目录
- 一、概念
- 1. Pinia => Pinia
- 2. Pinia和Vuex的对比
- 二、使用Pinia
- 1. 安装
- 2. 创建Pinia
- 3. 在main.js中引入
- 三、Store
- 1. 概念
- 2. 创建
- 3. 使用
- 4. 效果
- 四、核心概念State
- 1. 定义State
- 2. 读取写入State
- 3. 重置State
- 4. 改变State
- 5. 替换State
- 五、核心概念Getters
- 1. 基本使用
- 2. 在getter中使用其他的getter
- 3. getters支持返回一个函数
- 4. getters使用别的store中的数据
- 六、核心概念Actions
- 1. 基本使用
- 2. 异步操作
- 总结
一、概念
1. Pinia => Pinia
Pinia(发音为/piːnjʌ/,如英语中的“peenya”)是最接近piña(西班牙语中的菠萝)的词
- Pinia开始于大概2019年,最初是作为一个实验为Vue重新设计状态管理,让它用起来像组合式API(Composition API)
- 从那时到现在,最初的设计原则依然是相同的,并且目前同时兼容Vue2、Vue3,也并不要求你使用Composition API
- Pinia本质上依然是一个状态管理的库,用于跨组件、页面进行状态共享(这点和Vuex、Redux一样)

2. Pinia和Vuex的对比
01 - 不是已经有Vuex了吗?为什么还要用Pinia
- Pinia 最初是为了探索 Vuex 的下一次迭代会是什么样子,结合了 Vuex 5 核心团队讨论中的许多想法
- 最终,团队意识到Pinia已经实现了Vuex5中大部分内容,所以最终决定用Pinia来替代Vuex
- 与 Vuex 相比,Pinia 提供了一个更简单的 API,具有更少的仪式,提供了 Composition-API 风格的 API
- 最重要的是,在与 TypeScript 一起使用时具有可靠的类型推断支持
02 - 和Vuex相比,Pinia有很多的优势
- mutations 不再存在
- 他们经常被认为是 非常 冗长
- 他们最初带来了 devtools 集成,但这不再是问题
- 更友好的TypeScript支持,Vuex之前对TS的支持很不友好
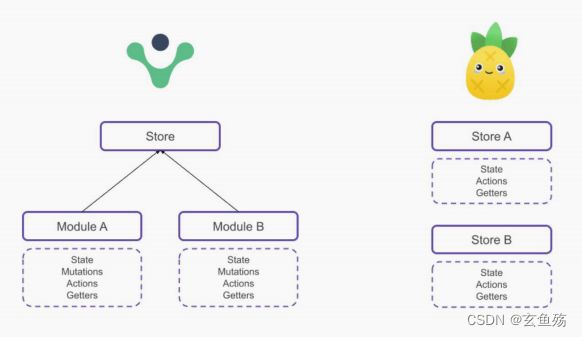
- 不再有modules的嵌套结构
- 可以灵活使用每一个store,它们是通过扁平化的方式来相互使用的
- 也不再有命名空间的概念,不需要记住它们的复杂关系
- Pinia的store中的 getters、actions 可以使用this,this代表当前sotre对象
二、使用Pinia
1. 安装
npm install pinia
2. 创建Pinia
创建stores文件夹,并在其中创建个index.js
| |
| import { createPinia } from 'pinia'; |
| |
| |
| const pinia = createPinia(); |
| |
| |
| export default pinia; |
3. 在main.js中引入
| import { createApp } from 'vue'; |
| import App from './App.vue'; |
| |
| import pinia from './stores'; |
| |
| createApp(App).use(pinia).mount('#app'); |
三、Store
1. 概念
Store :
- 一个 Store (如 Pinia)是一个实体,它会持有为绑定到你组件树的状态和业务逻辑,也就是保存了全局的状态
- 它有点像始终存在,并且每个人都可以读取和写入的组件
- 你可以在你的应用程序中定义任意数量的Store来管理你的状态
Store有三个核心概念 :
- state、getters、actions
- 等同于组件的data、computed、methods
- 一旦 store 被实例化,可以直接在 store 上面访问 state、getters 和 actions 中定义的任何属性
2. 创建
定义一个Store :
- Store 是使用 defineStore() 定义
- 并且它需要一个唯一名称,作为第一个参数传递
在stores文件夹创建 counter.js 文件
| |
| import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| const userCounterStore = defineStore('counterStore', { |
| state: () => ({ |
| count: |
| }) |
| }); |
| |
| export default userCounterStore; |
3. 使用
| <template> |
| <div class="app">App 页面</div> |
| <h>1. counterStore : {{ counterStore.count }}</h2> |
| <h>2. toRefs : {{ aCount }}</h2> |
| <h>3. storeToRefs : {{ bCount }}</h2> |
| |
| <button @click="changCount">改变count</button> |
| </template> |
| |
| <script setup> |
| import { toRefs } from 'vue'; |
| import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; |
| |
| import userCounterStore from '@/stores/module/counter'; |
| |
| |
| const counterStore = userCounterStore(); |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| const { count: aCount } = toRefs(counterStore); |
| |
| const { count: bCount } = storeToRefs(counterStore); |
| |
| |
| const changCount = () => { |
| |
| counterStore.count++; |
| }; |
| </script> |
4. 效果

