目录
- 一、安装vue
- 二、Vue模板案例
- 步骤
- 三、基础模板(记住)
- 四、vue的指令和插值
- 1、{{}}:插值表达式的语法
- 2、v-text:填充纯文本内容(data中的值)
- 3、v-html:填充html(data中的值)
- 4、v-pre:填充原始数据
- 5、v-bind:属性绑定
- 6、v-on:事件绑定
- 7、v-show:控制元素显示和隐藏的指令
- 8、v-model:数据的双向绑定
- 9、v-if、v-else-if、v-else:条件渲染
- 10、v-for:遍历对象、数组
Vue (读音 /vjuː/,类似于 view) 是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架。与其它大型框架不同的是,Vue 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还便于与第三方库或既有项目整合。另一方面,当与现代化的工具链以及各种支持类库结合使用时,Vue 也完全能够为复杂的单页应用提供驱动。
一、安装vue
直接使用script标签引入
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script>
二、Vue模板案例
步骤
1、引入vue框架
2、定义1个盒子(根节点)
3、定义1个script标签
3.1、定义js对象(根组件)
3.2、通过vue创建1个应用
3.3、将应用挂载到根节点(第二步中创建的盒子)
data():存放页面中显示数据的地方
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <!--2、定义1个盒子(根节点)--> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <h1>{{title}}</h1> | |
| <h1>{{name}}</h1> | |
| </div> | |
| <!--3、定义一个script标签--> | |
| <script> | |
| //3.1、定义js对象(根组件) | |
| const obj={ | |
| //data():存放页面中存放数据的地方 | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| title:'kobe', | |
| name:'cc' | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| //3.2、通过vue创建1个应用 | |
| const app=Vue.createApp(obj) | |
| //3.3、将应用挂载到根节点(第二步中创建的盒子) | |
| app.mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |
三、基础模板(记住)
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id='app'></div> | |
| <script> | |
| Vue.createApp({ | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }).mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |
四、vue的指令和插值
1、{{}}:插值表达式的语法
{{}}:可以在html中引用data中定义的数据
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
2、v-text:填充纯文本内容(data中的值)
效果和innerText一样
<h1 v-text='name'></h1>
3、v-html:填充html(data中的值)
效果和innerHtml一样
<div v-html='desc'></div>
4、v-pre:填充原始数据
防止vue对标签进行渲染(标签中写的什么,就显示什么)
| <div v-pre>显示两个花括号,中间为js:{{}}</div> | |
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <h1>{{name}}</h1> | |
| <h1>{{age}}</h1> | |
| <h1>{{sex}}</h1> | |
| <h2>info中的a1:{info.a1}</h2> | |
| <h2>info中的a2:{info.a2}</h2> | |
| <hr> | |
| <h1 v-text='name'></h1> | |
| <h1 v-text='arr[0]'></h1> | |
| <div v-html='desc'></div> | |
| <div v-pre>显示两个花括号,中间为js:{{}}</div> | |
| </div> | |
| <script> | |
| //obj是vue的组件对象 | |
| const obj={ | |
| //data方法(返回的是vue组件对象的属性)——》页面上要显示的数据全部放到这里 | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| name:'2022', | |
| age:18, | |
| sex:'男', | |
| info:{ | |
| a1:'66', | |
| a2:'88' | |
| }, | |
| desc:'<h1>js</h1>', | |
| arr:[8,24,23,24,25,66] | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| //3.2、通过vue创建1个应用 | |
| const app=Vue.createApp(obj) | |
| //3.3、将应用挂载到根节点(第二步中创建的盒子) | |
| app.mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |
效果展示:

5、v-bind:属性绑定
语法:
v-bind:属性=‘值’
简写 :属性=‘值’
<a v-bind:href="aInfo.addr" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >{{aInfo.title}}</a>
简写
| <a :href="aInfo.addr" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >{{aInfo.title}}</a> | |
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <a v-bind:href="aInfo.addr" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >{{aInfo.title}}</a> | |
| <!--简写--> | |
| <a :href="aInfo.addr" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >{{aInfo.title}}</a> | |
| </div> | |
| <script> | |
| Vue.createApp({ | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| aInfo:{ | |
| title:'百度', | |
| addr:'http://www.baidu.com' | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }).mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |
样式绑定
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| <style> | |
| .js{ | |
| width:200px; | |
| height:200px; | |
| background: red; | |
| } | |
| </style> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <!--样式绑定:class属性绑定--> | |
| <div :class='{js:isjs}'>js</div> | |
| </div> | |
| <hr /> | |
| <!--样式绑定 style属性--> | |
| <div :style="s1">py</div> | |
| <script> | |
| Vue.createApp({ | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| isjs:false, | |
| s1:{ | |
| width:'300px', | |
| height:'200px', | |
| background:'red', | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }).mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |
