目录
- 前言
- 安装准备
- 初始项目
- Cargo.toml
- 初始web项目
- 游戏规则
- 游戏设计
- Rust实现
- 测试
- 调试
前言
之前学了几遍,后来忘记了,通过制作该游戏再复习复习。
安装准备
- wasm-pack : https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-pack/installer/
- cargo-generate:
cargo install cargo-generate
初始项目
初始rust项目
使用wasm的项目模板:
cargo generate --git https://github.com/rustwasm/wasm-pack-template
- 提示输入project名wasm-game-of-life
- 在lib.rs中可以看见如下内容:
| mod utils; | |
| use wasm_bindgen::prelude::*; | |
| // When the `wee_alloc` feature is enabled, use `wee_alloc` as the global | |
| // allocator. | |
| static ALLOC: wee_alloc::WeeAlloc = wee_alloc::WeeAlloc::INIT; | |
| extern { | |
| fn alert(s: &str); | |
| } | |
| pub fn greet() { | |
| alert("Hello, wasm-game-of-life!"); | |
| } |
- 它导入 window.alertJavaScript 函数,并导出greet的Rust 函数。
Cargo.toml
- Cargo.toml预置了[lib]和[dependencies]。解释一下crate-type中f=“https://users.rust-lang.org/t/what-is-the-difference-between-dylib-and-cdylib/28847”>cdylib和rlib的作用:
- cdylib:顾名思义,是C的动态链接库的意思,可以被C和C++程序链接使用
- rlib:Rust静态链接库,用于静态连接其他crates
- 依赖中使用的:
- wasm-bindgen可以将Rust编写的函数和结构体暴露到JS中或者把JS的方法引入到Rust中使用
- console_error_panic_hook提供了Wasm输出Rust Panic的能力
- wee_alloc是一个轻量的Wasm内存分配器,但是会比默认分配器慢一些。
初始web项目
npm init wasm-app www
- 看到生成的pkg.json:
| { | |
| "name": "create-wasm-app", | |
| "version": "0.1.0", | |
| "description": "create an app to consume rust-generated wasm packages", | |
| "main": "index.js", | |
| "bin": { | |
| "create-wasm-app": ".bin/create-wasm-app.js" | |
| }, | |
| "scripts": { | |
| "build": "webpack --config webpack.config.js", | |
| "start": "webpack-dev-server" | |
| }, |
- html里导入boostrap.js,boostrap.js里导入index.js。 index.js里面导入了其已经制作好的一个包:
| import * as wasm from "hello-wasm-pack"; | |
| wasm.greet(); |
- 我们修改pkg.json,导入自己的包(该包需要使用
wasm-pack build生成)
"wasm-game-of-life": "file:../pkg"
- 将index.js更换下:
| import * as wasm from "wasm-game-of-life"; | |
| wasm.greet(); |
- 使用npm i 安装依赖。
- 使用npm run start 启动页面,打开http://localhost:8080/即可看见alert。
游戏规则
- Conway’s Game of Life是英国数学家约翰·何顿·康威在1970年发明的放置类无玩家参与的游戏
- 百度百科
- https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%BA%B7%E5%A8%81%E7%94%9F%E5%91%BD%E6%B8%B8%E6%88%8F/22668799?fr=aladdin主要规则如下:
- 1、任何少于两个活邻居的活细胞都会死亡,就像是由于人口不足造成的。
- 2、任何有两三个活邻居的活细胞都可以活到下一代。
- 3、任何有超过三个活邻居的活细胞都会死亡,就像人口过剩一样。
- 4、任何只有三个活邻居的死细胞都会变成活细胞,就像通过繁殖一样。
游戏设计
- 为啥说这个呢,因为2种语言去做这个东西会考虑哪个东西在哪个里面去实现。
- rust推荐大型、长寿命的数据结构被实现为 Rust 类型,这些类型存在于 WebAssembly 线性内存中,并作为不透明的句柄暴露给 JavaScript。JavaScript 调用导出的 WebAssembly 函数,这些函数采用这些不透明的句柄、转换它们的数据、执行繁重的计算、查询数据并最终返回一个可复制的结果。通过只返回计算结果,我们避免了在 JavaScript 垃圾收集堆和 WebAssembly 线性内存之间来回复制和/或序列化所有内容。
- 这个游戏中,会将universe的显示效果暴露给js渲染,其余计算在rust去实现。
- 由于宇宙是n*n的,所以我们可以用一维数组去表示它,比如4x4的宇宙就是这样:
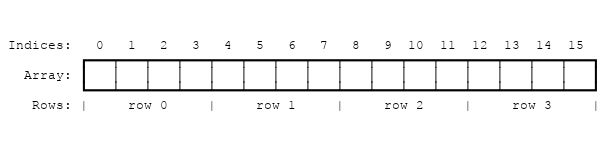