四、核心概念State
1. 定义State
| |
| import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| const userCounterStore = defineStore('counterStore', { |
| state: () => ({ |
| count:, |
| name: 'coder', |
| age: |
| }) |
| }); |
| |
| export default userCounterStore; |
2. 读取写入State
默认情况下,可以通过 store 实例访问状态来直接读取和写入状态
| <script setup> |
| import Home from './views/Home.vue'; |
| |
| import { toRefs } from 'vue'; |
| import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; |
| import userCounterStore from '@/stores/module/counter'; |
| |
| |
| const counterStore = userCounterStore(); |
| |
| const { count } = storeToRefs(counterStore); |
| |
| |
| const changCount = () => { |
| |
| console.log(counterStore.count); |
| |
| counterStore.count++; |
| }; |
| </script> |
3. 重置State
可以通过调用 store 上的 $reset() 方法将状态 重置 到其初始值
| |
| const resetState = () => { |
| |
| counterStore.$reset(); |
| }; |
4. 改变State
除了直接用 store.counter++ 修改 store,还可以调用 $patch 方法
允许同时应用多个更改
| |
| const changCount = () => { |
| |
| counterStore.$patch({ |
| count:, |
| name: 'star', |
| |
| buy: ref('abvc') |
| }); |
| console.log(counterStore); |
| }; |
5. 替换State
可以通过将其 $state 属性设置为新对象来替换 Store 的整个状态

五、核心概念Getters
1. 基本使用
代码
| const userCounterStore = defineStore('counterStore', { |
| state: () => ({ |
| count:, |
| name: 'coder', |
| age: |
| }), |
| getters: { |
| |
| doubleCount(state) { |
| |
| console.log(state.count); |
| |
| console.log(this.count); |
| } |
| } |
| }); |
使用
| <template> |
| <div>home</div> |
| <h>count : {{ counterStore.count }}</h2> |
| <hr /> |
| <h>count : {{ counterStore.doubleCount }}</h2> |
| |
| <button @click="changCount">改变count</button> |
| </template> |
| |
| <script setup> |
| import { toRefs } from 'vue'; |
| import userCounterStore from '@/stores/module/counter'; |
| |
| const counterStore = userCounterStore(); |
| |
| const { doubleCount } = toRefs(counterStore); |
| console.log(doubleCount); |
| |
| |
| const changCount = () => { |
| |
| counterStore.count++; |
| |
| console.log(doubleCount.value); |
| }; |
| </script> |
2. 在getter中使用其他的getter
| getters: { |
| doubleCount(state) { |
| return this.count *; |
| }, |
| othersGetter() { |
| |
| return this.doubleCount; |
| } |
| } |
3. getters支持返回一个函数
可以用来传递参数到getters
代码
| getters: { |
| doubleCount(state) { |
| return this.count *; |
| }, |
| formatName() { |
| |
| return (lastName) => { |
| return this.name + lastName; |
| }; |
| } |
| } |
使用
| <template> |
| <h>{{ counterStore.formatName('123') }}</h2> |
| <button @click="changCount">改变count</button> |
| </template> |
| |
| <script setup> |
| import { toRefs } from 'vue'; |
| import userCounterStore from '@/stores/module/counter'; |
| |
| const counterStore = userCounterStore(); |
| |
| const { formatName } = toRefs(counterStore); |
| |
| const changCount = () => { |
| |
| console.log(formatName.value('')); |
| |
| counterStore.formatName('') |
| }; |
| </script> |
4. getters使用别的store中的数据
导入其他的store,使用即可,很方便
| userOtherStore(){ |
| |
| const otherStore = userOtherStore() |
| |
| otherStore.getters() |
| } |
六、核心概念Actions
actions => 非常适合定义业务逻辑
1. 基本使用
代码
| const userCounterStore = defineStore('counterStore', { |
| state: () => ({ |
| count:, |
| name: 'coder', |
| age: |
| }), |
| actions: { |
| increment() { |
| this.count++; |
| }, |
| |
| incrementNum(num) { |
| this.count += num; |
| } |
| } |
| }); |
使用
| <script setup> |
| import userCounterStore from '@/stores/module/counter'; |
| |
| const counterStore = userCounterStore(); |
| |
| const { increment, incrementNum } = counterStore; |
| |
| increment(); |
| incrementNum(); |
| </script> |
2. 异步操作
代码
| const userCounterStore = defineStore('counterStore', { |
| state: () => ({ |
| arrList: [] |
| }), |
| actions: { |
| async fetchDataList() { |
| |
| const res = await fetch('http:xxxxx'); |
| const data = await res.json(); |
| this.arrList = data.list; |
| |
| return data; |
| } |
| } |
| }); |
使用
| <script setup> |
| import userCounterStore from '@/stores/module/counter'; |
| |
| const counterStore = userCounterStore(); |
| |
| const { fetchDataList } = counterStore; |
| |
| fetchDataList().then((res) => { |
| |
| console.log(res); |
| }); |
| </script> |



