前言
Hexo 属于静态博客,很多同学给自己的博客加上 Pjax 是为了音乐播放器等功能不中断。
之前我也想过对博客和主题加入 Pjax 支持,但经过一番分析后觉得,这不仅引入了一个巨大的 jquery.pjax.js,反而优化效果不明显。
原理
其实,Pjax 的原理并不复杂。或许说,README 一开始就告诉你了:
pjax = pushState + ajax
其中 ajax 用于页面的新内容,pushState 改变浏览器状态。
很简单吧。
事实上,pjax 并不应该应用于整个页面当中。而应该只是局部更改。
这样,Blog 当中的导航栏、样式文件等就不需要重复下载与预览。
分析
以我使用 Miracle 为主题的博客为例,进入首页,按 F12 查看页面 Elements.
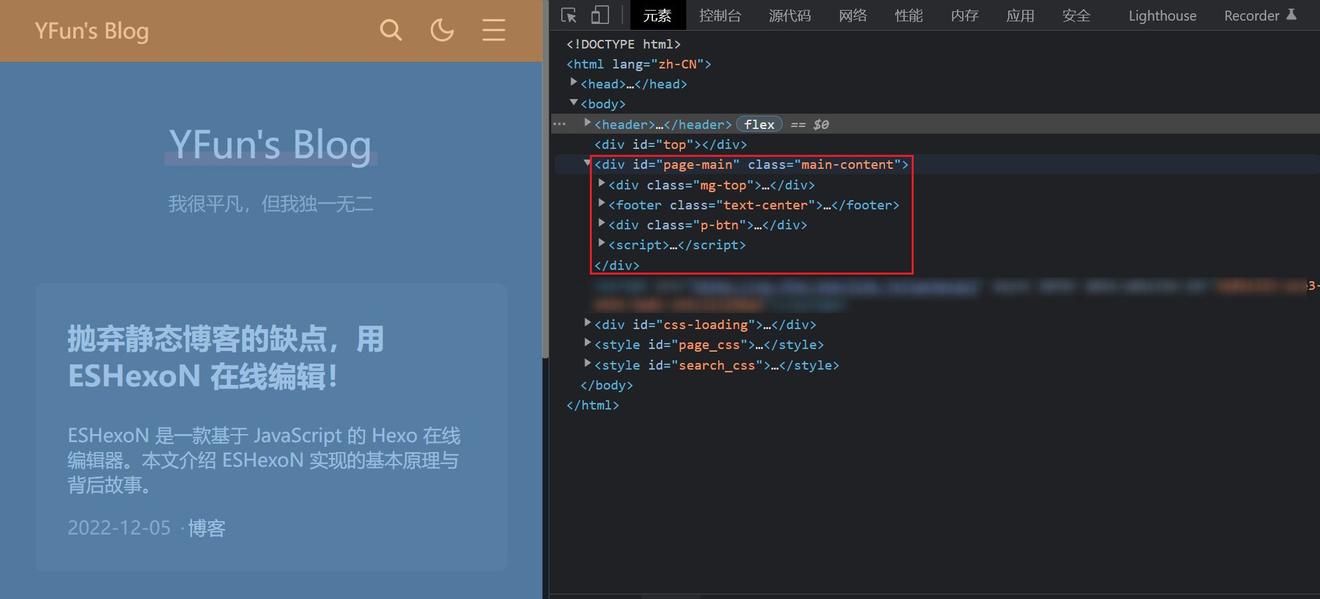
可以发现,页面主要更改的也就是 #page-main 部分,只需要实现动态刷新这部分的内容就可以了。
那怎么实现呢?
最小化的数据接口
现在生成的页面当中,有 <head> 部分声明大量样式与元信息,<body> 之下重复的页脚、导航栏,还有每个页面下方都有的一些 <script>。
很明显,我们不需要这些。我们只要 #page-main 中的主要内容。
最重要的是,Hexo 是静态博客,这一点只能在生成文件时进行。
载入 HTML
我是用 Cheerio 模块帮我完成这一工作。
| const cheerio = require('cheerio'); | |
| const fs = require("fs"); | |
| const path = require("path"); | |
| const filePath = path.resolve('public/'); |
定义一个 parse function,打开文件并解析相关信息,顺便把不是 HTML 的文件排除掉。
| const parse = (filename, fullpath) => { | |
| // 不是 .html 我不要 | |
| if (!filename.endsWith(".html")) { | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| } |
然后通过 Cheerio 解析 HTML:
| {... | |
| // 组合新文件名 | |
| let filepath = fullpath+".page.json"; | |
| // 读取文件内容 | |
| let pageContent = fs.readFileSync(fullpath).toString(); | |
| // 解析页面内容 | |
| let $pg = cheerio.load(pageContent); | |
| let rtData = {}; | |
| ...} |
然后获取页面的标题和 #page-main 下的 HTML.
