目录
- 一、Props 是什么
- 二、props children模式
- 1. props 插槽组件
- 2. render props模式
- 3. render props模式
- 三、进阶实践
一、Props 是什么
先来看一个 demo :
function Chidren(){
return <div> 我是子组件 </div>
}
/* props 接受处理 */
function Father(props) {
const { children , mes , renderName , say ,Component } = props
const renderFunction = children[0]
const renderComponent = children[1]
/* 对于子组件,不同的props是怎么被处理 */
return (
<div>
{ renderFunction() }
{ mes }
{ renderName() }
{ renderComponent }
<Component />
<button onClick={ () => say() } > 触发更改 </button>
</div> )
}
/* props 定义绑定 */
class App extends React.Component{
state={
mes: "hello,React"
}
node = null
say= () => this.setState({ mes:'let us learn React!' })
render(){
return <div>
<Father
mes={this.state.mes} // ① props 作为一个渲染数据源
say={ this.say } // ② props 作为一个回调函数 callback
Component={ Chidren } // ③ props 作为一个组件
renderName={ ()=><div> my name is YinJie </div> } // ④ props 作为渲染函数
>
{ ()=> <div>hello,world</div> } { /* ⑤render props */ }
<Chidren /> { /* ⑥render component */ }
</Father>
</div>
}
}
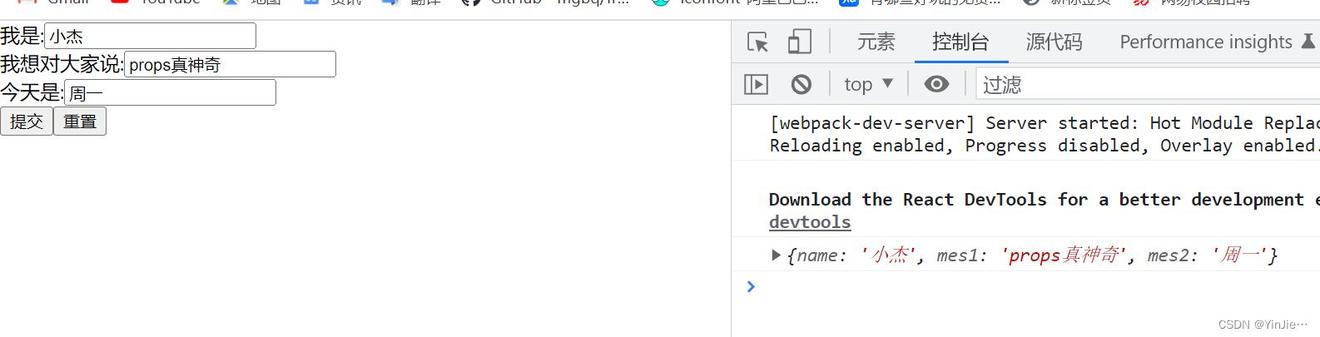
我们看一下输出结果:

当点击触发更改时就能够调用回调更改数据源:

所以 props 可以是:
① props 作为一个子组件渲染数据源。
② props 作为一个通知父组件的回调函数。
③ props 作为一个单纯的组件传递。
④ props 作为渲染函数。
⑤ render props , 和④的区别是放在了 children 属性上。
⑥ render component 插槽组件。
二、props children模式
我们先来看看 prop + children 的几个基本情况:
1. props 插槽组件
<Container>
<Children>
</Container>
上述可以在 Container 组件中,通过 props.children 属性访问到 Children 组件,为 React element 对象。
作用:
- 可以根据需要控制 Children 是否渲染。
- 像上一节所说的, Container 可以用 React.cloneElement 强化 props (混入新的 props ),或者修改 Children 的子元素。
举一个用React.cloneElement 强化 props 的例子,多用于编写组件时对子组件混入新的 props,下面我们要做一个导航组件,我们希望它的结构如下:
<Menu>
<MenuItem >
active
</MenuItem>
<MenuItem>
disabled
</MenuItem>
<MenuItem >
xyz
</MenuItem>
</Menu>
我们想给每个 MenuItem 子组件都添加 index 属性,这个事情不应该让用户手动添加,最好是可以在 Menu 组件中自动为每个 MenuItem 子组件添加上,并且 Menu 组件还应该判断子组件的类型,如果子组件的类型不是 MenuItem 组件就报错。
Menu.tsx:
const Menu: React.FC<MenuProps> = (props) => {
// ... 一些操作
const renderChildren = () => { // 让子级的children都是 menuItem,有不是的就报错
return React.Children.map(children, (child, index) => {
const childElement = child as React.FunctionComponentElement<MenuItemProps>
const { displayName } = childElement.type
if(displayName === 'MenuItem' || displayName === "SubMenu") {
return React.cloneElement(childElement, { index: index.toString() })
} else {
console.error('warning: Menu has a child whitch is not a MenuItem')
}
})
}
return (
<ul className={classes} style={style} data-testid="test-menu">
<MenuContext.Provider value={passedContext}>
{renderChildren()}
</MenuContext.Provider>
</ul>
)
}
在 Menu 组件中我们通过 React.children.map 来循环子组件,通过 child.type 可以获取到每个子组件的 displayName 静态属性,这个在子组件中有定义:
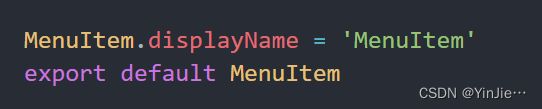
通过子组件的 displayName 来判断是否是我们需要的 MenuItem,如果是的话就调用 React.cloneElement 来为子组件添加 index 属性。
2. render props模式
<Container>
{ (ContainerProps)=> <Children {...ContainerProps} /> }
</Container>
这种情况,在 Container 中, props.children 属性访问到是函数,并不是 React element 对象,我们应该调用这个函数:
function Container(props) {
const ContainerProps = {
name: 'alien',
mes:'let us learn react'
}
return props.children(ContainerProps)
}
这种方式作用是:
1 根据需要控制 Children 渲染与否。
2 可以将需要传给 Children 的 props 直接通过函数参数的方式传递给执行函数 children 。
3. render props模式
如果 Container 的 Children 既有函数也有组件,这种情况应该怎么处理呢?
