目录
- 一、前言
- 二、Properties类
- 三、Properties常用方法实践
- 四、Java写入Properties
- 五、Java读取Properties
- 六、Properties配合Spring框架使用
- 七、完整代码
- 总结
一、前言
在做Java项目开发过程中,涉及到一些数据库服务连接配置、缓存服务器连接配置等,通常情况下我们会将这些不太变动的配置信息存储在以 .properties 结尾的配置文件中。当对应的服务器地址或者账号密码信息有所变动时,我们只需要修改一下配置文件中的信息即可。同时为了让Java程序可以读取 .properties配置文件中的值,Java的JDK中提供了java.util.Properties类可以实现读取配置文件。
二、Properties类
Properties 类位于 java.util.Properties中,是Java 语言的处理配置文件所使用的类,其中的xxx.Properties类主要用于集中的持久存储Java的配置文件内容,可以读取后缀是.properties和.cfg的配置文件。
Properties继承了Hashtable 类,以Map 的形式进行放置值,put(key,value) 和 get(key),文本注释信息可以用"#"来注释。
Properties 类表示了一个持久的属性集。Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
Properties 文件内容的格式是:键=值 形式,Key值不能够重复。 例如:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
Properties类的继承关系图:

Properties类的源码关系图:

主要方法介绍:

它提供了几个核心的方法:
- getProperty ( String key): 用指定的键在此属性列表中搜索属性。也就是通过参数 key ,得到 key 所对应的 value。
- load ( InputStream inStream): 从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)。通过对指定的文件(比如说上面的 test.properties 文件)进行装载来获取该文件中的所有键 - 值对。以供 getProperty ( String key) 来搜索。
- setProperty ( String key, String value) : 调用 Hashtable 的方法 put 。他通过调用基类的put方法来设置 键 - 值对。
- store ( OutputStream out, String comments): 以适合使用 load 方法加载到 Properties 表中的格式,将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出流。与 load 方法相反,该方法将键 - 值对写入到指定的文件中去。
- clear (): 清除所有装载的 键 - 值对。该方法在基类中提供。
三、Properties常用方法实践
Properties类我们从文件的写入和读取来实践其具体用法,下面演示练习将以下数据库配置信息写入到jdbc.properties文件中
| jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver | |
| jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf8 | |
| jdbc.username=root | |
| jdbc.password=123456 |
项目目录结构如下
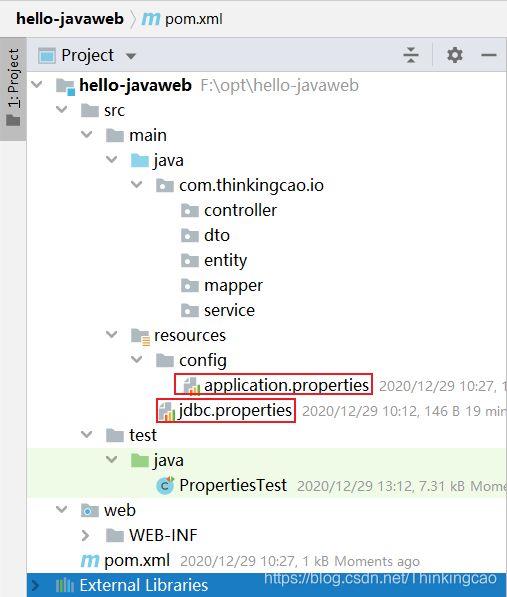
四、Java写入Properties
Properties类调用setProperty方法将键值对保存到内存中,此时可以通过getProperty方法读取,propertyNames方法进行遍历,但是并没有将键值对持久化到属性文件中,故需要调用store方法持久化键值对到属性文件中。
| import java.io.FileOutputStream; | |
| import java.io.IOException; | |
| import java.io.OutputStream; | |
| import java.util.Properties; | |
| /** | |
| * @desc: 写入Mysql数据库了连接信息到jdbc.properties中 | |
| * @author: cao_wencao | |
| * @date: 2020-12-29 13:41 | |
| */ | |
| public class PropertiesStoreTest { | |
| public static void main(String[] args) { | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| OutputStream output = null; | |
| try { | |
| output = new FileOutputStream("src/main/resources/jdbc.properties"); | |
| properties.setProperty("jdbc.driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); | |
| properties.setProperty("jdbc.url","jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf8" ); | |
| properties.setProperty("jdbc.username", "root"); | |
| properties.setProperty("jdbc.password", "123456"); | |
| // 保存键值对到文件中 | |
| properties.store(output, "Thinkingcao modify"); | |
| } catch (IOException io) { | |
| io.printStackTrace(); | |
| } finally { | |
| if (output != null) { | |
| try { | |
| output.close(); | |
| } catch (IOException e) { | |
| e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
输出结果,在resources目录下多一个文件jdbc.properties,内容如下:
| #Thinkingcao modify | |
| #Tue Dec 29 13:43:48 CST 2020 | |
| jdbc.url=jdbc\:mysql\://localhost\:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding\=utf8 | |
| jdbc.username=root | |
| jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver | |
| jdbc.password=123456 |
五、Java读取Properties
Java读取Properties文件的方法有很多,下面介绍8种方式,分别读取resource目录下的jdbc.properties和resource/config/application.properties。
application.properties文件内容如下
| minio.endpoint=http://localhost:9000 | |
| minio.accessKey=minioadmin | |
| minio.secretKey=minioadmin | |
| minio.bucketName=demo |
1. 从当前的类加载器的getResourcesAsStream来获取
| /** | |
| * 1. 方式一 | |
| * 从当前的类加载器的getResourcesAsStream来获取 | |
| * InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream(name) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test1() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("jdbc.url"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } |
2. 从当前的类加载器的getClassLoader().getResourcesAsStream来获取
| /** | |
| * 2. 方式二 | |
| * 从当前的类加载器的getResourcesAsStream来获取 | |
| * InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(name) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test2() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } |
3. 使用Class类的getSystemResourceAsStream静态方法 和使用当前类的ClassLoader是一样的
| /** | |
| * 3. 方式三 | |
| * 使用Class类的getSystemResourceAsStream方法 和使用当前类的ClassLoader是一样的 | |
| * InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test3() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } |
4. 使用Spring-core包中的ClassPathResource读取
| /** | |
| * 4. 方式四 | |
| * Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(path) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test4() throws IOException { | |
| Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } |
5. 从文件中读取,new BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
| /** | |
| * 5. 方式五 | |
| * 从文件中获取,使用InputStream字节,主要是需要加上当前配置文件所在的项目src目录地址。路径配置需要精确到绝对地址级别 | |
| * BufferedInputStream继承自InputStream | |
| * InputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(name) | |
| * 这种方法读取需要完整的路径,优点是可以读取任意路径下的文件,缺点是不太灵活 | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test5() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/config/application.properties")); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } |
6.从文件中读取,new FileInputStream(String name)
| /** | |
| * 6. 方式六 | |
| * 从文件中获取,使用InputStream字节,主要是需要加上当前配置文件所在的项目src目录地址。路径配置需要精确到绝对地址级别 | |
| * FileInputStream继承自InputStream | |
| * InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(name) | |
| * 这种方法读取需要完整的路径,优点是可以读取任意路径下的文件,缺点是不太灵活 | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test6() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } |
7. 使用PropertyResourceBundle读取InputStream流
| /** | |
| * 7. 方式七 | |
| * 使用InputStream流来进行操作ResourceBundle,获取流的方式由以上几种。 | |
| * ResourceBundle resourceBundle = new PropertyResourceBundle(inputStream); | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test7() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("config/application.properties"); | |
| ResourceBundle resourceBundle = new PropertyResourceBundle(inputStream); | |
| Enumeration<String> keys = resourceBundle.getKeys(); | |
| while (keys.hasMoreElements()) { | |
| String s = keys.nextElement(); | |
| System.out.println(s + " = " + resourceBundle.getString(s)); | |
| } | |
| } |
8. 使用ResourceBundle.getBundle读取
| /** | |
| * 8. 方式八 | |
| * ResourceBundle.getBundle的路径访问和 Class.getClassLoader.getResourceAsStream类似,默认从根目录下读取,也可以读取resources目录下的文件 | |
| * ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("b") //不需要指定文件名的后缀,只需要写文件名前缀即可 | |
| */ | |
| public void test8(){ | |
| //ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc"); //读取resources目录下的jdbc.properties | |
| ResourceBundle rb2 = ResourceBundle.getBundle("config/application");//读取resources/config目录下的application.properties | |
| for(String key : rb2.keySet()){ | |
| String value = rb2.getString(key); | |
| System.out.println(key + ":" + value); | |
| } | |
| } |
输出结果:
minio.endpoint:http://localhost:9000
minio.bucketName:demo
minio.secretKey:minioadmin
minio.accessKey:minioadmin
六、Properties配合Spring框架使用
加载.properties方式一
| <!-- 1.加载 jdbc.properties 配置文件 --> | |
| <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" system-properties-mode="NEVER"/> |
除了上面这种方式之外,还有下面这种List集合的方式
加载.properties方式二
| <!-- 4.引入外部配置文件 由于后期可能会引入多个配置文件 所以采用list的形式 --> | |
| <bean id="propertyPlaceholder" | |
| class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> | |
| <property name="locations"> | |
| <list> | |
| <value>classpath:/config/jdbc.properties</value> | |
| <value>classpath:/config/application.properties</value> | |
| </list> | |
| </property> | |
| </bean> |
七、完整代码
| import org.junit.Test; | |
| import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; | |
| import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; | |
| import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderUtils; | |
| import java.io.BufferedInputStream; | |
| import java.io.FileInputStream; | |
| import java.io.IOException; | |
| import java.io.InputStream; | |
| import java.util.*; | |
| /** | |
| * @desc: Properties读取配置文件属性值的方式 | |
| * @author: cao_wencao | |
| * @date: 2020-12-29 10:08 | |
| */ | |
| public class PropertiesTest { | |
| /** | |
| * 1. 方式一 | |
| * 从当前的类加载器的getResourcesAsStream来获取 | |
| * InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream(name) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test1() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("jdbc.url"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 2. 方式二 | |
| * 从当前的类加载器的getResourcesAsStream来获取 | |
| * InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(name) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test5() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 3. 方式三 | |
| * 使用Class类的getSystemResourceAsStream方法 和使用当前类的ClassLoader是一样的 | |
| * InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test4() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 4. 方式四 | |
| * Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(path) | |
| * | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test2() throws IOException { | |
| Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 5. 方式五 | |
| * 从文件中获取,使用InputStream字节,主要是需要加上当前配置文件所在的项目src目录地址。路径配置需要精确到绝对地址级别 | |
| * BufferedInputStream继承自InputStream | |
| * InputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(name) | |
| * 这种方法读取需要完整的路径,优点是可以读取任意路径下的文件,缺点是不太灵活 | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test3() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/config/application.properties")); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 6. 方式六 | |
| * 从文件中获取,使用InputStream字节,主要是需要加上当前配置文件所在的项目src目录地址。路径配置需要精确到绝对地址级别 | |
| * FileInputStream继承自InputStream | |
| * InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(name) | |
| * 这种方法读取需要完整的路径,优点是可以读取任意路径下的文件,缺点是不太灵活 | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test6() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/config/application.properties"); | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| properties.list(System.out); | |
| System.out.println("=============================================="); | |
| String property = properties.getProperty("minio.endpoint"); | |
| System.out.println("property = " + property); | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 7. 方式七 | |
| * 使用InputStream流来进行操作ResourceBundle,获取流的方式由以上几种。 | |
| * ResourceBundle resourceBundle = new PropertyResourceBundle(inputStream); | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| public void test7() throws IOException { | |
| InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("config/application.properties"); | |
| ResourceBundle resourceBundle = new PropertyResourceBundle(inputStream); | |
| Enumeration<String> keys = resourceBundle.getKeys(); | |
| while (keys.hasMoreElements()) { | |
| String s = keys.nextElement(); | |
| System.out.println(s + " = " + resourceBundle.getString(s)); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 8. 方式八 | |
| * ResourceBundle.getBundle的路径访问和 Class.getClassLoader.getResourceAsStream类似,默认从根目录下读取,也可以读取resources目录下的文件 | |
| * ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("b") //不需要指定文件名的后缀,只需要写文件名前缀即可 | |
| */ | |
| public void test8(){ | |
| //ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc"); //读取resources目录下的jdbc.properties | |
| ResourceBundle rb2 = ResourceBundle.getBundle("config/application");//读取resources/config目录下的application.properties | |
| for(String key : rb2.keySet()){ | |
| String value = rb2.getString(key); | |
| System.out.println(key + ":" + value); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 单独抽取的方法,用户检测能否正确操纵Properties | |
| * | |
| * @param inputStream | |
| * @throws IOException | |
| */ | |
| private void printKeyValue(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException { | |
| Properties properties = new Properties(); | |
| properties.load(inputStream); | |
| Set<Object> keys = properties.keySet(); | |
| for (Object key : keys) { | |
| System.out.println(key + " = " + properties.get(key)); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |