一、需求场景
在常见的业务中,比如我们要记录一个接口的最终处理结果记录到日志里,使用event就可以把记录日志的业务逻辑放在一个处理方法中,使得代码中的业务逻辑更明确。
二、配置监听
监听配置文件:app\EventServiceProvider.php
| namespace App\Providers; | |
| use Illuminate\Auth\Events\Registered; | |
| use Illuminate\Auth\Listeners\SendEmailVerificationNotification; | |
| use Illuminate\Foundation\Support\Providers\EventServiceProvider as ServiceProvider; | |
| use App\Events\TestEvent; | |
| class EventServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider | |
| { | |
| /** | |
| * The event listener mappings for the application. | |
| * | |
| * @var array | |
| */ | |
| protected $listen = [ | |
| // Registered::class => [ | |
| // SendEmailVerificationNotification::class, | |
| // ], | |
| 'App\Events\SendEvent' => [ | |
| // 'App\Listeners\PayEventListener', | |
| 'App\Listeners\SendEventListener', | |
| ], | |
| ]; | |
| /** | |
| * Register any events for your application. | |
| * | |
| * @return void | |
| */ | |
| public function boot() | |
| { | |
| parent::boot(); | |
| // | |
| } | |
| } |
其中,$listen属性中:
App\Events\ArticleEvent:是在App\Events目录下新建一个事件(ArticleEvent.php),控制器等的业务逻辑中实例化的是该文件。App\Listeners\PayEventListener:是在App\Listeners目录下新建一个监听器(PayEventListener.php)
注意:单个事件可以配置多个监听器(处理业务逻辑,如发送邮件,发送短信)。
配置多个监听器的写法:
| protected $listen = [ | |
| 'App\Events\SendEvent' => [ | |
| 'App\Listeners\SendEventListener', | |
| 'App\Listeners\PayEventListener', | |
| ], | |
| ]; |
表明一个调用ArticleEvent事件,会执行两个监听器。如果有多个监听器,会按照上方代码快中的数组下标依次进行处理。
三、生成事件及监听文件
执行命令:php artisan event:generate
会在Events目录下生成SendEvent.php,在Listenters目录下生成SendEventListener.php两个文件。
在SendEvent.php(事件)中,用来接收调用端传过来的参数。
| namespace App\Events; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\Channel; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\InteractsWithSockets; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\PresenceChannel; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\PrivateChannel; | |
| use Illuminate\Contracts\Broadcasting\ShouldBroadcast; | |
| use Illuminate\Foundation\Events\Dispatchable; | |
| use Illuminate\Queue\SerializesModels; | |
| use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log; | |
| class SendEvent | |
| { | |
| use Dispatchable, InteractsWithSockets, SerializesModels; | |
| /** | |
| * Create a new event instance. | |
| * | |
| * @return void | |
| */ | |
| public function __construct() | |
| { | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * Get the channels the event should broadcast on. | |
| * | |
| * @return \Illuminate\Broadcasting\Channel|array | |
| */ | |
| public function broadcastOn() | |
| { | |
| return new PrivateChannel('channel-name'); | |
| } | |
| } |
可以定义一个属性:
| namespace App\Events; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\Channel; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\InteractsWithSockets; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\PresenceChannel; | |
| use Illuminate\Broadcasting\PrivateChannel; | |
| use Illuminate\Contracts\Broadcasting\ShouldBroadcast; | |
| use Illuminate\Foundation\Events\Dispatchable; | |
| use Illuminate\Queue\SerializesModels; | |
| use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log; | |
| class SendEvent | |
| { | |
| use Dispatchable, InteractsWithSockets, SerializesModels; | |
| public $name; | |
| /** | |
| * Create a new event instance. | |
| * | |
| * @param $username | |
| */ | |
| public function __construct($username) | |
| { | |
| $this->name = $username; | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * Get the channels the event should broadcast on. | |
| * | |
| * @return \Illuminate\Broadcasting\Channel|array | |
| */ | |
| public function broadcastOn() | |
| { | |
| return new PrivateChannel('channel-name'); | |
| } | |
| } |
在SendEventListener.php(监听器)中,可以通过$event->name来接收参数,从而进行相应的业务逻辑处理:
| namespace App\Listeners; | |
| use App\Events\SendEvent; | |
| use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue; | |
| use Illuminate\Queue\InteractsWithQueue; | |
| use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log; | |
| class SendEventListener | |
| { | |
| /** | |
| * Create the event listener. | |
| * | |
| * @return void | |
| */ | |
| public function __construct() | |
| { | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * Handle the event. | |
| * | |
| * @param SendEvent $event | |
| * @return void | |
| */ | |
| public function handle(SendEvent $event) | |
| { | |
| echo $event->name; | |
| Log::info('事件1监听测试'.date('Y-m-d H:i:s')); | |
| } | |
| } |
四、调用事件
在控制器中,直接实例化事件类就行,也可以传相应的参数。:
| public function testEvent(){ | |
| // Log::info(date('Y-m-d H:i:s').'我进来了'); | |
| $username = '写代码的光头强'; | |
| event(new SendEvent()); | |
| // Log::info(date('Y-m-d H:i:s').'我结束了'); | |
| } |
至此,简单的event事件调用就实现了。以上都是带代码同步进行的。
同步执行顺序:控制器——事件——监听器1——监听器2——控制器结束
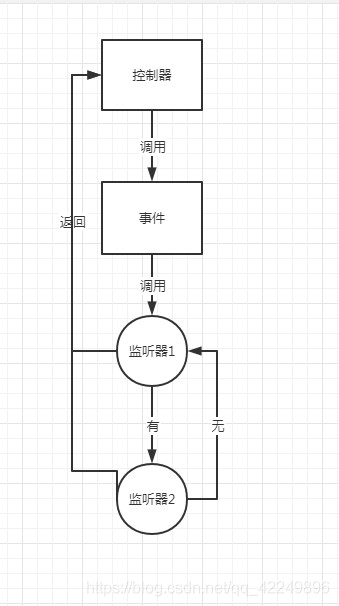
如果使用异步,可以配合着队列来用。
end~