6、v-on:事件绑定
语法:v-on:事件名称=‘执行的方法’
简写
@事件名=‘执行的方法’
<button v-on:click='switchShow'>切换显示</button>
简写
<button @click='switchShow'>切换显示</button>
7、v-show:控制元素显示和隐藏的指令
控制元素显示隐藏的指令:
v-show 值为True则显示,值为false为隐藏
<div v-show='status' :style="{width:'200px',height:'200px',background:'red'}">py</div>
methods:定义页面操作过程中调用的函数(vue组件的方法)
注意点:不要直接把方法定义为箭头函数
例如
switchShow()
定义页面操作过程中调用的函数(vue组件的方法)
注意点:不要直接把方法定义为箭头函数
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <button v-on:click='switchShow'>切换显示</button> | |
| <!--<button @click='switchShow'>切换显示</button>--> | |
| <!--控制元素显示隐藏的指令:v-show | |
| 值为True则显示,值为false为隐藏 | |
| --> | |
| <div v-show='status' :style="{width:'200px',height:'200px',background:'red'}">py</div> | |
| </div> | |
| <script> | |
| Vue.createApp({ | |
| //定义页面上显示数据的(组件的属性) | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| status:true | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| //定义页面操作过程中调用的函数(vue组件的方法) | |
| //注意点:不要直接把方法定义为箭头函数 | |
| methods:{ | |
| switchShow(){ | |
| //在方法中可以通过this获取组件中的数据 | |
| //方法中的this代表组件中的对象 | |
| this.status=!this.status | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }).mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> | |
8、v-model:数据的双向绑定
双向绑定只用于表单和组件
页面修改数据会变,数据改变,页面也会改
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <!--属性绑定是单向的--> | |
| <!--<div id='app'> | |
| <div>账号:<input type="text" :value='user'></div> | |
| <div>密码:<input type="password" :value='pwd'></div> | |
| </div>--> | |
| <!--双向绑定--> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <div>账号:<input type="text" v-model='user'></div> | |
| <div>密码:<input type="password" v-model='pwd'></div> | |
| <button @click='login'>登录</button> | |
| </div> | |
| <script> | |
| Vue.createApp({ | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| user:"root", | |
| pwd:123456 | |
| } | |
| }, | |
| methods:{ | |
| login(){ | |
| //发送请求到后端, | |
| console.log('提交了登录') | |
| console.log(this.user,this.pwd) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }).mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> | |
9、v-if、v-else-if、v-else:条件渲染
通过条件来控制元素是否渲染到页面
v-if
v-else-if
v-else
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <h1 v-if='item.result==="success"' style="color: green;">{{item}}</h1> | |
| <h1 v-else-if='item.result===fail' style="color: red;">{{item}}</h1> | |
| <h1 v-else>{{item}}</h1> | |
| </div> | |
| <script> | |
| Vue.createApp({ | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| item:{ | |
| case_id:1, | |
| title:'用例1', | |
| result:"success" | |
| }, | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }).mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> | |
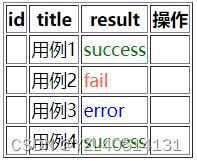
10、v-for:遍历对象、数组
案例:根据不同的结果,展示不同文字颜色
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | |
| <title></title> | |
| <!--1、引入vue框架--> | |
| <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id='app'> | |
| <table border='1'> | |
| <!--表头--> | |
| <tr> | |
| <th>id</th> | |
| <th>title</th> | |
| <th>result</th> | |
| <th>操作</th> | |
| </tr> | |
| <!--表格--> | |
| <tr v-for='item in cases'> | |
| <td>{{item.id}}</td> | |
| <td>{{item.title}}</td> | |
| <!--条件渲染--> | |
| <td v-if='item.result==="success"' style="color: green;">{{item.result}}</td> | |
| <td v-else-if='item.result==="error"' style="color:blue;">{{item.result}}</td> | |
| <td v-else-if='item.result==="fail"' style="color:tomato;">{{item.result}}</td> | |
| <td v-else>{{item.result}}</td> | |
| <td></td> | |
| </tr> | |
| </table> | |
| </div> | |
| <script> | |
| Vue.createApp({ | |
| data(){ | |
| return{ | |
| cases:[ | |
| { | |
| case_id:1, | |
| title:'用例1', | |
| result:"success" | |
| }, | |
| { | |
| case_id:2, | |
| title:'用例2', | |
| result:"fail" | |
| }, | |
| { | |
| case_id:3, | |
| title:'用例3', | |
| result:"error" | |
| }, | |
| { | |
| case_id:4, | |
| title:'用例4', | |
| result:"success" | |
| }, | |
| ] | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }).mount('#app') | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |