ | |
| public static List<MemoryPoolMXBean> getMemoryPoolMXBeans() { | |
| return ManagementFactoryHelper.getMemoryPoolMXBeans(); | |
| } |
要获取整个的内存大小,需要使用Runtime
| /** | |
| * Returns the amount of free memory in the Java Virtual Machine. | |
| * Calling the | |
| * <code>gc</code> method may result in increasing the value returned | |
| * by <code>freeMemory.</code> | |
| * | |
| * @return an approximation to the total amount of memory currently | |
| * available for future allocated objects, measured in bytes. | |
| */ | |
| public native long freeMemory(); | |
| /** | |
| * Returns the total amount of memory in the Java virtual machine. | |
| * The value returned by this method may vary over time, depending on | |
| * the host environment. | |
| * <p> | |
| * Note that the amount of memory required to hold an object of any | |
| * given type may be implementation-dependent. | |
| * | |
| * @return the total amount of memory currently available for current | |
| * and future objects, measured in bytes. | |
| */ | |
| public native long totalMemory(); | |
| /** | |
| * Returns the maximum amount of memory that the Java virtual machine will | |
| * attempt to use. If there is no inherent limit then the value {@link | |
| * java.lang.Long#MAX_VALUE} will be returned. </p> | |
| * | |
| * @return the maximum amount of memory that the virtual machine will | |
| * attempt to use, measured in bytes | |
| * @since 1.4 | |
| */ | |
| public native long maxMemory(); |
获取其它想要监控的信息
通过java.lang.management.ManagementFactory 获取 MBeanServer,平台所有的MBean都会注册到这个上面。然后通过获取ObjectName和属性就能获得值
JMX的架构
分成3块:Instrumentation,JMX agent和Remote management
- Instrumentation: 使用MBeans来实现资源检测(resources' instrumentation),MBeans有一套标准的规范,实现MBeans必须遵循,以实现标准化的处理
- JMX Agent: 用于直接的控制资源,并使得远程管理应用能够获取这些资源,它通常和控制的资源在同一台机器上。JMX Agent的核心组件是MBean server[]MBeans注册的地方]
- Remote management: JMX Agent实现的不同协议适配器和connector使得注册在MBean server上的MBeans都能够被看到,比如HTML的adaptor能够使得浏览器上能够展示MBean
MBean
一个MBean可以代表一个设备,应用或者任何可以被管理的资源。MBeans会暴漏具有如下特性的管理接口:
- 可读可写的属性集合:读对应着 get开头的方法,必须有返回值;写对应着set开头的方法
- 可调用操作的集合:自定义的一下方法
- 一段自我的描述
标准的MBeans
包含两个部分:MBean的接口和它的实现类。命名接口为 xxxMBean 。比如命名为 PaxiMBean,然后用一个java类 Paxi来实现这个接口。
MBean
| package main.jmx; | |
| public interface PaxiMBean { | |
| void sayHi(); | |
| String getName(); | |
| void setName(String name); | |
| } |
Mbean实现
| public class Paxi implements PaxiMBean { | |
| public void sayHi() { | |
| System.out.println("hi"); | |
| } | |
| public String getName() { | |
| return name; | |
| } | |
| public void setName(String name) { | |
| this.name=name; | |
| } | |
| private String name="paxi"; | |
| } |
Agent例子
| package main.jmx; | |
| public class MyAgent { | |
| public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| //1:获取平台已经创建并初始化的MBeanServer,没有就通过MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer()创建 | |
| MBeanServer mbs = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer(); | |
| try { | |
| //2:每个MBean必须有一个object name,name遵照标准格式 | |
| ObjectName name = new ObjectName("main.jmx:type=Paxi"); | |
| Paxi paxi = new Paxi(); | |
| //3:注册MBean | |
| mbs.registerMBean(paxi,name); | |
| System.out.println("wait for incoming request"); | |
| Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE); | |
| } catch (MalformedObjectNameException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (NotCompliantMBeanException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (InstanceAlreadyExistsException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (MBeanRegistrationException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (InterruptedException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
在命令行运行 jconsole,选中MBean,点击左侧栏 main.jmx

得到操作界面
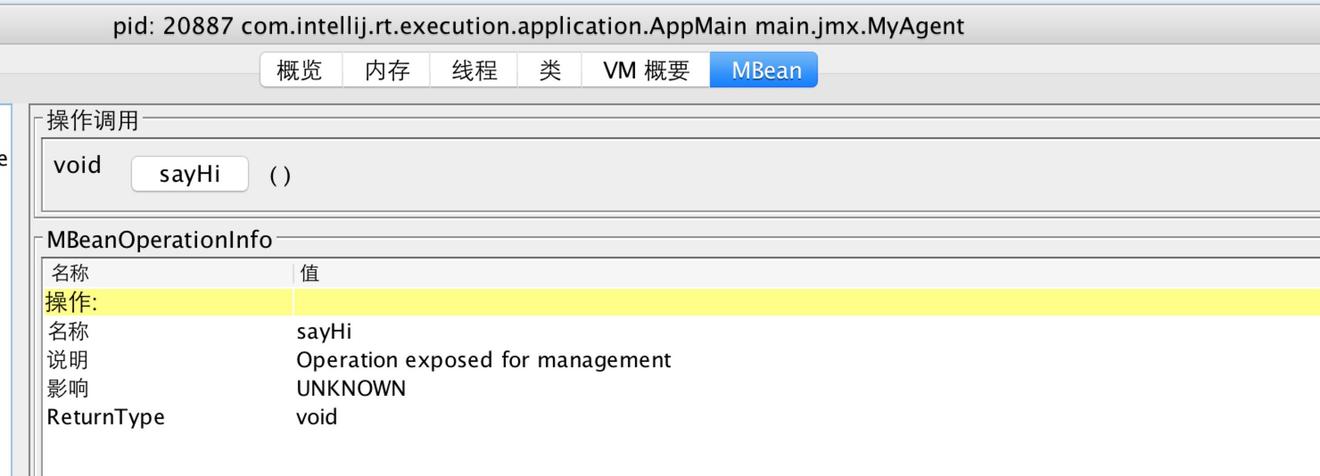
点击sayHi,会弹窗提示调用成功
此时界面上会出现 sayHi的内容
| wait for incoming request | |
| hi |
MXBeans
它是一种MBean的一种,仅用来引用一种预定义的数据类型。它的定义为 方式可以和MBean一样。接口后缀为MXBean然后在实现
| public interface PaxiQMXBean { | |
| PaxiQueue getPaxiQueue(); | |
| void clearQueue(); | |
| } |
或者是使用MXBean的注解
| @MXBean | |
| public interface PaxiQInAnnotation { | |
| PaxiQueue getPaxiQueue(); | |
| void clearQueue(); | |
| } |
实现
| public class PaxiQ implements PaxiQMXBean { | |
| private Queue<String> queue; | |
| public PaxiQ(Queue<String> queue) { | |
| this.queue = queue; | |
| } | |
| @Override | |
| public PaxiQueue getPaxiQueue() { | |
| synchronized (queue){ | |
| return new PaxiQueue(new Date(),queue.size(),queue.peek()); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| @Override | |
| public void clearQueue() { | |
| synchronized (queue){ | |
| queue.clear(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
其中的PaxiQueue是自己定义的一个对象
| public class PaxiQueue { | |
| private final Date date; | |
| private final int size; | |
| private final String head; | |
| ({"date","size","head"}) | |
| public PaxiQueue(Date date, int size, String head) { | |
| this.date = date; | |
| this.size = size; | |
| this.head = head; | |
| } | |
| public Date getDate() { | |
| return date; | |
| } | |
| public String getHead() { | |
| return head; | |
| } | |
| public int getSize() { | |
| return size; | |
| } | |
| } |
Agent的实现为
| public class MyAgent { | |
| public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| //1:获取平台已经创建并初始化的MBeanServer,没有就通过MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer()创建 | |
| MBeanServer mbs = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer(); | |
| try { | |
| ObjectName name = new ObjectName("main.jmx:type=PaxiQ"); | |
| Queue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(10); | |
| queue.add("r-1"); | |
| queue.add("r-2"); | |
| queue.add("r-3"); | |
| PaxiQ mxbean = new PaxiQ(queue); | |
| //3:注册MBean | |
| mbs.registerMBean(mxbean,name); | |
| System.out.println("wait for incoming request"); | |
| Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE); | |
| } catch (MalformedObjectNameException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (NotCompliantMBeanException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (InstanceAlreadyExistsException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (MBeanRegistrationException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (InterruptedException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
启动后运行jconsole
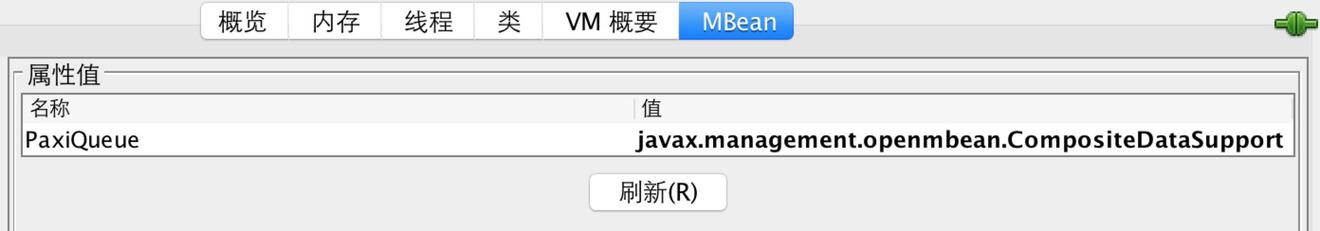
可以看到自定义的属性值为CompositeDataSupport,双击它可以看到等他的内容:
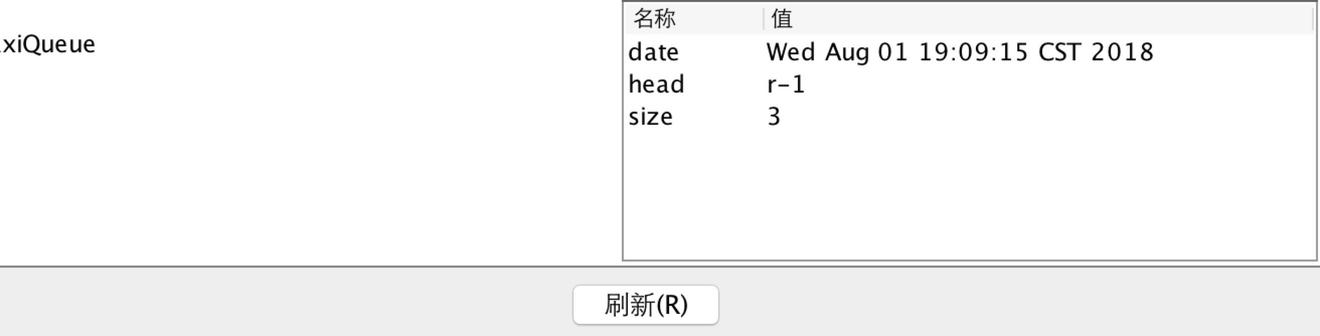
但是如果PaxiQMXBean是一个MBean,即名字是PaxiQMBean,这个时候通过jconsole是无法找到的。
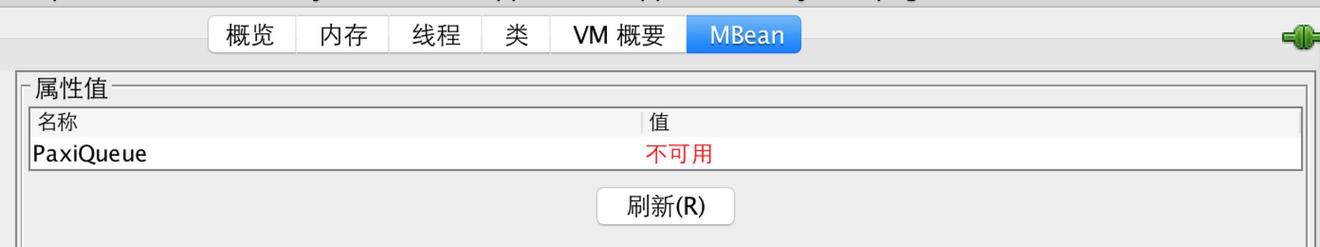
创建一个自己的JMX client
JMX client代码
| public class PaxiClient { | |
| public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| System.out.println("create RMI client"); | |
| try { | |
| JMXServiceURL url = new JMXServiceURL("service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://:9999/jmxrmi"); | |
| JMXConnector jmxConnector = JMXConnectorFactory.connect(url, null); | |
| MBeanServerConnection mBeanServerConnection = jmxConnector.getMBeanServerConnection(); | |
| System.out.println("domains"); | |
| String[] domains= mBeanServerConnection.getDomains(); | |
| Arrays.sort(domains); | |
| for (String domain:domains){ | |
| System.out.println(domain); | |
| } | |
| System.out.println("domain:"+mBeanServerConnection.getDefaultDomain()); | |
| System.out.println("MBean count:"+mBeanServerConnection.getMBeanCount()); | |
| Set<ObjectName> names = new TreeSet<ObjectName>(mBeanServerConnection.queryNames(null,null)); | |
| for (ObjectName name:names){ | |
| System.out.println("objectname:"+name); | |
| } | |
| ObjectName mbeanName = new ObjectName("main.jmx:type=Paxi"); | |
| PaxiMBean mbeanProxy = JMX.newMBeanProxy(mBeanServerConnection,mbeanName,PaxiMBean.class,true); | |
| System.out.println("add notification listener.."); | |
| // 自定义消息的监听 | |
| PaxiClientListener listener = new PaxiClientListener(); | |
| mBeanServerConnection.addNotificationListener(mbeanName,listener,null,null); | |
| mbeanProxy.setName("new name"); | |
| System.out.println("wait notifacaion"); | |
| TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); | |
| System.out.println(mbeanProxy.getName()); | |
| mbeanProxy.sayHi(); | |
| TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); | |
| jmxConnector.close(); | |
| } catch (MalformedURLException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (IOException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (MalformedObjectNameException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (InstanceNotFoundException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } catch (InterruptedException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
listener
| public class PaxiClientListener implements NotificationListener{ | |
| @Override | |
| public void handleNotification(Notification notification, Object handback) { | |
| System.out.println("r notification"); | |
| System.out.println("class:"+notification.getClass().getName()); | |
| System.out.println("Source:"+notification.getSource()); | |
| System.out.println("Type:"+notification.getType()); | |
| System.out.println("Message:"+notification.getMessage()); | |
| if (notification instanceof AttributeChangeNotification){ | |
| AttributeChangeNotification n= (AttributeChangeNotification) notification; | |
| System.out.println("attr name:"+n.getAttributeName()); | |
| System.out.println("attr type:"+n.getAttributeType()); | |
| System.out.println("attr new Value:"+n.getNewValue()); | |
| System.out.println("attr old Value:"+n.getOldValue()); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |