目录
- 1、什么是动态创建组件
- 2、Vue.extend()
- 3、通过extend实现弹窗的动态创建
- 3.1、创建动态组件
- 3.2、编辑动态组件的逻辑
- 3.3、在main.js中引入使用
- 3.4、在需要的地方通过触发事件显示弹窗
- 3.5、效果图
vue中通过extend动态创建全局组件;
1、什么是动态创建组件
只有在触发事件的时候,才产生某组件,平时它并不存在;
2、Vue.extend()
使用基础 Vue 构造器,创建一个“子类”。参数是一个包含组件选项的对象;其实就是一个子类构造器是Vue组件的核心api,实现思路就是使用原型继承的方法返回了Vue的子类,并且利用mergeOptions把传入组件的options和父类的options进行了合并。
extend创建的是一个组件构造器,而不是一个具体的实例;
接收一个对象(包含组件选项的对象)作为参数,需要使用new来创建实例,并且需要$mount手动挂载到一个元素上,才可以获取到这个元素的相应的信息。
- 脱离填鸭式的写法;代码自由
- 代码复用,解耦
- 原生JS语法结合vue(jsx)
- 通过传入参数,可以显示不同状态的模板
基础用法:
<div id="mount-point"></div>
// 创建构造器
/* Vue.extend( options )
参数:{Object} options
用法:使用基础 Vue 构造器,创建一个“子类”。参数是一个包含组件选项的对象;
data 选项是特例,需要注意: 在 Vue.extend() 中它必须是函数;*/
var Profile = Vue.extend({
template: '<p>{{firstName}} {{lastName}} aka {{alias}}</p>',
data: function () {
return {
firstName: 'Walter',
lastName: 'White',
alias: 'Heisenberg'
}
}
})
// 创建 Profile 实例,并挂载到一个元素上。
new Profile().$mount('#mount-point')
// 结果如下:
<p>Walter White aka Heisenberg</p>
/*
可以看到,extend 创建的是 Vue 构造器,而不是我们平时常写的组件实例,所以不可以通过 new Vue({ components: testExtend }) 来直接使用,需要通过 new Profile().$mount('#mount-point') 来挂载到指定的元素上。
*/
3、通过extend实现弹窗的动态创建
3.1、创建动态组件
<!--动态组件的模板-->
<template>
<!-- 可以用MessageBox做蒙尘-->
<div :class="['MessageBox',type]">
<div class="inner">
<header class="header">
<h1 class="title">{{ title }}</h1>
<span @click="$messageBox.hide()">x</span>
</header>
<div class="content">{{ content }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MessageBox",
props: {
title: {
type: String,
default: "this is title",
},
content: {
type: String,
default: "this is content",
},
type: {
type: String,
default: "primary",
//检测传进来的类型是否是这四种,通过ES6提供的includes方法模糊查询
validator(value) {
return [
"primary",
"success",
"warn",
"danger"
].includes(value);
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped lang="less">
.MessageBox {
position: fixed;
left: 50%;
top: 0;
//蒙尘的大小设置
width: 50%;
height: 400px;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .5);
//不同弹窗的样式
&.primary {
.header {
background-color: blue;
color: #fff;
}
}
&.success {
.header {
background-color: green;
color: #fff;
}
}
&.warn {
.header {
background-color: rgba(255, 138, 71, 0.96);
color: #fff;
}
}
&.danger {
.header {
background-color: red;
color: #fff;
}
}
.inner {
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 50%;
width: 500px;
margin-left: -250px;
background-color: #fff;
box-shadow: 1px 3px 5px #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
overflow: hidden;
.header {
height: 44px;
padding: 0 10px;
line-height: 44px;
box-sizing: border-box;
h1 {
margin: 0;
font-weight: normal;
}
.title {
font-size: 16px;
float: left;
}
span {
//将鼠标改为小手样式
cursor: pointer;
float: right;
}
}
.content {
padding: 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
}
}
</style>
3.2、编辑动态组件的逻辑
//引入需要动态创建的模板
import _MessageBox from "@/components/messageBox/MessageBox";
export default {
//install开发插件的方法,install带有Vue的构造器,可以使用Vue.extend,和Vue.component(注册组件)
//在Vue.use的时候就会调用这个install
install(Vue) {
let messageBox = null;
//使用Vue.component全局注册组件
Vue.component(_MessageBox.name, _MessageBox);
//将方法添加到Vue的prototype属性中,这样实例就可以继承里面的方法
Vue.prototype.$messageBox = {
show, hide,
info({title, content, type}, callback) {
this.show({title, content, type: "primary"}, callback)
},
success({title, content, type}, callback) {
this.show({title, content, type: "success"}, callback)
},
warn({title, content, type}, callback) {
this.show({title, content, type: "warn"}, callback)
},
danger({title, content, type}, callback) {
this.show({title, content, type: "danger"}, callback)
}
}
//显示弹窗
function show(props, callback) {
//判断这个组件是否存在,如果不存在
if (!messageBox) {
//生成构造函数、构造器
const MessageBox = Vue.extend({
/*
render该渲染函数接收一个 createElement 方法作为第一个参数用来创建 VNode(节点)。
如果组件是一个函数组件,渲染函数还会接收一个额外的 context 参数,为没有实例的函数组件提供上下文信息。
*/
//此处传入的是一个函数组件,所以渲染的函数还可以额外接收一个参数
render(h) {
//h函数就是vue中的createElement函数,这个函数作用就是创建虚拟dom,追踪dom变化的
return h("MessageBox", {
//用于接收传递的参数
props: {...props}
})
}
});
//将动态模板组件实例化
messageBox = new MessageBox();
//将这个实例手动挂载,挂载后可以通过$el获取这个元素
this.vm = messageBox.$mount();
//将组件添加到body上,脱离了根节点,不在"id=app中"
document.body.appendChild(this.vm.$el)
callback && callback();
}
}
//关闭弹窗
function hide(callback) {
//移出这个组件
document.body.removeChild(this.vm.$el);
//将这个实例销毁
messageBox.$destroy();
messageBox = null;
this.vm = null;
//如果存在才会执行
callback && callback();
}
}
}
3.3、在main.js中引入使用
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
//1、引入
import MessageBox from "@/components/messageBox";
//2、全局注册使用
Vue.use(MessageBox);
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
3.4、在需要的地方通过触发事件显示弹窗
<template>
<div>
<button @click="showMessageBox">show</button>
<button @click="showInfoMessageBox">info</button>
<button @click="showSuccessMessageBox">success</button>
<button @click="showWarnMessageBox">warn</button>
<button @click="showDangerMessageBox">danger</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Extend",
methods: {
//通过this.$messageBox可以访问到Vue实例的属性和方法
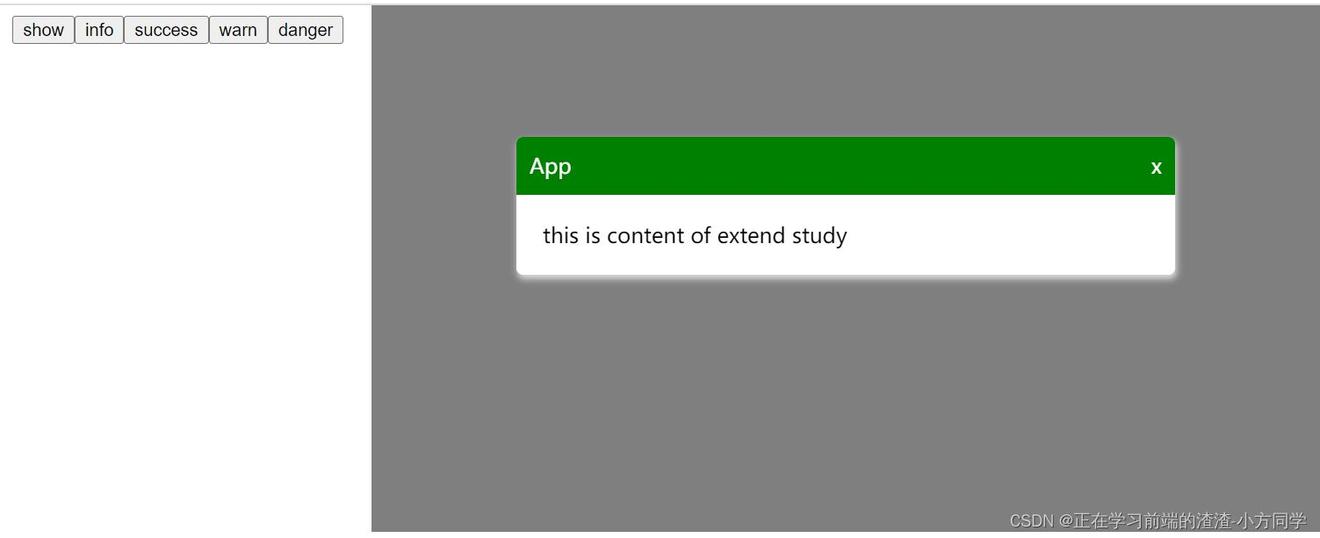
showMessageBox() {
this.$messageBox.success({
title: 'App',
content: 'this is content of extend study',
type: 'success'
}, () => {
console.log('show over')
})
},
showInfoMessageBox() {
this.$messageBox.info({
title: 'App',
content: 'this is content of extend study',
}, () => {
console.log('info over')
})
},
showSuccessMessageBox() {
this.$messageBox.success({
title: 'App',
content: 'this is content of extend study',
type: 'success'
}, () => {
console.log('success over')
})
},
showWarnMessageBox() {
this.$messageBox.warn({
title: 'App',
content: 'this is content of extend study',
type: 'warn'
}, () => {
console.log('warn over')
})
},
showDangerMessageBox() {
this.$messageBox.danger({
title: 'App',
content: 'this is content of extend study',
type: 'danger'
})
}
}
}
</script>
3.5、效果图