| {... | |
| // 页面标题 | |
| rtData.title = $pg("title").text(); | |
| // OR $pg("#page-main").html() | |
| // 我这么写是因为主题 #page-main 下还有 script 无法执行 | |
| rtData.page = ` | |
| <div class="mg-top"> | |
| ${$pg(".mg-top").html() || ""} | |
| </div> | |
| <footer class="text-center"> | |
| ${$pg("footer").html() || ""} | |
| </footer> | |
| <div class="p-btn"> | |
| ${$pg(".p-btn").html() || ""} | |
| </div> | |
| `; | |
| rtData.path = filename; | |
| ...} |
页面中还有一些 script,比如阅读进度、懒加载等。所以需要一个 extraJS 放置额外的 Script.
| {... | |
| rtData.extraJS = [] | |
| // 只解析 #page-main 下的 script | |
| let $pageMain = cheerio.load($pg("#page-main").html()); | |
| $pageMain('script').map(function(i, el) { | |
| // 尝试往 extraJS 中 push 相关代码 | |
| try {rtData.extraJS.push($pageMain(this)[0].children[0].data);} catch(e) {} | |
| $pageMain(this).remove(); | |
| }); | |
| ...} |
最后,将 JSON 写入文件中。
| {... | |
| fs.writeFileSync(filepath, JSON.stringify(rtData)); | |
| } |
文件递归
我们还需要一个函数递归 public 目录下的所有文件,这个不用多说。
| function fileDisplay(filePath) { | |
| // 根据文件路径读取文件,返回文件列表 | |
| fs.readdir(filePath, function(err, files) { | |
| if (err) { | |
| console.warn(err, "读取文件夹错误!") | |
| } else { | |
| // 遍历读取到的文件列表 | |
| files.forEach(function(filename) { | |
| // 获取当前文件的绝对路径 | |
| var filedir = path.join(filePath, filename); | |
| var fullname = filedir.split("public")[1]; | |
| fs.stat(filedir, function(eror, stats) { | |
| if (eror) { | |
| console.warn('获取文件 Stats 失败!'); | |
| } else { | |
| var isFile = stats.isFile(); // 是文件 | |
| var isDir = stats.isDirectory(); // 是文件夹 | |
| if (isFile) { | |
| parse(fullname, filedir); | |
| } | |
| if (isDir) { | |
| fileDisplay(filedir); // 递归,如果是文件夹,就继续遍历该文件夹下面的文件 | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }); | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| fileDisplay(filePath); |
最后运行这个 Node.js 文件,就可以看到 public/ 目录下多出很多 ***.page.json 文件。
基本结构
这些文件内容也很简单,基本如下:
| { | |
| // 页面的标题 | |
| "title": "Hello World", | |
| // 内容 | |
| "page": "...", | |
| // 路径 | |
| "path": "/foo/bar", | |
| // JS | |
| "extraJS": ['alert("Hello World");'] | |
| } |
前端 pjax.js
新建一个 pjax.js。
替换链接
我们需要先将页面当中所有本站链接转为 Pjax 的 Jump 函数。
判断条件是:有链接,不带 hash,且为本站链接
| // 转换页面中的链接为 Pjax 链接 | |
| const $pjax_convertAllLinks = () => { | |
| // 所有的 a 标签 | |
| const linkElements = document.querySelectorAll("a"); | |
| for (let i of linkElements) { | |
| // 有链接,不带 hash,且为本站链接 | |
| if (i.href && !i.href.includes("/#") && (i.href.startsWith("/") || i.href.match(new RegExp(window.location.hostname)))) { | |
| let thisLink = new URL(i.href).pathname+new URL(i.href).hash; | |
| i.href = `javascript:$pjax_jump('${thisLink}');`; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
另外,要转化页面链接为全路径。
这里参考了下 ChenYFan 的 Service Worker 函数,需要根据实际情况做出调整。
| // 转换路径为全路径 | |
| const $pjax_fullpath = (path) => { | |
| path = path.split('?')[0].split('#')[0] | |
| if (path.match(/\/$/)) { | |
| path += 'index.html'; | |
| } | |
| if (!path.match(/\.[a-zA-Z]+$/)) { | |
| path += '/index.html'; | |
| } | |
| return path; | |
| } | |
| // $pjax_fullpath('/') => /index.html |
跳转
| // 跳转页面 | |
| const $pjax_jump = async (path) => { | |
| try { | |
| // 是 # 就别跳转了 | |
| if (path.startsWith("#")) { | |
| window.hash = path; | |
| return false; | |
| } | |
| // 加载动画 | |
| let loading = document.createElement('div'); | |
| loading.innerHTML = `<div style="position: fixed;top:0;left:0;z-index:99999;display: block;width: 100%;height: 4px;overflow: hidden;background-color: rgba(63,81,181,.2);border-radius: 2px;"><div class="progress-indeterminate" style="background-color: #3f51b5;"></div><style>#page-main{transition:0.2s;}.progress-indeterminate::before{position:absolute;top:0;bottom:0;left:0;background-color:inherit;-webkit-animation:mdui-progress-indeterminate 2s linear infinite;animation:mdui-progress-indeterminate 2s linear infinite;content:' ';will-change:left,width;}.progress-indeterminate::after{position:absolute;top:0;bottom:0;left:0;background-color:inherit;-webkit-animation:mdui-progress-indeterminate-short 2s linear infinite;animation:mdui-progress-indeterminate-short 2s linear infinite;content:' ';will-change:left,width;}@keyframes mdui-progress-indeterminate{0%{left:0;width:0;}50%{left:30%;width:70%;}75%{left:100%;width:0;}}@keyframes mdui-progress-indeterminate-short{0%{left:0;width:0;}50%{left:0;width:0;}75%{left:0;width:25%;}100%{left:100%;width:0;}}</style></div>`; | |
| // 在 body 后加入 <div> | |
| document.body.appendChild(loading); | |
| // 如果页面中没有 page.css 或 search.css,为防止样式错乱,需要在加载过程中隐藏页面内容 | |
| if (!document.getElementById("page_css") || !document.getElementById("search_css")) document.getElementById("page-main").style.opacity = 0; | |
| // 获取页面数据 | |
| let pageData; | |
| // 看看 SessionStorage 里有没有缓存 | |
| // 依赖后文的 prefetch | |
| if (sessionStorage.getItem(`${location.protocol}//${location.hostname}${location.port ? ":"+location.port:location.port}${$pjax_fullpath(path)}`)) { | |
| console.log("FROM SESSIONSTORAGE"); | |
| try { | |
| pageData = JSON.parse(sessionStorage.getItem(`${location.protocol}//${location.hostname}${location.port ? ":"+location.port:location.port}${$pjax_fullpath(path)}`)); | |
| } catch(e) { | |
| // 还是出错就从服务器获取 | |
| console.log("FROM SERVER"); | |
| pageData = await fetch($pjax_fullpath(path) + ".page.json").then(res => res.json()); | |
| // 写到 SessionStorage 中 | |
| sessionStorage.setItem(`${location.protocol}//${location.hostname}${location.port ? ":"+location.port:location.port}${$pjax_fullpath(path)}`, JSON.stringify(pageData)); | |
| } | |
| } else { | |
| console.log("FROM SERVER"); | |
| // fetch JSON | |
| pageData = await fetch($pjax_fullpath(path) + ".page.json").then(res => res.json()); | |
| sessionStorage.setItem(`${location.protocol}//${location.hostname}${location.port ? ":"+location.port:location.port}${$pjax_fullpath(path)}`, JSON.stringify(pageData)); | |
| } | |
| // 补齐页面 CSS | |
| if (!document.getElementById("search_css")) { | |
| fetch("/css/search.css").then(res => res.text()).then(res => { | |
| let ele = document.createElement("style"); | |
| ele.innerHTML = res; | |
| ele.id = "search_css"; | |
| document.body.appendChild(ele); | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| if (!document.getElementById("page_css")) { | |
| fetch("/css/page.css").then(res => res.text()).then(res => { | |
| let ele = document.createElement("style"); | |
| ele.innerHTML = res; | |
| ele.id = "page_css"; | |
| document.body.appendChild(ele); | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| if (!pageData) return false; | |
| // 组合 state | |
| var state = { title: '', url: window.location.href.split("?")[0] }; | |
| // 利用 history.pushState() 修改地址栏而不跳转 | |
| history.pushState(state, '', path); | |
| // 修改页面标题 | |
| document.title = pageData.title; | |
| setTimeout(() => { | |
| // 滚动到页面顶部 | |
| window.scrollTo({top: 0, behavior: "smooth"}); | |
| // 写入 HTML | |
| document.getElementById("page-main").innerHTML = pageData.page; | |
| window.onscroll = null; | |
| for (let i in pageData.extraJS) { | |
| try { | |
| // eval() 执行 JS | |
| eval(pageData.extraJS[i]); | |
| } catch(e) {} | |
| } | |
| try{$pjax_prefetch();}catch(e){} | |
| // 再次转换所有链接 | |
| $pjax_convertAllLinks(); | |
| }, 200); | |
| setTimeout(() => { | |
| // 重新显示页面 | |
| document.getElementById("page-main").style.opacity = 1; | |
| loading.remove(); | |
| }, 1000); | |
| } catch(e) { | |
| // 有报错 直接跳转 | |
| console.warn(e); | |
| window.location.href = path; | |
| } | |
| } |
如果使用 window.location.href 修改,那么页面就会刷新。 为了实现无刷新跳转,必须要使用 pushState() 更改。
执行 JavaScript 方面使用 eval() 函数。
| // 组合 state | |
| var state = { title: '', url: window.location.href.split("?")[0] }; | |
| // 利用 history.pushState() 修改地址栏而不跳转 | |
| history.pushState(state, '', path); | |
| // 修改页面标题 | |
| document.title = pageData.title; | |
| // 滚动到页面顶部 | |
| window.scrollTo({top: 0, behavior: "smooth"}); | |
| // 写入 HTML | |
| document.getElementById("page-main").innerHTML = pageData.page; | |
| window.onscroll = null; | |
| for (let i in pageData.extraJS) { | |
| try { | |
| // eval() 执行 JS | |
| eval(pageData.extraJS[i]); | |
| } catch(e) {} | |
| } |
Prefetch & Refetch
此处借鉴乐特关于 Prefetch Page 的源码,当用户打开节流模式或为低速网络时就不要 Prefetch.
