目录
- 应用场景
- 效果预览
- 思路剖析
- 原生代码实现
- 迁移到React
- 总结
应用场景
懒加载列表或叫做无限滚动列表,也是一种性能优化的方式,其可疑不必一次性请求所有数据,可以看做是分页的另一种实现形式,较多适用于移动端提升用户体验,新闻、资讯浏览等。
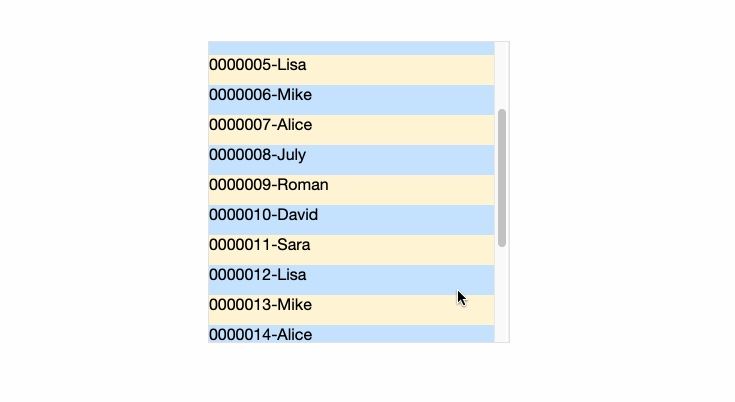
效果预览
思路剖析
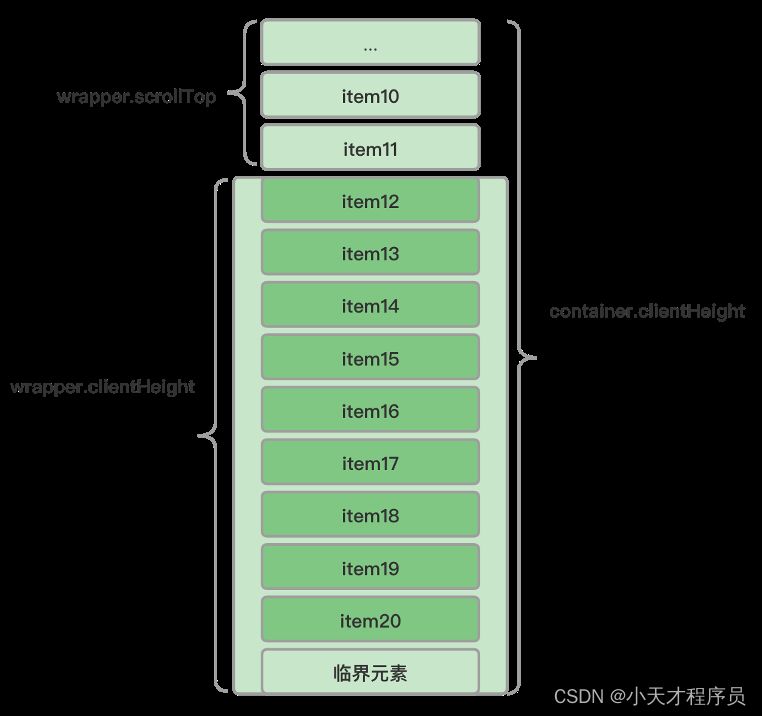
- 设置临界元素,当临界元素进入可视范围时请求并追加新数据。
- 根据可视窗口和滚动元素组建的关系确定数据加载时机。
container.clientHeight - wrapper.scrollTop <= wrapper.clientHeight
原生代码实现
index.html
| <body> | |
| <div id="wrapper" onscroll="handleScroll()"> | |
| <ul id="container"></ul> | |
| </div> | |
| <script type="text/javascript" src="./index.js"></script> | |
| </body> |
index.css
| * { | |
| margin:; | |
| padding:; | |
| } | |
| #wrapper { | |
| margin:px auto; | |
| width:px; | |
| height:px; | |
| border:px solid rgba(100, 100, 100, 0.2); | |
| overflow-y: scroll; | |
| } | |
| ul#container { | |
| list-style: none; | |
| padding:; | |
| width:%; | |
| } | |
| ul#container > li { | |
| height:px; | |
| width:%; | |
| } | |
| ul#container > li.green-item { | |
| background-color: #ce3ff; | |
| } | |
| ul#container > li.red-item { | |
| background-color: #fffd5; | |
| } |
index.js
| // 模拟数据构造 | |
| const arr = []; | |
| const nameArr = ['Alice', 'July', 'Roman', 'David', 'Sara', 'Lisa', 'Mike']; | |
| let curPage =; | |
| let noData = false; | |
| const curPageSize =; | |
| const getPageData = (page, pageSize) => { | |
| if (page >) return []; | |
| const arr = []; | |
| // const nameArr = ['Alice', 'July', 'Roman', 'David', 'Sara', 'Lisa', 'Mike']; | |
| for (let i =; i < pageSize; i++) { | |
| arr.push({ | |
| number: i + (page -) * pageSize, | |
| name: `${nameArr[i % nameArr.length]}`, | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| return arr; | |
| }; | |
| const wrapper = document.getElementById('wrapper'); | |
| const container = document.getElementById('container'); | |
| let plainWrapper = null; | |
| /** | |
| * @method handleScroll | |
| * @description: 滚动事件监听 | |
| */ | |
| const handleScroll = () => { | |
| // 当临界元素进入可视范围时,加载下一页数据 | |
| if ( | |
| !noData && | |
| container.clientHeight - wrapper.scrollTop <= wrapper.clientHeight | |
| ) { | |
| curPage++; | |
| console.log(curPage); | |
| const newData = getPageData(curPage, curPageSize); | |
| renderList(newData); | |
| } | |
| }; | |
| /** | |
| * @description: 列表渲染 | |
| * @param {Array} data | |
| */ | |
| const renderList = (data) => { | |
| // 没有更多数据时 | |
| if (!data.length) { | |
| noData = true; | |
| plainWrapper.innerText = 'no more data...'; | |
| return; | |
| } | |
| plainWrapper && container.removeChild(plainWrapper); //移除上一个临界元素 | |
| const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment(); | |
| data.forEach((item) => { | |
| const li = document.createElement('li'); | |
| li.className = item.number % === 0 ? 'green-item' : 'red-item'; //奇偶行元素不同色 | |
| const text = document.createTextNode( | |
| `${`${item.number}`.padStart(, '0')}-${item.name}` | |
| ); | |
| li.appendChild(text); | |
| fragment.appendChild(li); | |
| }); | |
| const plainNode = document.createElement('li'); | |
| const text = document.createTextNode('scroll to load more...'); | |
| plainNode.appendChild(text); | |
| plainWrapper = plainNode; | |
| fragment.appendChild(plainNode); //添加新的临界元素 | |
| container.appendChild(fragment); | |
| }; | |
| // 初始渲染 | |
| renderList(getPageData(curPage, curPageSize)); |
迁移到React
在 React 中实现时可以省去复杂的手动渲染逻辑部分,更关注数据。
store/data.ts
| import { IDataItem } from '../interface'; | |
| const nameArr = ['Alice', 'July', 'Roman', 'David', 'Sara', 'Lisa', 'Mike']; | |
| export const getPageData = ( | |
| page: number =, | |
| pageSize: number = | |
| ): Array<IDataItem> => { | |
| if (page >) return []; | |
| const arr = []; | |
| // const nameArr = ['Alice', 'July', 'Roman', 'David', 'Sara', 'Lisa', 'Mike']; | |
| for (let i =; i < pageSize; i++) { | |
| arr.push({ | |
| number: i + (page -) * pageSize, | |
| name: `${nameArr[i % nameArr.length]}`, | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| return arr; | |
| }; |
LazyList.tsx
| /* | |
| * @Description: 懒加载列表(无限滚动列表) | |
| * @Date:-12-20 15:12:15 | |
| * @LastEditTime:-12-20 16:04:18 | |
| */ | |
| import React, { FC, useCallback, useEffect, useReducer, useRef } from 'react'; | |
| import { getPageData } from './store/data'; | |
| import { IDataItem } from './interface'; | |
| import styles from './index.module.css'; | |
| export interface IProps { | |
| curPageSize?: number; | |
| } | |
| export interface IState { | |
| curPage: number; | |
| noData: boolean; | |
| listData: Array<IDataItem>; | |
| } | |
| const LazyList: FC<IProps> = ({ curPageSize = }: IProps) => { | |
| const clientRef: any = useRef(null); | |
| const scrollRef: any = useRef(null); | |
| const [state, dispatch] = useReducer( | |
| (state: IState, action: any): IState => { | |
| switch (action.type) { | |
| case 'APPEND': | |
| return { | |
| ...state, | |
| listData: [...state.listData, ...action.payload.listData], | |
| }; | |
| default: | |
| return { ...state, ...action.payload }; | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| { | |
| curPage:, | |
| noData: false, | |
| listData: [], | |
| } | |
| ); | |
| /** | |
| * @method handleScroll | |
| * @description: 滚动事件监听 | |
| */ | |
| const handleScroll = useCallback(() => { | |
| const { clientHeight: wrapperHeight } = scrollRef.current; | |
| const { scrollTop, clientHeight } = clientRef.current; | |
| // 当临界元素进入可视范围时,加载下一页数据 | |
| if (!state.noData && wrapperHeight - scrollTop <= clientHeight) { | |
| console.log(state.curPage); | |
| const newData = getPageData(state.curPage, curPageSize); | |
| dispatch({ | |
| type: 'APPEND', | |
| payload: { listData: newData }, | |
| }); | |
| dispatch({ | |
| payload: { | |
| curPage: state.curPage +, | |
| noData: !(newData.length >), | |
| }, | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| }, [state.curPage, state.noData]); | |
| useEffect(() => { | |
| const newData = getPageData(, curPageSize); | |
| dispatch({ | |
| type: 'APPEND', | |
| payload: { listData: newData }, | |
| }); | |
| dispatch({ | |
| payload: { | |
| curPage:, | |
| noData: !(newData.length >), | |
| }, | |
| }); | |
| }, []); | |
| return ( | |
| <div className={styles[`wrapper`]} ref={clientRef} onScroll={handleScroll}> | |
| <ul className={styles[`container`]} ref={scrollRef}> | |
| {state.listData.map(({ number, name }) => ( | |
| <li | |
| key={number} | |
| className={ | |
| number % === 0 ? styles[`green-item`] : styles[`red-item`] | |
| } | |
| > | |
| {number}-{name} | |
| </li> | |
| ))} | |
| {<li>{state.noData ? 'no more' : 'scroll'}</li>} | |
| </ul> | |
| </div> | |
| ); | |
| }; | |
| export default LazyList; |