- 将数组每个row换下来就是需要的4x4的显示了。因为这种表现形式,所以我们需要对数组索引和行列进行转换,公式为:
index(row, column, universe) = row * width(universe) + column
- 就比如我要知道4行4列是索引几,根据公式就是3*4 + 3。
- 每个单元格有一个字节,其中0表示死亡,1表示存活。
Rust实现
首先我们需要定义每个单元格:
| pub enum Cell { | |
| Dead = 0, | |
| Alive = 1, | |
| } |
枚举类型,0是死亡,1是存活,#[repr(u8)]表示一个单元格1字节。复习下:
长度 | 有符号 | 无符号 |
8-bit | i8 | u8 |
16-bit | i16 | u16 |
32-bit | i32 | u32 |
64-bit | i64 | u64 |
128-bit | i128 | u128 |
arch | isize | usize |
接下来定义宇宙:
| pub struct Universe { | |
| width: u32, | |
| height: u32, | |
| cells: Vec<Cell>, | |
| } |
- 宇宙是长宽和一个动态数组。
- 我们对universe实现一些方法便于操作:
| impl Universe { | |
| fn get_index(&self, row: u32, column: u32) -> usize { | |
| (row * self.width + column) as usize | |
| } | |
| } |
- get_index就是上面公式做索引。
- 从前面游戏规则上可知,我们需要对每个单元格求出周围格子的存活数量,于是加上这个函数:
| fn live_neighbor_count(&self, row: u32, column: u32) -> u8 { | |
| let mut count = 0; | |
| for delta_row in [self.height - 1, 0, 1].iter().cloned() { | |
| for delta_col in [self.width - 1, 0, 1].iter().cloned() { | |
| if delta_row == 0 && delta_col == 0 { | |
| continue; | |
| } | |
| let neighbor_row = (row + delta_row) % self.height; | |
| let neighbor_col = (column + delta_col) % self.width; | |
| println!("{},{}-s-", neighbor_row, neighbor_col); | |
| let idx = self.get_index(neighbor_row, neighbor_col); | |
| count += self.cells[idx] as u8; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| count | |
| } |
- 解释下这个函数,其中迭代height-1 , 0 , 1 以及 width-1,0,1就是求传入row与col的周围的格子里存活数量。当迭代到0,0时,这个格子代表其自身,所以直接忽略。
- 比如64x64的宇宙,查询2,2周围的格子就是:
1,1
1,2
1,3
2,1
2,3
3,1
3,2
3,3
- 边界处理靠取余,这样也能避免无符号向下溢出,所以0,0的周围格子就是:
63,63
63,0-
63,1
0,63
0,1
1,63
1,0
1,1
- 再从当前宇宙中获取格子的状态,如果是0,那么加上也不会增加,这样最终返回的就是周围格子的存活数量了。
- 下面根据规则迭代每个细胞状态,暴露出来:
| pub fn tick(&mut self) { | |
| let mut next = self.cells.clone(); | |
| for row in 0..self.height { | |
| for col in 0..self.width { | |
| let idx = self.get_index(row, col); | |
| let cell = self.cells[idx]; | |
| let live_neighbors = self.live_neighbor_count(row, col); | |
| let next_cell = match (cell, live_neighbors) { | |
| // Rule 1: Any live cell with fewer than two live neighbours | |
| // dies, as if caused by underpopulation. | |
| (Cell::Alive, x) if x < 2 => Cell::Dead, | |
| // Rule 2: Any live cell with two or three live neighbours | |
| // lives on to the next generation. | |
| (Cell::Alive, 2) | (Cell::Alive, 3) => Cell::Alive, | |
| // Rule 3: Any live cell with more than three live | |
| // neighbours dies, as if by overpopulation. | |
| (Cell::Alive, x) if x > 3 => Cell::Dead, | |
| // Rule 4: Any dead cell with exactly three live neighbours | |
| // becomes a live cell, as if by reproduction. | |
| (Cell::Dead, 3) => Cell::Alive, | |
| // All other cells remain in the same state. | |
| (otherwise, _) => otherwise, | |
| }; | |
| next[idx] = next_cell; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| self.cells = next; | |
| } |
- 最后需要对universe实现输出功能,先将其输出成文本,实现display方法:
| impl fmt::Display for Universe { | |
| fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result { | |
| for line in self.cells.as_slice().chunks(self.width as usize) { | |
| for &cell in line { | |
| let symbol = if cell == Cell::Dead { '◻' } else { '◼' }; | |
| write!(f, "{}", symbol)?; | |
| } | |
| write!(f, "\n")?; | |
| } | |
| Ok(()) | |
| } | |
| } |
最后进行暴露初始化和渲染方法:
| pub fn new() -> Universe { | |
| let width = 64; | |
| let height = 64; | |
| let cells = (0..width * height) | |
| .map(|i| { | |
| if i % 2 == 0 || i % 7 == 0 { | |
| Cell::Alive | |
| } else { | |
| Cell::Dead | |
| } | |
| }) | |
| .collect(); | |
| Universe { | |
| width, | |
| height, | |
| cells, | |
| } | |
| } | |
| pub fn render(&self) -> String { | |
| self.to_string() | |
| } |
- 使用wasm-pack build打包
- 使用js渲染,修改html加入标签:
<pre id="game-of-life-canvas"></pre>
index.js加入下面代码:
| import { Universe } from "wasm-game-of-life"; | |
| const pre = document.getElementById("game-of-life-canvas"); | |
| const universe = Universe.new(); | |
| const renderLoop = () => { | |
| pre.textContent = universe.render(); | |
| universe.tick(); | |
| requestAnimationFrame(renderLoop); | |
| }; | |
| renderLoop(); |
- 即可看见效果。
- 下面使用canvas进行渲染,将universe中暴露其属性:
| pub fn width(&self) -> u32 { | |
| self.width | |
| } | |
| pub fn height(&self) -> u32 { | |
| self.height | |
| } | |
| pub fn cells(&self) -> *const Cell { | |
| self.cells.as_ptr() | |
| } |
- html中替换为canvas:
<canvas id="game-of-life-canvas"></canvas>
修改js:
| import { Universe, Cell } from "wasm-game-of-life"; | |
| import { memory } from "wasm-game-of-life/wasm_game_of_life_bg"; | |
| const CELL_SIZE = 5; // px | |
| const GRID_COLOR = "#CCCCCC"; | |
| const DEAD_COLOR = "#FFFFFF"; | |
| const ALIVE_COLOR = "#000000"; | |
| const universe = Universe.new(); | |
| const width = universe.width(); | |
| const height = universe.height(); | |
| // Give the canvas room for all of our cells and a 1px border | |
| // around each of them. | |
| const canvas = document.getElementById("game-of-life-canvas"); | |
| canvas.height = (CELL_SIZE + 1) * height + 1; | |
| canvas.width = (CELL_SIZE + 1) * width + 1; | |
| const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"); | |
| const drawGrid = () => { | |
| ctx.beginPath(); | |
| ctx.strokeStyle = GRID_COLOR; | |
| // Vertical lines. | |
| for (let i = 0; i <= width; i++) { | |
| ctx.moveTo(i * (CELL_SIZE + 1) + 1, 0); | |
| ctx.lineTo(i * (CELL_SIZE + 1) + 1, (CELL_SIZE + 1) * height + 1); | |
| } | |
| // Horizontal lines. | |
| for (let j = 0; j <= height; j++) { | |
| ctx.moveTo(0, j * (CELL_SIZE + 1) + 1); | |
| ctx.lineTo((CELL_SIZE + 1) * width + 1, j * (CELL_SIZE + 1) + 1); | |
| } | |
| ctx.stroke(); | |
| }; | |
| const getIndex = (row, column) => { | |
| return row * width + column; | |
| }; | |
| const drawCells = () => { | |
| const cellsPtr = universe.cells(); | |
| const cells = new Uint8Array(memory.buffer, cellsPtr, width * height); | |
| ctx.beginPath(); | |
| for (let row = 0; row < height; row++) { | |
| for (let col = 0; col < width; col++) { | |
| const idx = getIndex(row, col); | |
| ctx.fillStyle = cells[idx] === Cell.Dead ? DEAD_COLOR : ALIVE_COLOR; | |
| ctx.fillRect( | |
| col * (CELL_SIZE + 1) + 1, | |
| row * (CELL_SIZE + 1) + 1, | |
| CELL_SIZE, | |
| CELL_SIZE | |
| ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| ctx.stroke(); | |
| }; | |
| const renderLoop = () => { | |
| universe.tick(); | |
| drawGrid(); | |
| drawCells(); | |
| requestAnimationFrame(renderLoop); | |
| }; | |
| renderLoop(); |
即可看见效果:
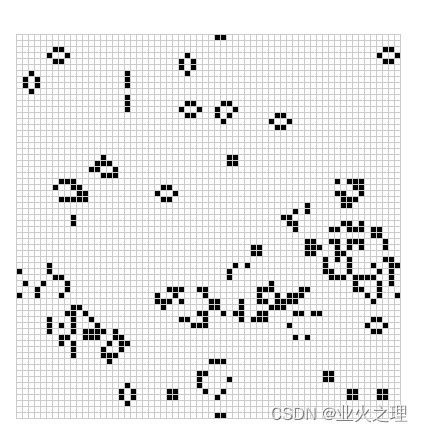
测试
- 一般代码需要写单元测试,看一下rust的测试怎么写。
- 首先,对Universe增加2个实现,可以将元组转换为universe的cell:
| impl Universe { | |
| /// Get the dead and alive values of the entire universe. | |
| pub fn get_cells(&self) -> &[Cell] { | |
| &self.cells | |
| } | |
| /// Set cells to be alive in a universe by passing the row and column | |
| /// of each cell as an array. | |
| pub fn set_cells(&mut self, cells: &[(u32, u32)]) { | |
| for (row, col) in cells.iter().cloned() { | |
| let idx = self.get_index(row, col); | |
| self.cells[idx] = Cell::Alive; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
新增重置的方法:
| /// Set the width of the universe. | |
| /// | |
| /// Resets all cells to the dead state. | |
| pub fn set_width(&mut self, width: u32) { | |
| self.width = width; | |
| self.cells = (0..width * self.height).map(|_i| Cell::Dead).collect(); | |
| } | |
| /// Set the height of the universe. | |
| /// | |
| /// Resets all cells to the dead state. | |
| pub fn set_height(&mut self, height: u32) { | |
| self.height = height; | |
| self.cells = (0..self.width * height).map(|_i| Cell::Dead).collect(); | |
| } |
- 下面编写测试,测试在tests文件夹下的web.rs中。
- 增加以下代码:
| extern crate wasm_bindgen_test; | |
| use std::assert_eq; | |
| use wasm_bindgen_test::*; | |
| extern crate wasm_game_of_life; | |
| use wasm_game_of_life::Universe; | |
| wasm_bindgen_test_configure!(run_in_browser); | |
| pub fn input_spaceship() -> Universe { | |
| let mut universe = Universe::new(); | |
| universe.set_width(6); | |
| universe.set_height(6); | |
| universe.set_cells(&[(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3)]); | |
| universe | |
| } | |
| pub fn expected_spaceship() -> Universe { | |
| let mut universe = Universe::new(); | |
| universe.set_width(6); | |
| universe.set_height(6); | |
| universe.set_cells(&[(2, 1), (2, 3), (3, 2), (3, 3), (4, 2)]); | |
| universe | |
| } | |
| pub fn test_tick() { | |
| // Let's create a smaller Universe with a small spaceship to test! | |
| let mut input_universe = input_spaceship(); | |
| // This is what our spaceship should look like | |
| // after one tick in our universe. | |
| let expected_universe = expected_spaceship(); | |
| // Call `tick` and then see if the cells in the `Universe`s are the same. | |
| input_universe.tick(); | |
| assert_eq!(&input_universe.get_cells(), &expected_universe.get_cells()); | |
| } |
- 然后使用
wasm-pack test --firefox --headless即可运行测试结果。如果安装浏览器失败,可以使用谷歌,或者去掉无头属性,直接网页上看测试结果。
调试
- 我们知道,web上使用console.log去输出调试内容,rust的代码如何在web中调试呢?
- 这里需要安装下web-sys
| [dependencies.web-sys] | |
| version = "0.3" | |
| features = [ | |
| "console", | |
| ] |
- 导入外部websys,制作自定义宏:
| extern crate web_sys; | |
| // A macro to provide `println!(..)`-style syntax for `console.log` logging. | |
| macro_rules! log { | |
| ( $( $t:tt )* ) => { | |
| web_sys::console::log_1(&format!( $( $t )* ).into()); | |
| } | |
| } |
format宏与其他几个输出区别在于其使用write,不输出到标准输出中:
| format!: write formatted text to String | |
| print!: same as format! but the text is printed to the console (io::stdout). | |
| println!: same as print! but a newline is appended. | |
| eprint!: same as format! but the text is printed to the standard error (io::stderr). | |
| eprintln!: same as eprint!but a newline is appended. |
然后就可以在需要的地方console了,比如neighbours那:
| let live_neighbors = self.live_neighbor_count(row, col); | |
| log!( | |
| "cell[{}, {}] is initially {:?} and has {} live neighbors", | |
| row, | |
| col, | |
| cell, | |
| live_neighbors | |
| ); | |
| let next_cell = match (cell, live_neighbors) { | |
| // Rule 1: Any live cell with fewer than two live neighbours | |
| // dies, as if caused by underpopulation. | |
| (Cell::Alive, x) if x < 2 => Cell::Dead, | |
| // Rule 2: Any live cell with two or three live neighbours | |
| // lives on to the next generation. | |
| (Cell::Alive, 2) | (Cell::Alive, 3) => Cell::Alive, | |
| // Rule 3: Any live cell with more than three live | |
| // neighbours dies, as if by overpopulation. | |
| (Cell::Alive, x) if x > 3 => Cell::Dead, | |
| // Rule 4: Any dead cell with exactly three live neighbours | |
| // becomes a live cell, as if by reproduction. | |
| (Cell::Dead, 3) => Cell::Alive, | |
| // All other cells remain in the same state. | |
| (otherwise, _) => otherwise, | |
| }; | |
| log!(" it becomes {:?}", next_cell); | |
| next[idx] = next_cell; |
打开web,即可看见console的内容。