背景
如果想在 Java 进程退出时,包括正常和异常退出,做一些额外处理工作,例如资源清理,对象销毁,内存数据持久化到磁盘,等待 线程池 处理完所有任务等等。特别是进程异常挂掉的情况,如果一些重要状态没及时保留下来,或线程池的任务没被处理完,有可能会造成严重问题。那该怎么办呢?
Java 中的 Shutdown Hook 提供了比较好的方案。我们可以通过 Java.Runtime.addShutdownHook(Thread hook) 方法向 JVM 注册关闭钩子,在 JVM 退出之前会自动调用执行钩子方法,做一些结尾操作,从而让进程平滑优雅地退出,保证了业务的完整性。
Shutdown Hook 介绍
其实, shutdown hook 就是一个简单的 已初始化 但是 未启动 的 线程 。当虚拟机开始关闭时,它将会调用所有已注册的钩子,这些钩子执行是并发的,执行顺序是不确定的。
在 虚拟机 关闭的过程中,还可以继续注册新的钩子,或者撤销已经注册过的钩子。不过有可能会抛出 IllegalStateException 。注册和注销钩子的方法定义如下:
| public void add shutdown Hook(Thread hook) { | |
| // 省略 | |
| } | |
| public void removeShutdownHook(Thread hook) { | |
| // 省略 | |
| } |
关闭钩子被调用场景
关闭钩子可以在以下几种场景被调用:
- 程序正常退出
- 程序调用 System.exit() 退出
- 终端使用 Ctrl+C 中断程序
- 程序抛出异常导致程序退出,例如 OOM,数组越界等异常
- 系统事件,例如用户注销或关闭系统
- 使用 Kill pid 命令杀掉进程,注意使用 kill -9 pid 强制杀掉不会触发执行钩子
验证程序正常退出情况
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法..."))); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| Thread .sleep(2000); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 程序即将退出... | |
| 执行钩子方法... | |
| Process finished with exit code |
验证程序调用 System.exit() 退出情况
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法..."))); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| System.exit(-); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 执行钩子方法... | |
| Process finished with exit code - |
验证终端使用 Ctrl+C 中断程序,在命令行窗口中运行程序,然后使用 Ctrl+C 中断
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法..."))); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| D:IdeaProjectsjava-demojava ShutdownHookDemo | |
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 执行钩子方法... |
演示抛出异常导致程序异常退出
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法..."))); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| int a =; | |
| System.out.println( / a); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 执行钩子方法... | |
| Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero | |
| at com.chenpi.ShutdownHookDemo.main(ShutdownHookDemo.java:) | |
| Process finished with exit code |
至于系统被关闭,或者使用 Kill pid 命令杀掉进程就不演示了,感兴趣的可以自行验证。
注意事项
可以向虚拟机注册多个关闭钩子,但是注意这些钩子执行是并发的,执行顺序是不确定的。
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法A..."))); | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法B..."))); | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法C..."))); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 程序即将退出... | |
| 执行钩子方法B... | |
| 执行钩子方法C... | |
| 执行钩子方法A... |
向虚拟机注册的钩子方法需要尽快执行结束,尽量不要执行长时间的操作,例如 I/O 等可能被阻塞的操作, 死锁 等,这样就会导致程序短时间不能被关闭,甚至一直关闭不了。我们也可以引入超时机制强制退出钩子,让程序正常结束。
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> { | |
| // 模拟长时间的操作 | |
| try { | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| } catch (InterruptedException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| })); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
以上的钩子执行时间比较长,最终会导致程序在等待很长时间之后才能被关闭。
如果 JVM 已经调用执行关闭钩子的过程中,不允许注册新的钩子和注销已经注册的钩子,否则会报 IllegalStateException 异常。通过源码分析,JVM 调用钩子的时候,即调用 ApplicationShutdownHooks#runHooks() 方法,会将所有钩子从变量 hooks 取出,然后将此变量置为 null 。
| // 调用执行钩子 | |
| static void runHooks() { | |
| Collection<Thread> threads; | |
| synchronized(ApplicationShutdownHooks.class) { | |
| threads = hooks.keySet(); | |
| hooks = null; | |
| } | |
| for (Thread hook : threads) { | |
| hook.start(); | |
| } | |
| for (Thread hook : threads) { | |
| try { | |
| hook.join(); | |
| } catch (InterruptedException x) { } | |
| } | |
| } |
在注册和注销钩子的方法中,首先会判断 hooks 变量是否为 null ,如果为 null 则抛出异常。
| // 注册钩子 | |
| static synchronized void add(Thread hook) { | |
| if(hooks == null) | |
| throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress"); | |
| if (hook.isAlive()) | |
| throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook already running"); | |
| if (hooks.containsKey(hook)) | |
| throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook previously registered"); | |
| hooks.put(hook, hook); | |
| } | |
| // 注销钩子 | |
| static synchronized boolean remove(Thread hook) { | |
| if(hooks == null) | |
| throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress"); | |
| if (hook == null) | |
| throw new NullPointerException(); | |
| return hooks.remove(hook) != null; | |
| } |
我们演示下这种情况
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> { | |
| System.out.println("执行钩子方法..."); | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread( | |
| () -> System.out.println("在JVM调用钩子的过程中再新注册钩子,会报错IllegalStateException"))); | |
| // 在JVM调用钩子的过程中注销钩子,会报错IllegalStateException | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(Thread.currentThread()); | |
| })); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 程序即将退出... | |
| 执行钩子方法... | |
| Exception in thread "Thread-" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Shutdown in progress | |
| at java.lang.ApplicationShutdownHooks.add(ApplicationShutdownHooks.java:) | |
| at java.lang.Runtime.addShutdownHook(Runtime.java:) | |
| at com.chenpi.ShutdownHookDemo.lambda$static$(ShutdownHookDemo.java:8) | |
| at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:) |
如果调用 Runtime.getRuntime().halt() 方法停止 JVM,那么虚拟机是不会调用钩子的。
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("执行钩子方法..."))); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().halt(); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 程序即将退出... | |
| Process finished with exit code |
如果要想终止执行中的钩子方法,只能通过调用 Runtime.getRuntime().halt() 方法,强制让程序退出。在Linux环境中使用 kill -9 pid 命令也是可以强制终止退出。
| package com.chenpi; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> { | |
| System.out.println("开始执行钩子方法..."); | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().halt(-); | |
| System.out.println("结束执行钩子方法..."); | |
| })); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| System.out.println("程序即将退出..."); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果
| 程序开始启动... | |
| 程序即将退出... | |
| 开始执行钩子方法... | |
| Process finished with exit code - |
如果程序使用 Java Security Managers ,使用 shutdown Hook 则需要安全权限 RuntimePermission(“shutdownHooks”) ,否则会导致 SecurityException 。
实践
例如,我们程序自定义了一个线程池,用来接收和处理任务。如果程序突然崩溃异常退出,这时线程池的所有任务有可能还未处理完成,如果不处理完程序就直接退出,可能会导致数据丢失,业务异常等重要问题。这时钩子就派上用场了。
| import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; | |
| import java.util.concurrent.Executors; | |
| import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; | |
| public class ShutdownHookDemo { | |
| // 线程池 | |
| private static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(); | |
| static { | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> { | |
| System.out.println("开始执行钩子方法..."); | |
| // 关闭线程池 | |
| executorService.shutdown(); | |
| try { | |
| // 等待秒 | |
| System.out.println(executorService.awaitTermination(, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); | |
| } catch (InterruptedException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| System.out.println("结束执行钩子方法..."); | |
| })); | |
| } | |
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |
| System.out.println("程序开始启动..."); | |
| // 向线程池添加个任务 | |
| for (int i =; i < 10; i++) { | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| final int finalI = i; | |
| executorService.execute(() -> { | |
| try { | |
| Thread.sleep(); | |
| } catch (InterruptedException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| System.out.println("Task " + finalI + " execute..."); | |
| }); | |
| System.out.println("Task " + finalI + " is in thread pool..."); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
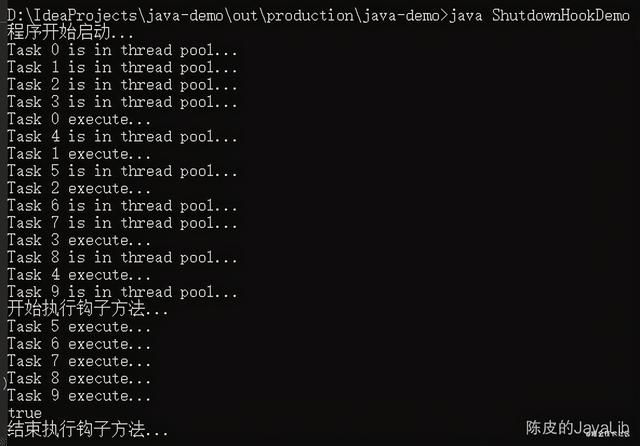
在命令行窗口中运行程序,在10个任务都提交到线程池之后,任务都还未处理完成之前,使用 Ctrl+C 中断程序,最终在虚拟机关闭之前,调用了关闭钩子,关闭线程池,并且等待60秒让所有任务执行完成。
Shutdown Hook 在 Spring 中的运用
Shutdown Hook 在 Spring 中是如何运用的呢。通过源码分析,Springboot 项目启动时会判断 registerShutdownHook 的值是否为 true,默认是 true,如果为真则向虚拟机注册关闭钩子。
| private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { | |
| refresh(context); | |
| if (this.registerShutdownHook) { | |
| try { | |
| context.registerShutdownHook(); | |
| } | |
| catch (AccessControlException ex) { | |
| // Not allowed in some environments. | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| @ Override | |
| public void registerShutdownHook() { | |
| if (this.shutdownHook == null) { | |
| // No shutdown hook registered yet. | |
| this.shutdownHook = new Thread() { | |
| public void run() { | |
| synchronized (startupShutdownMonitor) { | |
| // 钩子方法 | |
| doClose(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }; | |
| // 底层还是使用此方法注册钩子 | |
| Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook); | |
| } | |
| } |
在关闭钩子的方法 doClose 中,会做一些虚拟机关闭前处理工作,例如销毁容器里所有单例 Bean,关闭 BeanFactory,发布关闭事件等等。
| protected void doClose() { | |
| // Check whether an actual close attempt is necessary... | |
| if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) { | |
| if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { | |
| logger.debug("Closing " + this); | |
| } | |
| LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this); | |
| try { | |
| // 发布Spring 应用上下文的关闭事件,让监听器在应用关闭之前做出响应处理 | |
| publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this)); | |
| } | |
| catch (Throwable ex) { | |
| logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex); | |
| } | |
| // Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction. | |
| if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) { | |
| try { | |
| // 执行lifecycleProcessor的关闭方法 | |
| this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose(); | |
| } | |
| catch (Throwable ex) { | |
| logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| // 销毁容器里所有单例Bean | |
| destroyBeans(); | |
| // 关闭BeanFactory | |
| closeBeanFactory(); | |
| // Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish... | |
| onClose(); | |
| // Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state. | |
| if (this.earlyApplicationListeners != null) { | |
| this.applicationListeners.clear(); | |
| this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners); | |
| } | |
| // Switch to inactive. | |
| this.active.set(false); | |
| } | |
| } |
我们知道,我们可以定义 bean 并且实现 DisposableBean 接口,重写 destroy 对象销毁方法。destroy 方法就是在 Spring 注册的关闭钩子里被调用的。例如我们使用 Spring 框架的 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 线程池内,它就实现了 DisposableBean 接口,重写了 destroy 方法,从而在程序退出前,进行线程池销毁工作。源码如下:
| public void destroy() { | |
| shutdown(); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * Perform a shutdown on the underlying ExecutorService. | |
| * @see java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService#shutdown() | |
| * @see java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService#shutdownNow() | |
| */public void shutdown() { | |
| if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { | |
| logger.info("Shutting down ExecutorService" + (this.beanName != null ? " '" + this.beanName + "'" : "")); | |
| } | |
| if (this.executor != null) { | |
| if (this.waitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown) { | |
| this.executor.shutdown(); | |
| } | |
| else { | |
| for (Runnable remainingTask : this.executor.shutdownNow()) { | |
| cancelRemainingTask(remainingTask); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| awaitTerminationIfNecessary(this.executor); | |
| } | |
| } |