Prefetch 可以提前缓存部分数据。
| const $pjax_prefetch = () => { | |
| // 节流和低速网络不要 Prefetch | |
| const nav = navigator; | |
| const { saveData, effectiveType } = nav.connection || nav.mozConnection || nav.webkitConnection || {}; | |
| if (saveData || /2g/.test(effectiveType)) return false; | |
| // 此处是 Blog 的一些常见链接 | |
| let posts_list = document.querySelectorAll(".index-header a"); | |
| for (let i in posts_list) { | |
| // 全路径 | |
| let thisLink = $pjax_fullpath(posts_list[i].href); | |
| // Session Storage 没有才 Fetch | |
| if (!sessionStorage.getItem(thisLink)) { | |
| fetch(thisLink + ".page.json").then(res => res.text()).then(res => { | |
| sessionStorage.setItem(thisLink,res); | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
Refetch 用于刷新已有的缓存(虽然 SessionStorage 关闭页面就没了)
其原理也很简单,SessionStorage 中所有的 Pjax 缓存重新获取就完事了。
| const $pjax_refetch = () => { | |
| let sst = sessionStorage; | |
| for (let i in sst) { | |
| if (i.startsWith("http://") || i.startsWith("https://")) { | |
| fetch(i + ".page.json").then(res => res.text()).then(res => { | |
| sessionStorage.setItem(i, res); | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
一些优化
Prefetch CSS 文件
既然 CSS 文件需要补齐,那么打开页面 5s 后自动 Prefetch 可以提升速度。
5s 后再获取是为了防止阻塞页面。
| setTimeout(() => { | |
| // Prefetch CSS 文件 | |
| if (!document.getElementById("search_css")) { | |
| fetch("/css/search.css").then(res => res.text()).then(res => { | |
| let ele = document.createElement("style") | |
| ele.innerHTML = res; | |
| ele.id = "search_css"; | |
| document.body.appendChild(ele); | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| if (!document.getElementById("page_css")) { | |
| fetch("/css/page.css").then(res => res.text()).then(res => { | |
| let ele = document.createElement("style") | |
| ele.innerHTML = res; | |
| ele.id = "page_css"; | |
| document.body.appendChild(ele); | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| }, 5000); |
关于 Robots
当你运行 pjax_convertAllLinks(); 后,你肯定会发现所有的链接都变成了 javascript:pjax_jump('/xxx');。这对机器人来说很不友好。
所以,我们需要排除这些机器人。
| var runningOnBrowser = typeof window !== "undefined"; | |
| var isBot = runningOnBrowser && !("onscroll" in window) || typeof navigator !== "undefined" && /(gle|ing|ro|msn)bot|crawl|spider|yand|duckgo/i.test(navigator.userAgent); | |
| if (runningOnBrowser && !isBot) { | |
| setTimeout(() => { | |
| try{$pjax_prefetch();}catch(e){} | |
| $pjax_convertAllLinks(); | |
| }, 100); | |
| } |
最后
在启用 Pjax 后,YFun's Blog 传输大小理论上最高缩小 3/4,性能速度均有提升。
如果你也在使用 Pjax,不妨试试看。
还有一些错误
如果你定义了 onload 等事件,页面没有刷新即代表没有变化,你需要在 $pjax_jump() 中简单清除一下这些信息。