<Container>
<Children />
{ (ContainerProps)=> <Children {...ContainerProps} name={'haha'} /> }
</Container>
const Children = (props)=> (<div>
<div>hello, my name is { props.name } </div>
<div> { props.mes } </div>
</div>)
function Container(props) {
const ContainerProps = {
name: 'alien',
mes:'let us learn react'
}
return props.children.map(item=>{
if(React.isValidElement(item)){ // 判断是 react elment 混入 props
return React.cloneElement(item,{ ...ContainerProps },item.props.children)
}else if(typeof item === 'function'){
return item(ContainerProps)
}else return null
})
}
const Index = ()=>{
return <Container>
<Children />
{ (ContainerProps)=> <Children {...ContainerProps} name={'haha'} /> }
</Container>
}
这种情况需要先遍历 children ,判断 children 元素类型:
- 针对 element 节点,通过 cloneElement 混入 props ;
- 针对函数,直接传递参数,执行函数。
三、进阶实践
实现一个简单的<Form> <FormItem>嵌套组件
接下来到实践环节了。需要编写一个实践 demo ,用于表单状态管理的<Form>和<FormItem>组件
<Form>用于管理表单状态;<FormItem>用于管理<Input>输入框组件。,
编写的组件能够实现的功能是:
①Form组件可以被 ref 获取实例。然后可以调用实例方法submitForm获取表单内容,用于提交表单,resetForm方法用于重置表单。
②Form组件自动过滤掉除了FormItem之外的其他React元素
③FormItem中 name 属性作为表单提交时候的 key ,还有展示的 label 。
④FormItem可以自动收集<Input/>表单的值。
App.js:
import React, { useState, useRef } from "react";
import Form from './Form'
import FormItem from './FormItem'
import Input from './Input'
function App () {
const form = useRef(null)
const submit =()=>{
/* 表单提交 */
form.current.submitForm((formValue)=>{ // 调用 form 中的submitForm方法
console.log(formValue)
})
}
const reset = ()=>{
/* 表单重置 */
form.current.resetForm() //调用 form 中的 resetForm 方法
}
return <div className='box' >
<Form ref={ form } >
<FormItem name="name" label="我是" >
<Input />
</FormItem>
<FormItem name="mes" label="我想对大家说" >
<Input />
</FormItem>
<FormItem name="lees" label="ttt" >
<Input />
</FormItem>
</Form>
<div className="btns" >
<button className="searchbtn" onClick={ submit } >提交</button>
<button className="concellbtn" onClick={ reset } >重置</button>
</div>
</div>
}
export default App
Form.js:
class Form extends React.Component{
state={
formData:{}
}
/* 用于提交表单数据 */
submitForm=(cb)=>{
cb({ ...this.state.formData })
}
/* 获取重置表单数据 */
resetForm=()=>{
const { formData } = this.state
Object.keys(formData).forEach(item=>{
formData[item] = ''
})
this.setState({
formData
})
}
/* 设置表单数据层 */
setValue=(name,value)=>{
this.setState({
formData:{
...this.state.formData,
[name]:value
}
})
}
render(){
const { children } = this.props
const renderChildren = []
React.Children.forEach(children,(child)=>{
if(child.type.displayName === 'formItem'){
const { name } = child.props
/* 克隆`FormItem`节点,混入改变表单单元项的方法 */
const Children = React.cloneElement(child,{
key:name , /* 加入key 提升渲染效果 */
handleChange:this.setValue , /* 用于改变 value */
value:this.state.formData[name] || '' /* value 值 */
},child.props.children)
renderChildren.push(Children)
}
})
return renderChildren
}
}
/* 增加组件类型type */
Form.displayName = 'form'
设计思想:
- 首先考虑到
<Form>在不使用forwardRef前提下,最好是类组件,因为只有类组件才能获取实例。 - 创建一个 state 下的 formData属性,用于收集表单状态。
- 要封装重置表单,提交表单,改变表单单元项的方法。
- 要过滤掉除了
FormItem元素之外的其他元素,那么怎么样知道它是不是FormItem,这里教大家一种方法,可以给函数组件或者类组件绑定静态属性来证明它的身份,然后在遍历 props.children 的时候就可以在 React element 的 type 属性(类或函数组件本身)上,验证这个身份,在这个 demo 项目,给函数绑定的 displayName 属性,证明组件身份。 - 要克隆
FormItem节点,将改变表单单元项的方法 handleChange 和表单的值 value 混入 props 中。
FormItem.js:
function FormItem(props){
const { children , name , handleChange , value , label } = props
const onChange = (value) => {
/* 通知上一次value 已经改变 */
handleChange(name,value)
}
return <div className='form' >
<span className="label" >{ label }:</span>
{
React.isValidElement(children) && children.type.displayName === 'input'
? React.cloneElement(children,{ onChange , value })
: null
}
</div>
}
FormItem.displayName = 'formItem'
设计思想:
FormItem一定要绑定 displayName 属性,用于让<Form>识别<FormItem />- 声明
onChange方法,通过 props 提供给<Input>,作为改变 value 的回调函数。 FormItem过滤掉除了input以外的其他元素。
Input.js:
/* Input 组件, 负责回传value值 */
function Input({ onChange , value }){
return <input className="input" onChange={ (e)=>( onChange && onChange(e.target.value) ) } value={value} />
}
/* 给Component 增加标签 */
Input.displayName = 'input'
设计思想:
- 绑定 displayName 标识
input。 inputDOM 元素,绑定 onChange 方法,用于传递 value 。
下面通过函数组件再重写一下:
App.js,FormItem.js 和 Input.js 还是一样的,Form.js使用了 hooks 钩子来管理状态,并且通过forwardRef, useImperativeHandle,让 App 组件访问到 Form 中的方法:
import React, { useState, forwardRef, useImperativeHandle } from "react"
const Form = (props, ref) =>{
const { children } = props
const [ formData, setFormData ] = useState({})
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
submitForm: submitForm,
resetForm: resetForm
}))
/* 用于提交表单数据 */
const submitForm=(cb)=>{
cb(formData)
}
/* 获取重置表单数据 */
const resetForm=()=>{
const newData = formData
Object.keys(newData).forEach(item=>{
newData[item] = ''
})
setFormData(newData)
}
/* 设置表单数据层 */
const setValue=(name,value)=>{
setFormData({
...formData,
[name]:value
})
}
const renderChildren = () => {
return React.Children.map(children,(child)=>{
if(child.type.displayName === 'formItem'){
const { name } = child.props
/* 克隆`FormItem`节点,混入改变表单单元项的方法 */
const Children = React.cloneElement(child,{
key:name , /* 加入key 提升渲染效果 */
handleChange: setValue , /* 用于改变 value */
value: formData[name] || '' /* value 值 */
},child.props.children)
return Children
}
})
}
return (
renderChildren()
)
}
/* 增加组件类型type */
Form.displayName = 'form'
export default forwardRef(Form)
启动项目,查看效果:
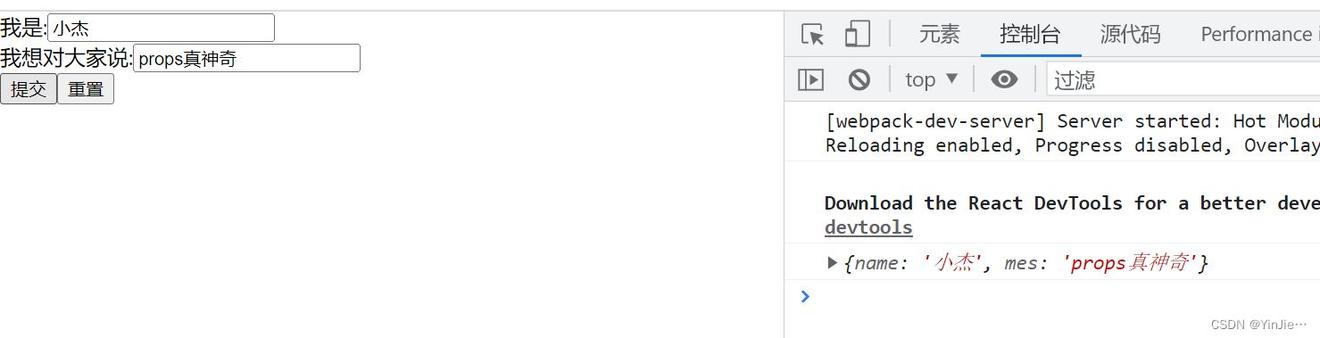
点击提交,我们在输入框里输入的内容就能显示在控制台上。
为了体现出咱们这个嵌套组件的高可复用性,我们可以在根组件中随意添加子项: